
The Role of Wastewater Treatment in Sustainable Urban Development
Introduction
Wastewater treatment and sustainable urban development play crucial roles in ensuring a healthy environment and quality of life for urban dwellers. This article provides an in-depth overview of the historical background, key concepts, main discussion points, case studies, current trends, challenges, future outlook, and the importance of wastewater treatment and sustainable urban development.
Historical Background
The evolution of wastewater treatment practices can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as the Indus Valley and Mesopotamia, where early systems were used to manage waste. These practices have since evolved into sophisticated treatment processes. Similarly, early initiatives towards sustainable urban development focused on improving sanitation and waste management systems to promote healthier living conditions.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Wastewater treatment refers to the processes and technologies used to remove contaminants from wastewater, making it safe for discharge or reuse. Sustainable urban development is an approach that aims to achieve social, economic, and environmental sustainability in urban areas. The objectives include promoting efficient resource use, enhancing quality of life, and minimizing negative environmental impacts.
Main Discussion Points
Point: Importance of wastewater treatment for public health and environmental sustainability:
Untreated wastewater can have a detrimental impact on water bodies and ecosystems, contributing to water pollution, depleting oxygen levels, and disrupting aquatic life. Wastewater treatment plays a critical role in preventing waterborne diseases by removing harmful pathogens and chemicals.
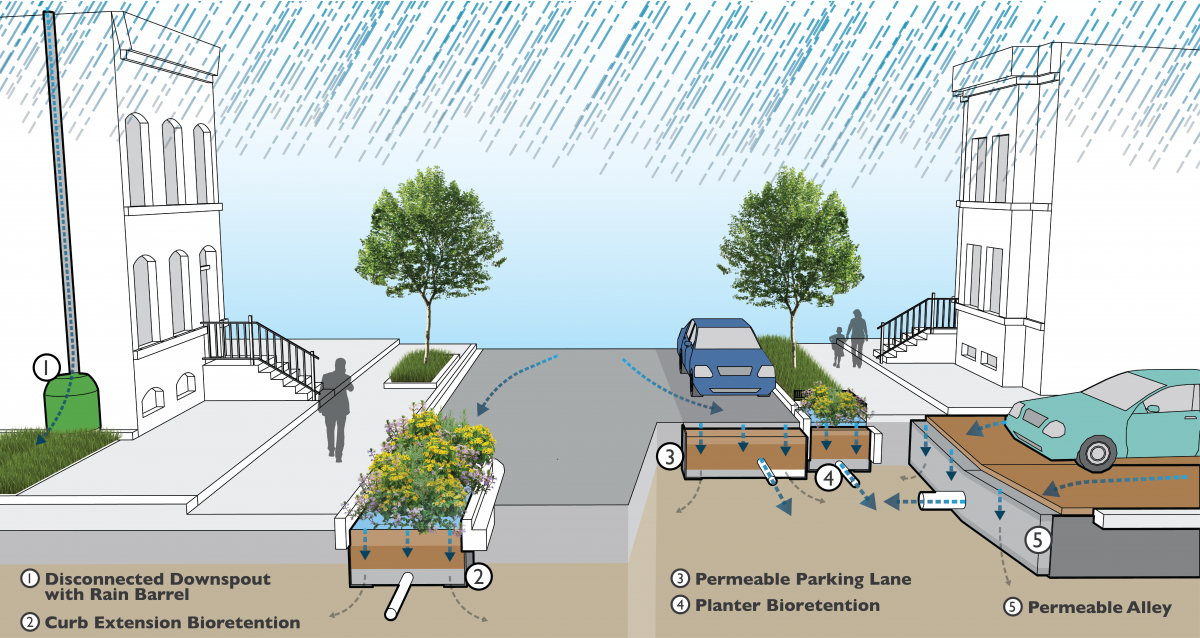
Point: Integration of wastewater treatment with sustainable urban development:
Water-sensitive urban design is a concept that promotes the effective management of water resources by integrating wastewater treatment systems into urban planning. Decentralized wastewater treatment systems offer numerous benefits, including reduced environmental impact, improved water quality, and increased resilience to climate change.
Point: Economic and social aspects of wastewater treatment and sustainable urban development:
Reclaimed water and nutrient recovery have economic value, as they can be used for irrigation, industrial processes, and even drinking water. Additionally, improved sanitation and access to clean water have significant social benefits, including reduced disease burden, improved quality of life, and gender equality.
Case Studies or Examples
Case study: Singapore’s NEWater initiative and its impact on water security:
Singapore’s innovative approach to wastewater treatment, known as NEWater, has helped the country achieve water security. By treating wastewater to ultra-pure standards, Singapore has reduced its reliance on imported water and diversified its water sources, ensuring a sustainable water supply for its residents.
Case study: The Copenhagen Harbor Bath project and its contribution to sustainable urban development:
The Copenhagen Harbor Bath project transformed a polluted harbor into a recreational area, highlighting the potential of sustainable urban development. By incorporating wastewater treatment systems into the design, the project not only improved water quality but also revitalized the surrounding area, enhancing the overall livability of the city.

Current Trends or Developments
Advances in wastewater treatment technologies:
Recent advancements have focused on improving the efficiency and effectiveness of wastewater treatment processes. Technologies such as membrane bioreactors, advanced oxidation, and anaerobic digestion have emerged as promising solutions to address emerging contaminants and improve resource recovery.
Integration of renewable energy sources in wastewater treatment plants:
Wastewater treatment plants have the potential to become energy self-sufficient and even generate surplus energy. Integration of renewable energy sources such as solar and biogas can reduce operational costs, carbon emissions, and dependence on fossil fuels.
Research findings on the potential of wastewater for resource recovery:
Wastewater contains valuable resources such as nutrients, energy, and water. Research has shown that the recovery of these resources can contribute to a more circular economy, reducing environmental impacts and promoting sustainability.
Challenges or Controversies
Financial constraints and affordability of wastewater treatment infrastructure:
Implementing wastewater treatment infrastructure requires substantial investments. Financial constraints and affordability issues can hinder the development and expansion of treatment facilities, particularly in low-income communities.
Public perception and acceptance of reclaimed water:
Despite its safety and potential benefits, there may be public resistance and skepticism towards the use of reclaimed water for purposes such as drinking or irrigation. Overcoming these perceptions through education and effective communication is crucial to promote acceptance and adoption.
Trade-offs between centralized and decentralized wastewater treatment systems:
Centralized wastewater treatment systems offer economies of scale and centralized management, while decentralized systems provide localized benefits and increased resilience. Choosing the appropriate system requires careful consideration of factors such as cost, efficiency, and environmental impact.
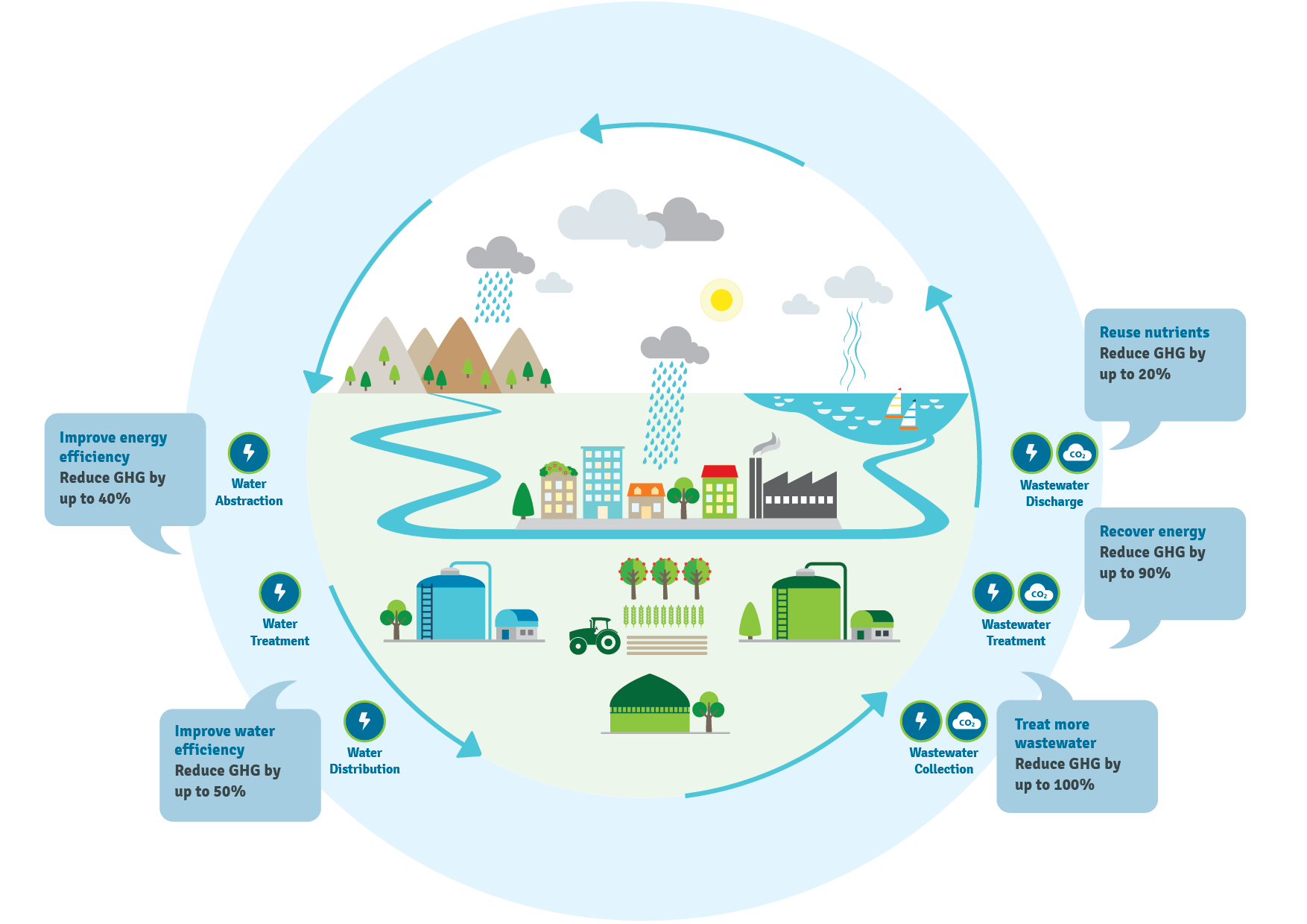
Future Outlook
Potential for innovative technologies and approaches in wastewater treatment:
The future holds promise for the development of innovative technologies, such as nanomaterials, advanced sensors, and artificial intelligence, to enhance wastewater treatment processes. Additionally, adopting nature-based solutions and circular economy principles can further improve sustainability.
Importance of policy and regulations to drive sustainable urban development:
To realize the full potential of wastewater treatment and sustainable urban development, supportive policies and regulations are essential. Governments and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in creating an enabling environment for investments, promoting research and development, and ensuring compliance with environmental standards.
Conclusion
Wastewater treatment and sustainable urban development are integral for public health, environmental sustainability, and improved quality of life. Through advancements in technology, innovative approaches, and supportive policies, we can create a future where wastewater is seen as a valuable resource rather than a waste, driving sustainable urban development.




