
The Social Impact of Biofuels: Exploring the Benefits and Challenges
Introduction
The social impact of biofuels has gained significant attention in recent years due to the increasing need to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and combat climate change. This article aims to delve into the social implications of biofuels, examining both the positive and negative aspects. By understanding the broader social impact of biofuels, we can make informed decisions and take necessary actions to ensure a sustainable future.
Historical Background
Biofuels have a rich history that dates back several decades. Initially, biofuel production was limited to small-scale applications, such as powering agricultural machinery. However, with the growing concerns over climate change and the need for renewable energy sources, biofuels gained traction. The development of biofuel technologies and the exploration of various feedstocks have paved the way for their widespread use in transportation, heating, and electricity generation.
Key Concepts and Definitions
To understand the social impact of biofuels, it is crucial to define the key concepts associated with this topic. Biofuels encompass a range of renewable fuels derived from organic matter, including biodiesel and ethanol. Social impact refers to the effects that biofuels have on society and communities. It involves assessing factors like sustainability, food security, and land use change, which are central to understanding the broader implications of biofuel production and use.
Main Discussion Points
Positive Social Impacts of Biofuels
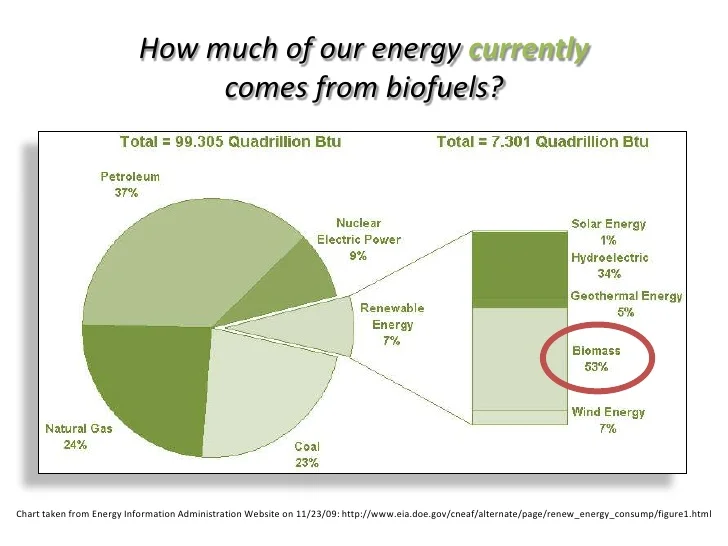
Biofuels offer several positive social impacts. Firstly, they contribute to energy security by reducing dependence on fossil fuels and providing an alternative source of energy. Additionally, the production and use of biofuels can create job opportunities and stimulate economic development, particularly in rural areas where feedstocks are grown. Furthermore, biofuels play a significant role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating the adverse effects of climate change.
Negative Social Impacts of Biofuels
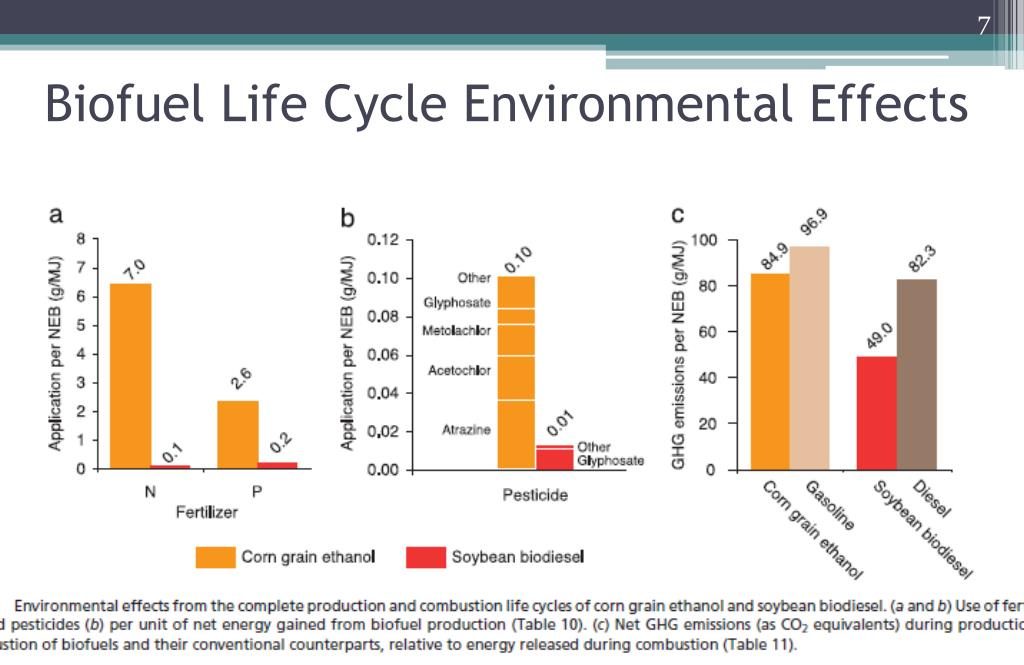
While biofuels offer benefits, they also entail negative social impacts. One concern is the potential impact on food security due to land use change. It is crucial to address this issue and ensure that biofuel production does not compromise the availability of food resources. Moreover, increased competition for resources, such as water and fertile land, can have social implications, including conflicts and inequalities. Another significant concern is the potential displacement of small-scale farmers and indigenous communities, who may face challenges in adapting to changes brought about by biofuel production.
Ethical Considerations of Biofuel Production and Use
The ethical considerations surrounding biofuel production and use are complex. One ethical concern is the use of food crops for biofuel production. Critics argue that diverting resources from food production to biofuels may exacerbate food insecurity in vulnerable communities. Additionally, the impact of biofuel production on biodiversity raises ethical questions, as it may lead to habitat destruction and loss of valuable ecosystems. Furthermore, biofuel policies and practices must be scrutinized for their social justice implications, ensuring that they do not disproportionately affect marginalized communities.
Case Studies or Examples
Real-world examples provide insights into the social impact of biofuels. In Brazil, the introduction of sugarcane-based ethanol has led to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and job creation in the agricultural sector. However, concerns have been raised about the potential social and environmental consequences, particularly regarding land use change and labor conditions. Similarly, in the United States, the production of corn-based ethanol has shown positive impacts on energy security and rural economies. Yet, its reliance on a food crop has sparked debates on food prices and availability.

Current Trends or Developments
Ongoing research continues to shed light on the social impact of biofuels. Recent studies have focused on evaluating the sustainability of different feedstocks and assessing the social implications of biofuel policies. Current trends in biofuel production highlight the shift towards advanced biofuels, which utilize non-food feedstocks like algae and agricultural residues. Additionally, new technologies and policies, such as the development of bioelectrochemical systems and the implementation of renewable fuel standards, have the potential to shape the future of biofuels and their social impact.
Challenges or Controversies
Biofuel production and implementation face various challenges. One major concern is the competition between biofuel production and food production. Balancing the need for renewable energy with ensuring food security is a complex task. Furthermore, controversies and differing viewpoints surround biofuels, particularly in relation to their overall sustainability and effectiveness in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Conflicts may also arise between biofuel production and other social priorities, such as water scarcity and conservation.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, biofuels hold great potential, but it is essential to address the challenges and mitigate negative social impacts. Strategies for achieving this include promoting the development of advanced biofuels that do not rely on food crops, implementing sustainable land use practices, and supporting research on innovative technologies. The future of biofuels and their social impact will be shaped by technological advancements, policy frameworks, and public opinion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the social impact of biofuels is crucial for making informed decisions and ensuring a sustainable future. While biofuels offer positive benefits like energy security, job creation, and reduced greenhouse gas emissions, their production and use also pose challenges. Addressing concerns related to land use change, food security, and social justice is essential. By considering these factors and actively seeking solutions, we can maximize the positive social impacts of biofuels while minimizing the negative ones.
References
Smith, K. R., & Haq, G. (2010). Biofuels, air pollution, and health: A global review. Health Effects Institute.
Tilman, D., Socolow, R., Foley, J. A., Hill, J., Larson, E., Lynd, L., … & Williams, R. (2009). Beneficial biofuels: the food, energy, and environment trilemma. Science, 325(5938), 270-271.
Zilberman, D., Hochman, G., & Rajagopal, D. (2013). The impact of biofuels on commodity food prices: Assessment of findings. American Journal of Agricultural Economics, 95(2), 275-281.




