
International Agreements on Biofuel Trade: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction:
The topic of international agreements on biofuel trade is of significant importance in today’s global context. As countries strive to transition to more sustainable and renewable sources of energy, biofuels have emerged as a viable alternative to fossil fuels. These agreements play a crucial role in facilitating the trade and adoption of biofuels on an international scale.
Historical Background:
Biofuel trade has a rich history, with its origins dating back to the early 20th century. However, it was not until the 21st century that international agreements began to shape the biofuel trade landscape. These agreements aimed to promote the production and consumption of biofuels while addressing concerns related to sustainability, environmental impact, and energy security.
Key Concepts and Definitions:
Biofuels can be defined as fuels derived from renewable biological resources, such as plant-based feedstocks or organic waste materials. The two main types of biofuels are ethanol and biodiesel, which are produced through different processes.
International agreements refer to legally binding commitments between countries to cooperate and address common challenges in specific areas. In the context of biofuel trade, these agreements are designed to facilitate the global exchange of biofuels, establish common standards, and promote sustainable practices.
Main Discussion Points:
Overview of major international agreements on biofuel trade:
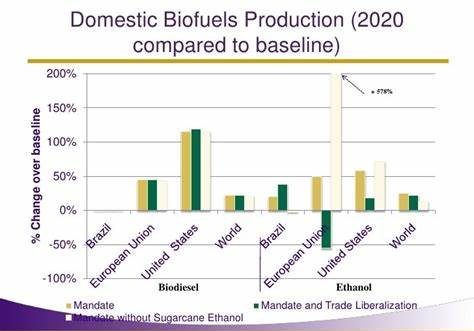
Several international agreements have been instrumental in shaping the biofuel trade landscape. The Renewable Energy Directive in the European Union and the Kyoto Protocol at the global level are among the key agreements. These agreements set goals and targets for biofuel production and consumption, establish sustainability criteria, and provide a framework for cooperation among nations.
Impact of international agreements on biofuel production and consumption:
International agreements play a significant role in influencing biofuel production and consumption patterns. By setting targets and standards, these agreements incentivize countries to invest in biofuel infrastructure and promote the use of renewable energy sources. Moreover, they encourage the adoption of sustainable practices, such as the use of feedstocks with low carbon intensity.

Challenges and limitations of international agreements on biofuel trade:
Implementing and monitoring international agreements on biofuel trade pose various challenges. These challenges include the need for harmonization of regulations and sustainability criteria, addressing conflicting national interests, and differing viewpoints on the role of biofuels in achieving climate change mitigation goals. Overcoming these challenges requires robust international cooperation and ongoing dialogue among stakeholders.
Case Studies or Examples:
Case study: The European Union’s Renewable Energy Directive:
The Renewable Energy Directive is one of the most prominent international agreements on biofuel trade. It sets binding targets for renewable energy consumption, including biofuels, within the EU. The directive has had a significant impact on biofuel trade within the EU, promoting the use of sustainable feedstocks and encouraging investments in biofuel production facilities.
Case study: The United States’ Renewable Fuel Standard:
The Renewable Fuel Standard in the United States mandates the blending of biofuels, primarily ethanol, into transportation fuels. It has played a pivotal role in stimulating domestic biofuel production and has also influenced international biofuel markets. However, it has also faced criticism for its impact on food security and land use.
Current Trends or Developments:
Recent trends in international biofuel trade reflect the growing importance of sustainability and environmental considerations. Countries are increasingly adopting stricter sustainability criteria for biofuel production and focusing on advanced biofuels that have lower greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, emerging research findings are shedding light on the potential of biofuels derived from algae and other non-food feedstocks.
Challenges or Controversies:
Implementing and enforcing international agreements on biofuel trade presents numerous challenges. These include the need to address compliance issues, ensure transparency in supply chains, and prevent potential negative impacts on food security and land use. Controversies surrounding biofuel production’s contribution to greenhouse gas emissions and its potential trade-offs with food production have sparked debates among policymakers and stakeholders.
Future Outlook:
The future of international agreements on biofuel trade holds various implications and directions. With increasing emphasis on sustainability, there is a need for further innovation and investment in advanced biofuels. Additionally, international cooperation must be strengthened to address emerging challenges and ensure the long-term viability of biofuel trade.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, international agreements on biofuel trade have a pivotal role in shaping the global transition towards sustainable energy sources. These agreements provide a framework for cooperation, set targets and standards, and promote sustainable practices. However, challenges and controversies persist, emphasizing the need for ongoing dialogue and innovation. International cooperation and collaboration will be key to realizing the full potential of biofuel trade and achieving a more sustainable future.




