Introduction
Solar cell efficiency is a critical factor in harnessing the power of the sun to generate electricity. As renewable energy sources gain popularity, understanding how solar cell efficiency is measured becomes crucial for advancements in solar energy. This article explores the historical background, key concepts, main discussion points, case studies, current trends or developments, challenges or controversies, future outlook, and the importance of improving solar cell efficiency.
Historical Background
Solar cell efficiency has come a long way since its inception. The first solar cell, built in 1954, had an efficiency of only around 6%. Since then, significant advancements have been made. Breakthroughs such as the discovery of the photovoltaic effect and the development of the first silicon solar cell paved the way for further improvements in solar cell efficiency.
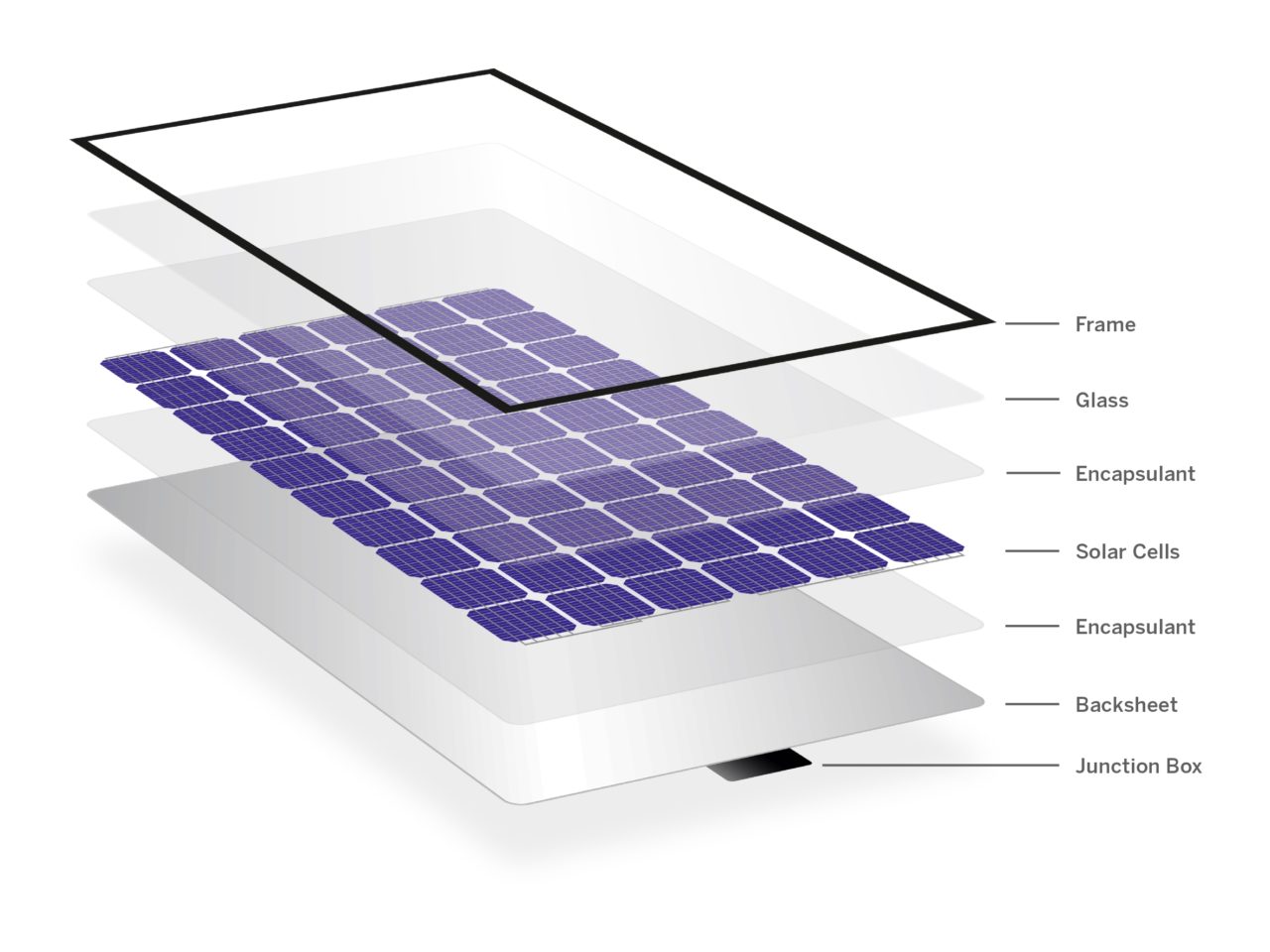
Key Concepts and Definitions
Solar cell efficiency refers to the ability of a solar cell to convert sunlight into electricity. It is usually measured as a percentage of the total energy in sunlight that the cell can convert into usable electrical energy. Terms such as power output, open-circuit voltage, short-circuit current, and fill factor are important in understanding solar cell efficiency. Power output refers to the amount of electrical power generated by the solar cell, while open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current are key parameters in determining its performance. Fill factor represents the ratio of the maximum power output of the solar cell to the product of open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current. It is an important factor in determining the overall efficiency.
Main Discussion Points
Factors influencing solar cell efficiency are multifaceted. Material properties such as bandgap and absorption coefficient play a crucial role. The bandgap determines the range of wavelengths of light that the solar cell can absorb, while the absorption coefficient represents the ability of the material to absorb photons. Additionally, the structure and design of the solar cell, such as single-junction vs. multi-junction configurations, can significantly impact its efficiency. Temperature and environmental conditions also affect efficiency, as higher temperatures can reduce the performance of the solar cell.
Measurement methods for solar cell efficiency include standard testing conditions (STC) and nominal operating cell temperature (NOCT). STC provides a standardized set of conditions under which solar cell efficiency is measured, allowing for accurate comparisons between different cells. Efficiency calculations, such as the efficiency equation and power conversion efficiency, help quantify the performance of the solar cell. External quantum efficiency (EQE) and internal quantum efficiency (IQE) are measurements that assess the efficiency of the solar cell in converting photons to electrons.
Advances in improving solar cell efficiency have been driven by the use of novel materials. Perovskites have shown promising results in enhancing efficiency due to their unique properties. Tandem solar cells, which combine different materials to capture a broader range of wavelengths, further improve efficiency. Light trapping techniques, such as textured surfaces and anti-reflective coatings, also contribute to maximizing absorption of sunlight. Enhancements in manufacturing processes, like passivation and surface texturing, play a crucial role in reducing energy losses and improving overall efficiency.

Case Studies or Examples
Successful solar cell efficiency projects or installations highlight the progress made in the field. For instance, the Solar Impulse 2 aircraft completed a historic flight around the world solely powered by solar energy. This achievement showcases the potential of high-efficiency solar cells. Different types of solar cells, such as monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film cells, exhibit varying efficiency ratings. Monocrystalline cells are known for their high efficiency, while thin-film cells offer flexibility and lower manufacturing costs.
Current Trends or Developments
Recent research findings have sparked exciting advancements in solar cell efficiency. Scientists have discovered new materials and technologies that hold promise for improving efficiency. For example, perovskite solar cells have seen rapid efficiency gains in a short period. Emerging technologies like tandem solar cells and organic solar cells offer the potential for even higher efficiencies. Furthermore, advancements in manufacturing processes and the integration of artificial intelligence in solar energy systems are expected to further improve efficiency.
Challenges or Controversies
Achieving higher solar cell efficiency is not without its challenges. One major obstacle is balancing efficiency with cost-effectiveness. High-efficiency solar cells often come with higher production costs, limiting their widespread adoption. Additionally, there are controversies surrounding the accuracy of efficiency measurements or claims made by manufacturers. Standardization and independent testing are crucial to ensure transparency and reliability in solar cell efficiency measurements.
Future Outlook
The future of solar cell efficiency looks promising. Ongoing research and development efforts aim to push the limits of efficiency even further. Advancements in materials, manufacturing processes, and design principles are expected to increase solar cell efficiency and reduce costs. Higher efficiency solar cells have the potential to revolutionize the energy landscape by making solar energy more accessible and sustainable.
Conclusion
Solar cell efficiency plays a vital role in harnessing the power of sunlight to generate electricity. Understanding the factors, measurement methods, and advancements in solar cell efficiency is crucial for the development and adoption of solar energy technologies. With ongoing research and technological advancements, the future holds great potential for increasing solar cell efficiency and accelerating the transition towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
References
- Green, M. A., Emery, K., Hishikawa, Y., Warta, W., & Dunlop, E. D. (2015). Solar cell efficiency tables (version 45). Progress in Photovoltaics: Research and Applications, 23(1), 1-9.
- Polman, A., Knight, M., & Garnett, E. C. (2016). The road to 30% efficient photovoltaics: perspectives from silicon-based tandem cells. Advanced Materials, 28(31), 6268-6383.
- Singh, S., & Williams, J. (2015). Textured antireflective coatings for solar cells. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A, 33(6), 060801.




