
Introduction
Ocean energy devices play a crucial role in renewable energy generation, harnessing the power of waves, tides, and offshore winds. These devices are essential in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating the effects of climate change. In order to improve the efficiency and durability of these devices, continuous advancements in materials are of utmost importance.
Historical Background
Ocean energy has been utilized since ancient times, with early civilizations using simple devices such as paddle wheels and tidal mills. Over time, the evolution of ocean energy devices has led to more sophisticated technologies that can harness the immense power of the ocean. In the early days, basic materials like wood and metal were used in the construction of these devices.
Key Concepts and Definitions
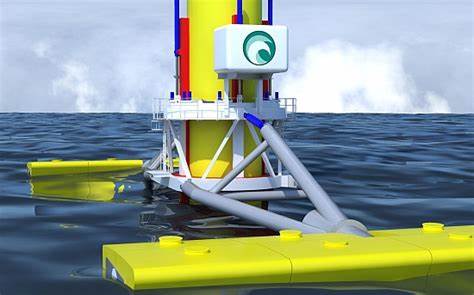
Ocean energy devices are structures designed to capture the energy from the ocean and convert it into usable electricity. Wave energy converters, tidal turbines, and floating offshore wind turbines are some of the key devices in this domain. The materials used in the design and construction of these devices are crucial in ensuring their performance and longevity.
Main Discussion Points
Advances in materials for wave energy converters have greatly impacted their efficiency and durability. Different types of converters, such as oscillating water columns and point absorbers, have been developed. Innovative materials like composites and polymers have been used in these converters, improving their energy conversion efficiency and extending their lifespan.
Innovations in materials for tidal turbines have also significantly enhanced their performance. Tidal turbines are used to harness the kinetic energy of tidal currents. Materials like carbon fiber composites and titanium alloys are now being utilized in the construction of turbine blades and components. These materials offer improved strength, corrosion resistance, and fatigue life, leading to enhanced turbine performance and reliability.
Floating offshore wind turbines are another area where materials innovation is crucial. These turbines are mounted on floating platforms, enabling deployment in deeper waters where traditional fixed-bottom turbines are not feasible. Novel materials, such as advanced composites and coatings, are being used to withstand harsh environmental conditions and combat corrosion. These materials ensure the durability and efficiency of the turbines.
Case Studies or Examples
In a successful project, innovative materials were implemented, leading to improved performance and reliability. The use of advanced composites in the construction of the converter allowed for increased energy capture and reduced maintenance requirements, resulting in enhanced project viability.
A real-world example of improved performance through advanced materials can be seen in a tidal turbine project. The use of carbon fiber composite blades significantly increased the turbine’s power output and reduced the overall weight, leading to improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness.

In a floating offshore wind turbine project, cutting-edge materials were utilized to enhance durability and efficiency. The use of advanced composites in the construction of the turbine blades and floating platforms improved corrosion resistance and structural integrity, ensuring long-term operation in harsh marine environments.
Current Trends or Developments
Recent research has focused on optimizing materials for ocean energy devices. Advancements in nanotechnology and biomimicry have led to the development of new materials with superior properties. Additionally, the integration of smart materials and sensors has enabled real-time monitoring and control of device performance.
Emerging trends in the field include the exploration of bio-based materials and additive manufacturing techniques. Bio-based materials offer sustainability benefits while additive manufacturing allows for complex geometries and customization. These trends aim to further improve the efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness of ocean energy devices.
Challenges or Controversies
One of the challenges in material selection for ocean energy devices lies in their exposure to harsh marine conditions, including seawater corrosion and biofouling. Finding materials that can withstand these challenges while maintaining performance is crucial for the long-term operation of these devices.
Controversies surround the environmental impact of certain materials used in ocean energy devices. It is important to prioritize materials that have a lower carbon footprint and can be recycled or reused at the end of their life cycle.
Differing viewpoints exist on the prioritization of certain material characteristics over others. Some emphasize the importance of cost-effectiveness, while others prioritize sustainability and environmental considerations. Balancing these viewpoints is essential to drive the industry forward.
Future Outlook
Innovations in materials for ocean energy devices are expected to continue in the future. Advancements in material science and engineering will lead to increased efficiency, sustainability, and durability of these devices. The use of bio-inspired materials, advanced composites, and nanomaterials will play a significant role in this progress.

The growth and commercialization of ocean energy technologies heavily rely on the development of optimized materials. As more countries and industries embrace renewable energy, the demand for efficient and reliable ocean energy devices will increase. Materials innovation will be a driving force in meeting these demands and achieving a sustainable energy future.
Conclusion
Innovations in materials are crucial for improving the efficiency and durability of ocean energy devices. Advances in materials for wave energy converters, tidal turbines, and floating offshore wind turbines have already shown significant improvements in performance and reliability. Through case studies, it can be seen how the use of advanced materials has led to enhanced project viability and improved cost-effectiveness. Continued research and development, along with the integration of emerging trends and technologies, will pave the way for a more sustainable and efficient ocean energy sector.




