Biofuels: A Sustainable Solution for Renewable Energy
Introduction
Biofuels have emerged as a promising solution in the quest for renewable energy and environmental sustainability. As the world faces the urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and shift away from fossil fuels, understanding the different types of biofuels becomes crucial. By harnessing the power of organic matter, biofuels offer an alternative that can address climate change while reducing our dependence on finite resources.
Historical Background
The history of biofuels dates back to ancient times when biomass, such as wood and animal waste, was used as a fuel source. However, significant milestones in biofuel technologies were achieved in the early 20th century. The production of ethanol from corn marked the beginning of ethanol’s prominence as a biofuel.
Key Concepts and Definitions
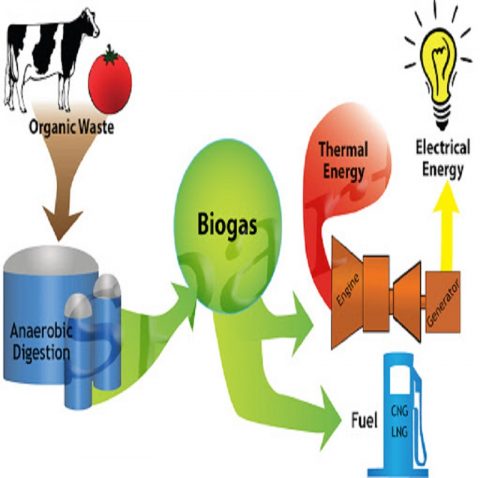
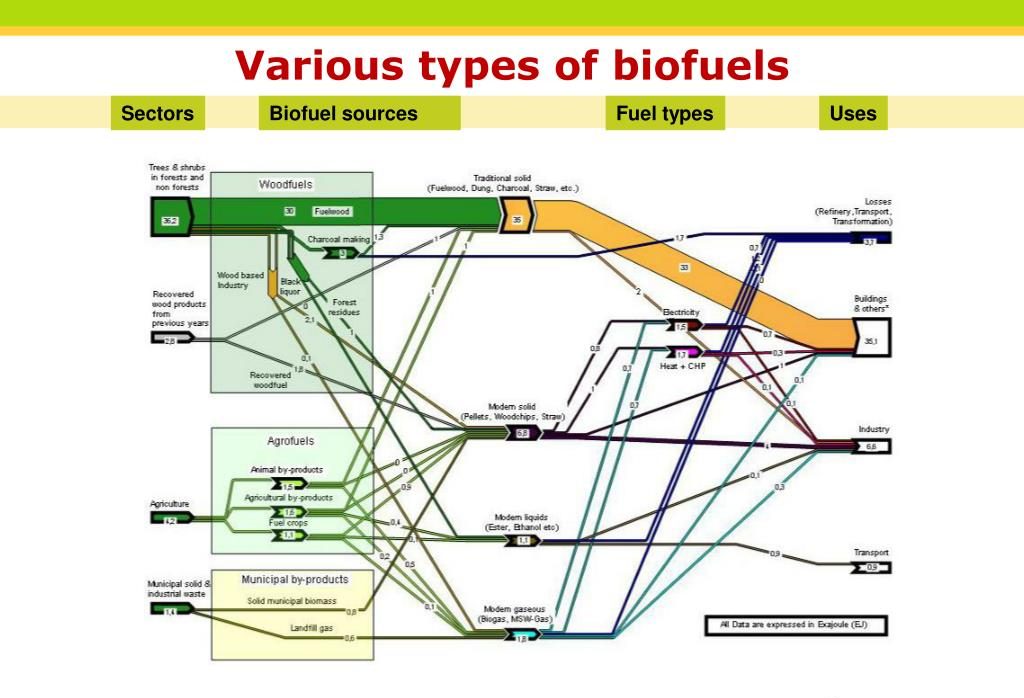
Biofuels are fuels derived from organic matter, commonly known as biomass. The production of biofuels involves various processes, including the conversion of biomass into usable fuel through biochemical or thermochemical methods. Key terms and concepts related to biofuels include feedstocks (the raw materials used), conversion processes, and the distinction between first-generation and advanced biofuels.
Main Discussion Points
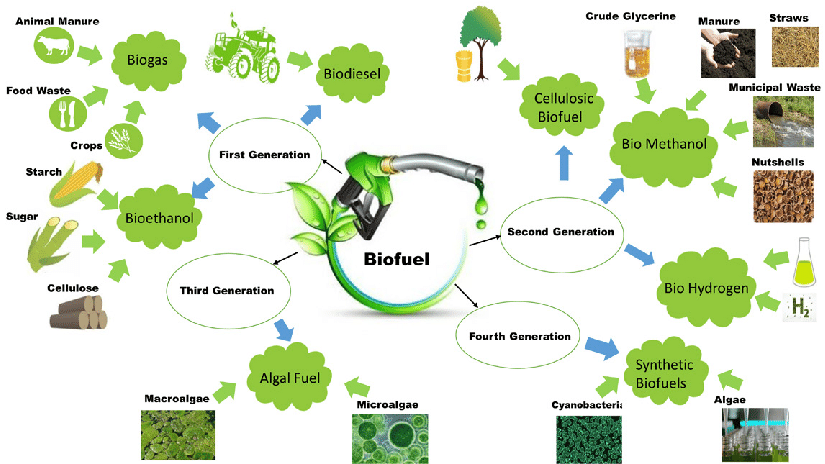
First-Generation Biofuels
First-generation biofuels refer to those derived from edible crops, such as corn and sugarcane, or vegetable oils. Ethanol and biodiesel are the most common types of first-generation biofuels. These biofuels have limitations, including competition for agricultural land and potential impacts on food prices. However, they also offer advantages such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels.
Advanced Biofuels
Advanced biofuels are produced from non-edible feedstocks, such as agricultural residues or algae. They offer several advantages over first-generation biofuels, including higher energy efficiency and lower land-use requirements. Types of advanced biofuels include cellulosic ethanol, algae-based biofuels, and renewable diesel. Challenges in advanced biofuel production include scaling up production processes and ensuring economic viability.
Emerging Biofuels
Emerging biofuels are currently under development or in the early stages of commercialization. Breakthrough technologies, such as bioelectrochemical systems and synthetic biology approaches, show promise in improving the efficiency and sustainability of biofuel production. However, challenges lie in the scalability and cost-effectiveness of these emerging biofuels.
Case Studies or Examples
Real-world examples of successful biofuel projects showcase the potential of biofuels in various industries and countries. Countries like Brazil and the United States have made significant advancements in biofuel production, particularly in ethanol from sugarcane and corn, respectively. Companies like ExxonMobil and Solazyme have also made strides in the production of advanced biofuels.
Current Trends or Developments
The biofuel industry is experiencing notable trends and developments. Policy changes, such as renewable fuel standards and carbon pricing, are driving investments and market growth. Technological advancements, including improved feedstock selection and conversion processes, are enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of biofuel production. Market dynamics, such as fluctuating oil prices and increasing consumer demand for sustainable alternatives, also shape the biofuel industry.
Challenges or Controversies
Biofuels face challenges and controversies surrounding their sustainability and environmental impact. Competition for land and resources raises concerns about deforestation and food security. Additionally, the indirect land-use changes resulting from biofuel production can have unintended consequences. Different viewpoints exist regarding the overall sustainability and environmental benefits of biofuels, necessitating careful evaluation and regulation.

Future Outlook
The future of biofuels holds great potential. Ongoing research and development efforts aim to overcome current limitations and make biofuel production more efficient and sustainable. Innovations in feedstock selection, conversion processes, and technology advancements will contribute to the continued growth of biofuels. Moreover, biofuels can play a vital role in achieving global climate change mitigation goals by reducing carbon emissions in the transportation sector.
Conclusion
In conclusion, biofuels offer a viable solution for transitioning towards a more sustainable energy system. Understanding the various types of biofuels, from first-generation to advanced and emerging biofuels, is essential for addressing climate change and reducing dependence on fossil fuels. While challenges exist, ongoing advancements and research efforts provide hope for a future where biofuels contribute significantly to renewable energy sources.




