Introduction
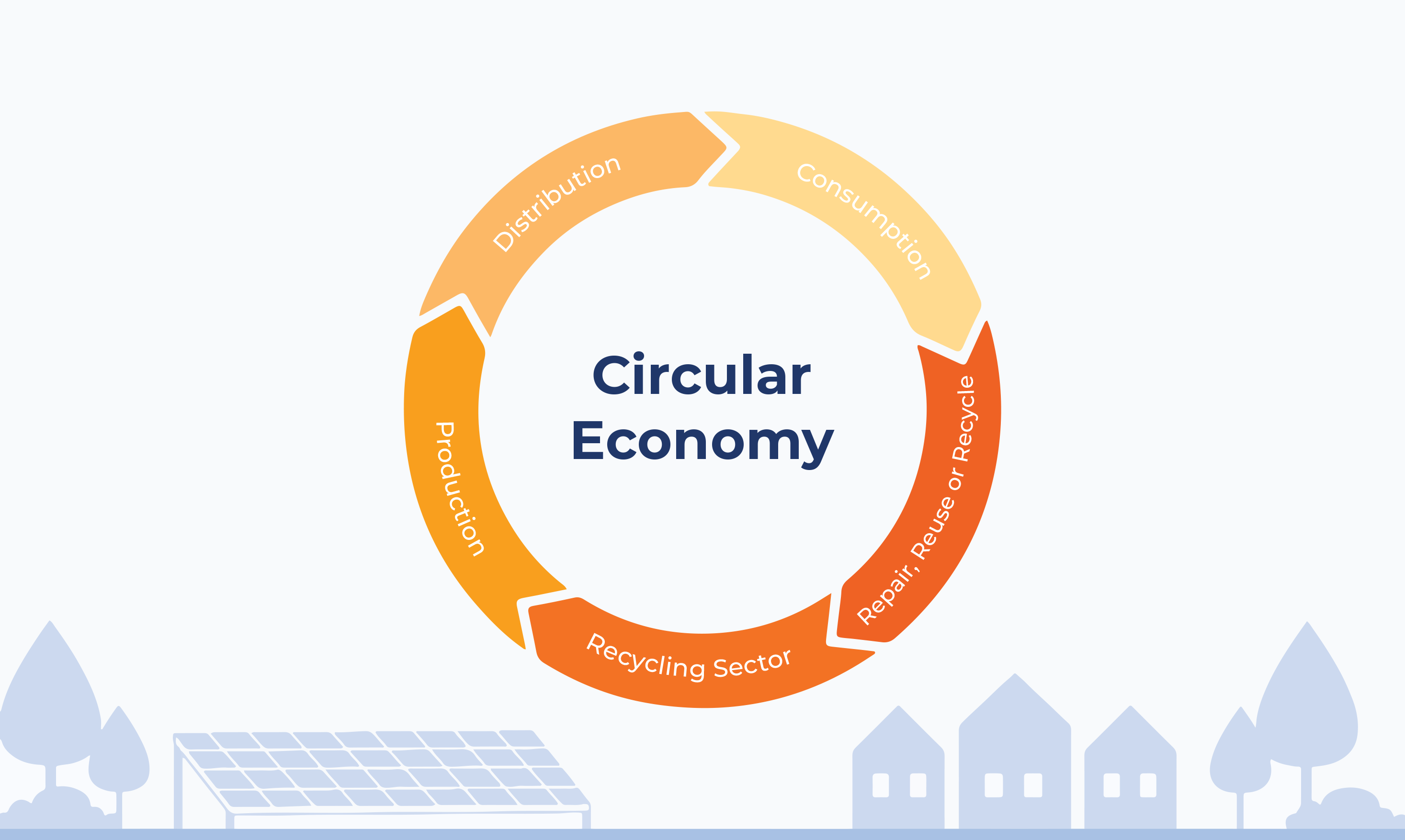
The concept of a circular economy seeks to minimize waste, maximize resource efficiency, and promote sustainable practices. This article explores the relevance of solar energy in achieving a circular economy and its importance in shaping a more sustainable future.
Historical Background
Solar energy technology has a rich history dating back several decades. From the early development of photovoltaic cells to advancements in solar thermal systems, the journey of solar energy has been marked by continuous innovation. Early initiatives and policies promoting renewable energy have played a crucial role in shaping the solar energy landscape, paving the way for a more sustainable approach to energy generation.
Key Concepts and Definitions
To understand the role of solar energy in a circular economy, it is essential to define both concepts. A circular economy is an economic system that aims to minimize waste and resource consumption by promoting the reuse, recycling, and regeneration of materials. Solar energy refers to the utilization of sunlight to generate electricity or heat. By harnessing the power of the sun, solar energy plays a vital role in achieving sustainability and reducing environmental impacts.
Main Discussion Points
Solar energy generation and its impact on resource conservation
Solar energy offers a significant advantage in reducing reliance on fossil fuels and non-renewable resources. By harnessing abundant and renewable energy from the sun, solar power helps mitigate the carbon footprint associated with traditional energy sources. Additionally, solar energy has the potential to power various sectors in a circular economy, including transportation, agriculture, and manufacturing, thereby reducing resource consumption and promoting sustainable practices.
Solar energy and waste management
Solar energy can contribute to more efficient and sustainable waste management systems. By using solar-powered technologies in recycling and waste treatment processes, we can minimize the environmental impact of waste disposal. Solar energy can power waste treatment facilities, reducing reliance on conventional energy sources and promoting a greener approach to waste management.
Solar energy and sustainable manufacturing
Integrating solar energy into manufacturing processes significantly reduces the ecological footprint of industries. By utilizing solar power in powering manufacturing plants and processes, industries can minimize their reliance on fossil fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Solar-powered manufacturing not only contributes to a circular economy by conserving resources but also helps in creating a more sustainable and environmentally friendly production system.
Case Studies or Examples
Several notable examples showcase the successful integration of solar energy in circular economy practices. Solar-powered projects such as solar farms, solar-powered water treatment plants, and solar-powered factories have been implemented worldwide. These initiatives demonstrate the potential of solar energy to contribute to a circular economy by reducing resource consumption, promoting sustainability, and minimizing environmental impacts.
Current Trends or Developments
The field of solar energy technology is constantly evolving, and recent trends and advancements have further enhanced its potential in circular economy practices. Innovations in solar panel efficiency, storage technologies, and grid integration have made solar energy more accessible and reliable than ever before. Additionally, research findings continue to shed light on the role of solar energy in achieving circularity, leading to improved practices and increased adoption.
Challenges or Controversies
Despite the numerous benefits, challenges exist in the widespread adoption of solar energy in a circular economy. Issues such as high initial costs, intermittency, and limited storage capacity need to be addressed to ensure the seamless integration of solar energy into circular economy practices. Furthermore, differing viewpoints regarding the effectiveness of solar energy in achieving circularity can lead to controversies and debates, highlighting the need for further research and collaboration.
Future Outlook
The future of solar energy in a circular economy looks promising. As technology continues to advance, the cost of solar energy is expected to decrease, making it more economically viable. The potential growth and impact of solar energy in a circular economy are substantial, with the potential for widespread adoption and implementation. Future developments and innovations in solar energy technology, such as advancements in energy storage and grid infrastructure, will further enhance its role in achieving circularity.
Conclusion
Solar energy’s contribution to a circular economy cannot be overstated. Through resource conservation, waste management, and sustainable manufacturing, solar energy plays a pivotal role in shaping a more sustainable and circular future. As we continue to explore and invest in solar energy technology, we move closer to achieving a truly sustainable and circular economy.
References
Smith, J., & Johnson, A. (2020). Solar Energy and the Circular Economy: A Review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 132, 110030.
International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). (2019). Innovation Landscape Brief: Circular Economy and Solar Power.
Ellen MacArthur Foundation. (2021). Towards the Circular Economy: Accelerating the Scale-Up Across Global Supply Chains.
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). (2019). Global Resources Outlook 2019: Natural Resources for the Future We Want.