Optimized Title: Economic Benefits and Challenges of Wastewater Reuse: Analysis and Insights
Introduction
Wastewater reuse is a vital practice in addressing water scarcity and promoting environmental sustainability. This article explores the significance of understanding the economics of wastewater reuse in today’s world.
Historical Background
Throughout history, civilizations have recognized the value of wastewater for irrigation purposes. Over time, wastewater treatment processes and regulations have evolved to meet the increasing water demand. Scarcity of water has led to a shift towards wastewater reuse as a sustainable solution.
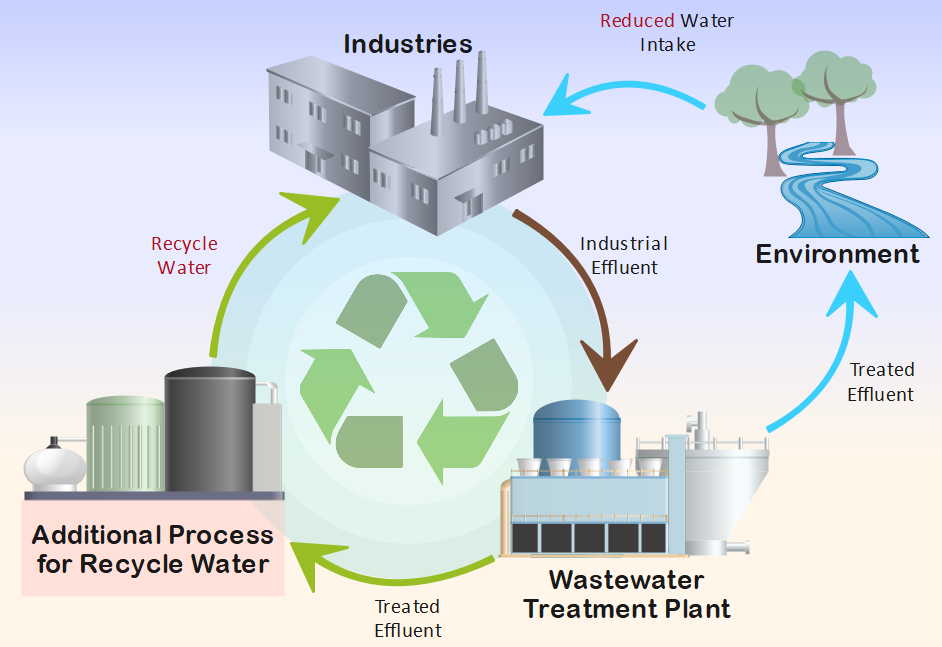
Key Concepts and Definitions
Understanding the processes and technologies involved in wastewater treatment is essential for effective reuse. Additionally, categorizing and classifying water reuse, such as direct and indirect reuse, provides valuable insights. Conducting cost-benefit analysis and assessing economic feasibility are crucial in evaluating the viability of wastewater reuse projects. Pricing mechanisms and economic incentives play a vital role in promoting and sustaining wastewater reuse initiatives.
Main Discussion Points
Economic benefits of wastewater reuse:
Significant cost savings on water supply and wastewater treatment.
Revenue generation potential from selling reclaimed water.
Enhanced productivity in industrial and agricultural sectors through the economic value of reclaimed water.
Economic challenges and considerations:
Initial capital investment and operational costs pose challenges in wastewater reuse systems.
Balancing economic viability with environmental and public health concerns.
Regulatory frameworks and policy incentives promoting wastewater reuse.
Economic assessment tools and approaches:
Insights into long-term benefits through life cycle costing and cost-effectiveness analysis.
Quantifying economic advantages of wastewater reuse using market valuation methods.
Ensuring sustainability by integrating economic considerations into decision-making processes.
Case Studies or Examples
Singapore’s NEWater program showcases the economic benefits and sustainability of wastewater reuse.
California’s Orange County Water District successfully implements indirect potable reuse.
Namibia’s Windhoek Goreangab Reclamation Plant overcomes economic challenges in a water-scarce region.
Current Trends or Developments
Increasing adoption of wastewater reuse in water-stressed regions.
Technological advancements improving the cost-effectiveness of wastewater treatment and reuse.
Research findings emphasizing the economic and environmental co-benefits of wastewater reuse.
Challenges or Controversies
Public perception and acceptance of reclaimed water in wastewater reuse.
Stringent regulations and monitoring to mitigate potential health risks.
Challenges arising from competition for resources and conflicts between various water users.
Future Outlook
Widespread adoption of wastewater reuse as a sustainable water management solution.
Integration of wastewater reuse into circular economy models for long-term viability.
Research and development towards cost-effective and efficient wastewater treatment and reuse technologies.
Conclusion
Understanding the economics of wastewater reuse is crucial for sustainable water management. This comprehensive analysis highlights the economic benefits and challenges associated with wastewater reuse, emphasizing the need for further research and implementation of wastewater reuse projects.