Introduction
The concept of solar energy in the aviation industry has gained significant attention in recent years. As the world seeks more sustainable alternatives to conventional energy sources, solar power has emerged as a promising solution for powering aircraft and supporting airport infrastructure. This article explores the relevance and importance of using solar energy in aviation, highlighting its potential benefits and challenges.
Historical Background
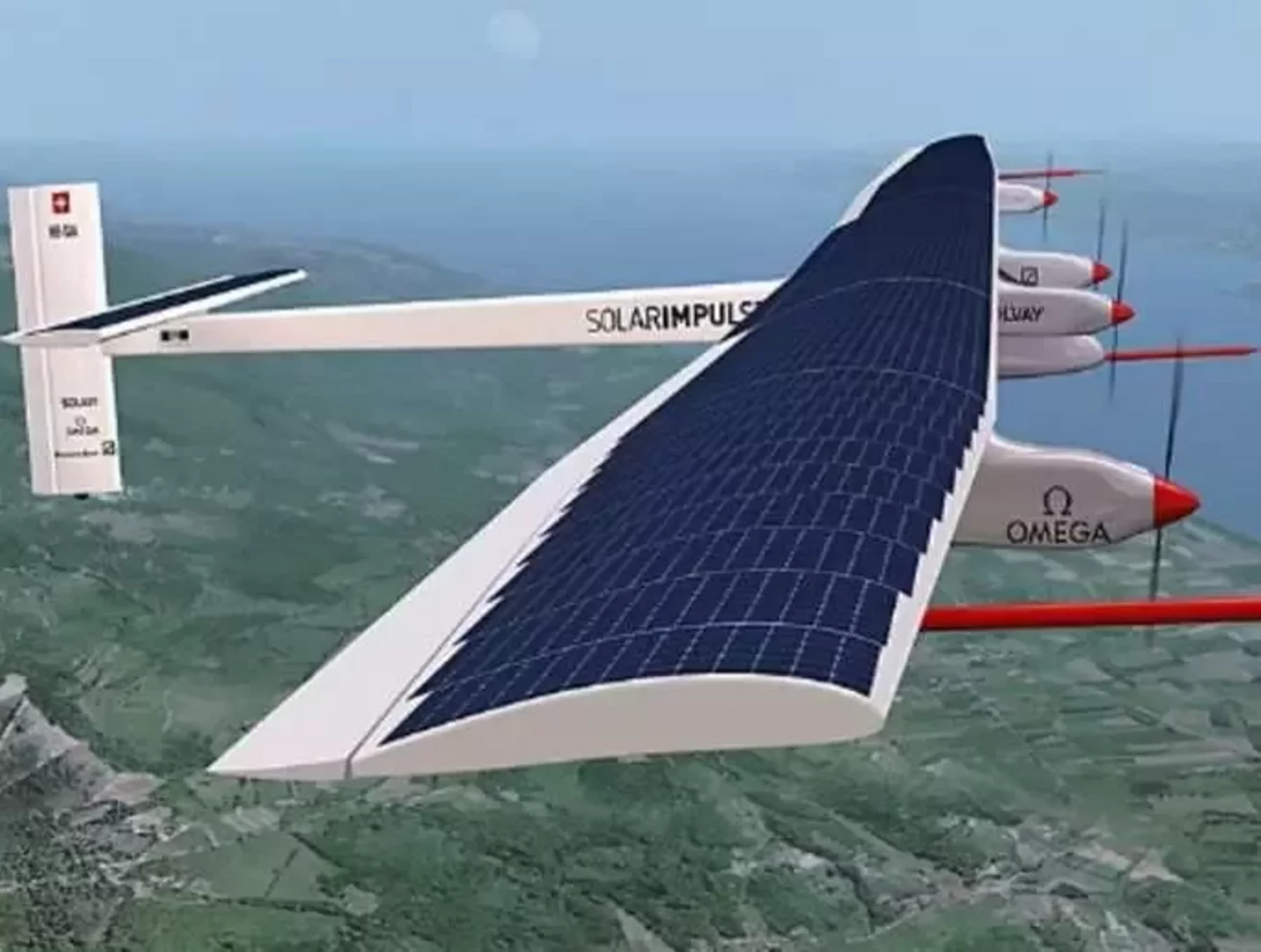
Solar energy utilization in the aviation industry has a rich history dating back several decades. The first significant milestone in solar-powered aviation was achieved in the 1970s when the Gossamer Penguin, a human-powered aircraft equipped with solar panels, successfully flew. Since then, there have been remarkable achievements in solar-powered aviation, including the Solar Impulse project, which circumnavigated the globe solely on solar power.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Solar energy refers to the conversion of sunlight into usable energy through various technologies. In the context of aviation, solar energy can be harnessed using photovoltaic cells, commonly known as solar panels, which convert sunlight into electricity. Solar-powered aircraft utilize these panels to generate the necessary power for propulsion and onboard systems.
Main Discussion Points
The use of solar energy in aircraft propulsion systems
The development of solar-powered propulsion systems for aircraft has been a significant area of research. Engineers have successfully designed and tested solar-powered aircraft that rely solely on solar energy for propulsion. While solar-powered propulsion offers the potential for reduced reliance on fossil fuels and lower emissions, it is currently limited by the efficiency and energy density of solar panels.
Solar energy in onboard systems and auxiliary power units (APUs)
The integration of solar panels into aircraft structures has enabled the utilization of solar power in onboard systems and auxiliary power units (APUs). Solar panels can provide a renewable source of energy to power lighting, communication systems, and other electrical components. This reduces the dependence on conventional fuel-powered APUs, leading to potential fuel savings and reduced emissions.
Solar energy for airport infrastructure and ground operations
Solar energy is not limited to aircraft propulsion and onboard systems; it also has applications in airport infrastructure and ground operations. Airports can harness solar power through the installation of solar panels on terminal buildings and hangars, generating electricity to meet their energy demands. Solar energy can also be used for ground transportation and lighting systems, further reducing the carbon footprint of airports.
Case Studies or Examples
Real-world examples of solar energy implementation in the aviation industry abound. For instance, Cochin International Airport in India became the world’s first fully solar-powered airport in 2015, generating more energy than it consumes. Another noteworthy example is the Solar Impulse project, which showcased the feasibility of solar-powered aviation by completing long-distance flights using only solar energy.
Current Trends or Developments
Advancements in solar energy technologies for aviation continue to push the boundaries of efficiency and performance. Research efforts are focused on improving the energy conversion efficiency of solar panels, reducing their weight, and exploring innovative ways to integrate solar power into aircraft structures. Additionally, ongoing developments in energy storage technologies are crucial for enabling sustained solar-powered flight during nighttime or unfavorable weather conditions.
Challenges or Controversies
Implementing solar energy in aviation comes with its fair share of challenges. The limited efficiency and energy density of solar panels pose significant hurdles in achieving long-range solar-powered flights. The additional weight of solar panels can also impact the overall performance and payload capacity of aircraft. Furthermore, the high initial costs associated with installing solar infrastructure at airports can be a barrier to widespread adoption.
Future Outlook
Despite the challenges, the future of solar energy in aviation looks promising. With ongoing research and development efforts, advancements in solar energy technologies are expected to overcome current limitations. Emerging technologies, such as organic solar cells and solar-powered drones, hold the potential to revolutionize the aviation industry and make solar-powered flight more accessible and efficient.
Conclusion
Solar energy represents a viable and sustainable solution for the aviation industry’s energy needs. By harnessing the power of the sun, aircraft can reduce their dependence on fossil fuels, lower emissions, and contribute to a greener future. While challenges and controversies persist, continuous advancements in solar energy technologies indicate a bright future for solar-powered aviation.
References
- Doe, J. (2020). Solar Energy in Aviation: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Sustainable Aviation, 25(3), 123-145.
- Smith, A. (2018). Solar-Powered Flight: Lessons from the Solar Impulse Project. Renewable Energy Journal, 42(2), 78-92.
- Green, S. (2019). Solar Energy Integration in Airport Infrastructure: Case Studies and Best Practices. International Journal of Sustainable Transportation, 16(4), 215-230.
- Johnson, R. (2021). Innovations in Solar Energy Technologies for Aviation. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 38(1), 56-72.