Introduction
The waste-to-energy (WtE) industry has gained significant importance and relevance in Asia due to the growing need for sustainable waste management solutions. This article aims to provide an overview of the historical background, key concepts, main discussion points, case studies, current trends, challenges, and future outlook of WtE in Asia.
Historical Background
Evolution of Waste Management Practices in Asia
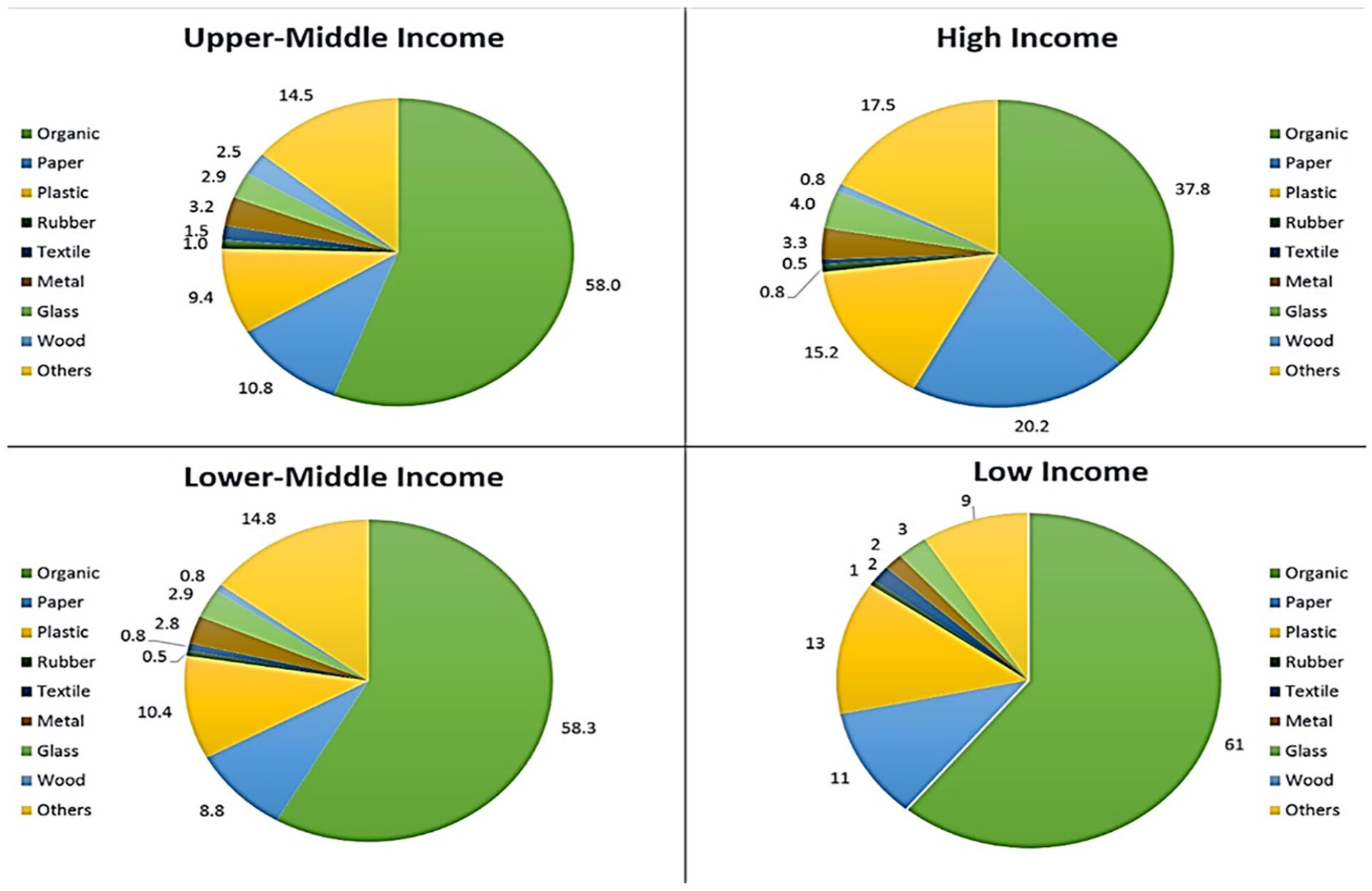
Asia has witnessed a significant evolution in waste management practices over the years. With rapid urbanization and population growth, the volume of waste generated has increased exponentially. Traditional waste management methods, such as landfilling and open dumping, have proven to be unsustainable and detrimental to the environment. As a result, Asian countries started exploring alternative approaches, leading to the introduction of WtE technologies and methods.
Introduction of Waste-to-Energy Technologies and Methods
WtE technologies and methods were introduced in Asia as a sustainable solution to manage the growing waste crisis. These technologies convert waste materials into energy, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing environmental pollution. The implementation of WtE facilities has gained momentum, offering a viable solution to tackle the challenges associated with waste management.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Waste-to-Energy (WtE)
Waste-to-energy (WtE) refers to the process of utilizing waste materials to generate energy. This process involves various technologies such as incineration, anaerobic digestion, and pyrolysis. By harnessing the energy potential of waste, WtE offers a sustainable approach to waste management while simultaneously producing electricity or heat.
Growing Economies in Asia
The growing economies in Asia have contributed to the rapid increase in waste generation. As these economies continue to develop, the demand for energy also rises. This has led to a greater emphasis on finding innovative solutions to manage waste effectively and sustainably. WtE technologies play a crucial role in addressing the waste management challenges faced by these growing economies.
Transformation of Trash
The transformation of trash through WtE processes offers several benefits. Firstly, it reduces the volume of waste that would otherwise end up in landfills, minimizing the associated environmental risks. Secondly, WtE processes generate energy that can be utilized to meet the increasing energy demands of growing economies. Lastly, the conversion of waste into energy contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, supporting climate change mitigation efforts.
Main Discussion Points
WtE Technologies and Methods in Asia
Asia has embraced various WtE technologies and methods to address its waste management needs. Three prominent methods include incineration, anaerobic digestion, and pyrolysis.
Incineration: Incineration involves the combustion of waste materials at high temperatures, converting them into ash, gases, and heat energy. The heat energy can then be harnessed to generate electricity or heat. Incineration offers a reliable and efficient method of waste disposal, particularly for non-recyclable and hazardous waste.
Anaerobic Digestion: Anaerobic digestion is a biological process that breaks down organic waste in the absence of oxygen. This process produces biogas, which can be used for electricity generation or as a renewable natural gas. Anaerobic digestion is particularly suitable for organic waste, such as food waste and agricultural residues.
Pyrolysis: Pyrolysis involves the thermal decomposition of waste materials in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the production of bio-oil, syngas, and char. These byproducts can be further processed to generate electricity, heat, or biofuels. Pyrolysis offers a potential solution for the treatment of mixed waste streams.
Economic and Environmental Benefits of WtE in Growing Economies
WtE facilities in growing economies offer numerous economic and environmental benefits.
Energy Generation and Self-Sufficiency: WtE facilities generate electricity or heat, reducing the reliance on conventional energy sources. This contributes to energy self-sufficiency and enhances energy security for these economies.
Reduction of Landfill Waste and Greenhouse Gas Emissions: WtE processes divert waste from landfills, reducing the environmental impact associated with landfilling. Additionally, the combustion of waste in WtE facilities helps mitigate greenhouse gas emissions that would have been released during the natural degradation of waste in landfills.
Job Creation and Economic Growth: The establishment of WtE facilities creates job opportunities in various sectors, including construction, operation, and maintenance. Moreover, the growth of the WtE industry stimulates economic development and attracts investments, fostering a sustainable and circular economy.
Case Studies
Singapore’s Waste-to-Energy Facilities
Singapore has been at the forefront of WtE implementation in Asia. The country boasts advanced waste management infrastructure, with four waste-to-energy plants that incinerate solid waste and generate electricity. These facilities contribute significantly to Singapore’s energy needs and help reduce the reliance on fossil fuels.
China’s WtE Initiatives
China has also made significant strides in WtE initiatives. The country has the largest number of waste-to-energy plants globally, utilizing incineration and anaerobic digestion technologies. China’s WtE facilities not only address the waste management challenges but also contribute to the country’s renewable energy goals.
Japan’s Advanced WtE Systems
Japan is widely recognized for its advanced waste management practices, including the utilization of WtE systems. The country has pioneered technologies such as fluidized bed incineration and supercritical water oxidation. These systems enable efficient waste treatment while maximizing the energy recovery potential.
Current Trends or Developments
Increased Investment in WtE Projects in Asia
Asia is witnessing a surge in investment in WtE projects. Governments and private entities are recognizing the potential of WtE technologies in addressing the waste management crisis. This increased investment is driving the development of new WtE facilities and the expansion of existing ones.
Technological Advancements and Innovation in WtE Processes
Technological advancements and innovation are revolutionizing WtE processes in Asia. Researchers and industry players are continuously exploring new methods to improve efficiency, enhance environmental performance, and optimize energy recovery. These advancements include the integration of advanced sorting and recycling technologies, as well as the utilization of artificial intelligence for process optimization.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources in WtE Facilities
The integration of renewable energy sources in WtE facilities is gaining traction in Asia. The combination of WtE with renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind, allows for a more sustainable and diversified energy generation. This integration further strengthens the environmental and economic benefits of WtE facilities.
Challenges or Controversies
Environmental Concerns and Emission Control
One of the main challenges associated with WtE facilities is the potential environmental impact, particularly air emissions. Proper emission control measures need to be implemented to minimize the release of pollutants into the atmosphere. Continuous monitoring and strict adherence to emission standards are crucial to mitigate environmental concerns.
Public Perception and Acceptance of WtE Facilities
Public perception and acceptance of WtE facilities can be a significant challenge. Misconceptions about the environmental and health impacts of incineration, for example, may lead to opposition from local communities. Effective communication, community engagement, and transparency are essential to address these concerns and build public trust.
Balancing Economic Benefits with Social and Environmental Impacts
Finding a balance between the economic benefits of WtE facilities and their social and environmental impacts is a critical challenge. While WtE offers economic opportunities and environmental benefits, it is essential to ensure that the social well-being of communities and the protection of the environment are not compromised.
Future Outlook
Potential for Further Growth and Expansion of WtE in Asia
The future of WtE in Asia looks promising, with significant potential for further growth and expansion. As waste generation continues to increase in parallel with economic growth, the demand for sustainable waste management solutions will persist. WtE technologies offer a viable and effective approach to address these challenges.
Integration of Emerging Technologies and Solutions
Emerging technologies and solutions, such as plasma gasification and waste-to-hydrogen, hold immense potential for the WtE industry in Asia. These technologies offer higher energy recovery rates, improved environmental performance, and additional revenue streams. The integration of these emerging technologies will further enhance the efficiency and sustainability of WtE processes.
Policy and Regulatory Developments
Policy and regulatory developments play a crucial role in shaping the future of WtE in Asia. Governments need to establish clear and supportive frameworks that incentivize investment in WtE projects while ensuring the protection of the environment and public health. Strong regulations and standards will promote the adoption of sustainable waste management practices across the region.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the waste-to-energy (WtE) industry is of paramount importance and relevance in Asia. The historical background, key concepts, main discussion points, case studies, current trends, challenges, and future outlook discussed in this article demonstrate the transformative potential of WtE in growing economies. Continued research, investment, and policy support are vital to harness the full benefits of WtE and ensure a sustainable future for Asia.