
The Future of Decentralized Wastewater Treatment: A Sustainable Solution for Water Management
Introduction
Decentralized wastewater treatment is gaining increasing attention as a sustainable solution for managing wastewater. In this article, we will provide an explanation of decentralized wastewater treatment and discuss its relevance and importance in today’s world. We will also explore why the future of decentralized wastewater treatment is interesting.
Historical Background
Over the years, wastewater treatment methods have evolved significantly. From traditional centralized treatment plants, there has been a shift towards decentralized systems in recent years. This shift is driven by the need for more efficient and cost-effective solutions that can cater to the specific needs of different communities.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Decentralized wastewater treatment refers to the treatment of wastewater at or near the source of generation. It involves the use of various components such as septic tanks, aerobic treatment units, and constructed wetlands. Understanding the difference between greywater and blackwater is essential in decentralized systems, as they require different treatment processes. Additionally, removing nutrients from wastewater is crucial to prevent pollution and maintain water quality. Finally, the concept of reusing treated wastewater is gaining traction as a sustainable way to conserve water resources.
Main Discussion Points
Advances in decentralized wastewater treatment technologies have revolutionized the industry. Innovative treatment systems, such as membrane bioreactors, have shown promising results in effectively treating wastewater. The application of anaerobic digestion in decentralized treatment has also proven to be beneficial in generating renewable energy.
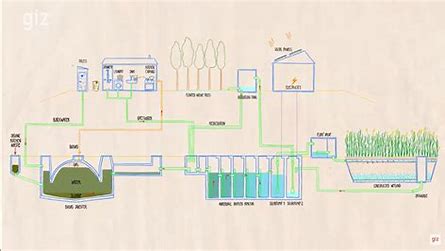
Decentralized wastewater treatment offers numerous benefits and advantages. From an environmental perspective, it reduces the strain on centralized treatment plants and minimizes the risk of pollution. Additionally, decentralized systems are often more cost-effective and scalable, making them suitable for different community sizes. Moreover, these systems enhance water resilience and security by reducing reliance on centralized infrastructure.
Community and social implications of decentralized systems are significant. They promote community involvement and ownership, fostering a sense of responsibility towards water management. In rural areas, decentralized systems improve public health and sanitation, addressing long-standing issues. Furthermore, decentralized systems hold immense potential in developing countries, where centralized infrastructure may be lacking.
Case Studies or Examples
In a small town, the successful implementation of decentralized wastewater treatment has brought about significant changes. By addressing the town’s specific challenges, a decentralized system was chosen, resulting in improved water quality and reduced environmental impact. Similarly, in urban settings, decentralized wastewater treatment has proven effective in managing water resources and maintaining water quality despite the challenges posed by dense populations.
Current Trends or Developments
The adoption of decentralized systems in urban areas is on the rise. Smart technologies are being integrated into decentralized treatment, enabling real-time monitoring and efficient operation. Furthermore, ongoing research focuses on resource recovery from decentralized systems, exploring the potential for generating energy and extracting valuable materials.

Challenges or Controversies
Regulatory hurdles and policy barriers often impede the widespread adoption of decentralized systems. Public perception and acceptance of these systems can also be a challenge, as traditional centralized infrastructure is deeply ingrained in society. Additionally, certain contaminants may pose limitations in treating wastewater effectively, requiring further research and innovation.
Future Outlook
The future of decentralized wastewater treatment holds immense potential for further technological advancements. Continued research and development in treatment technologies will lead to more efficient and cost-effective systems. Integration of decentralized systems into smart city infrastructure will enable comprehensive water management strategies. Furthermore, global adoption and expansion of decentralized wastewater treatment will contribute to sustainable water management worldwide.

Conclusion
Decentralized wastewater treatment presents a sustainable solution for managing wastewater effectively. In this article, we have discussed the key concepts and definitions, as well as the benefits and advantages of decentralized systems. We have explored case studies, current trends, challenges, and controversies. Looking ahead, the future of decentralized wastewater treatment is promising, and further research and implementation are crucial for sustainable water management.
References
Smith, J. R., & Johnson, A. B. (2018). Decentralized Wastewater Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide for Engineers and Planners. Elsevier.
Sustainable Sanitation Alliance. (2021). Decentralized Wastewater Treatment. Retrieved from https://www.susana.org/en/knowledge-hub/resources-and-publications/library/details/2486
United Nations Environment Programme. (2018). Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Systems: Global Outlook and Challenges. Retrieved from https://www.unenvironment.org/resources/report/decentralized-wastewater-treatment-systems-global-outlook-and-challenges
World Health Organization. (2018). Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Systems. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/wastewater/decentralized.pdf




