
Ocean Energy: Harnessing the Power of the Sea for Environmental Sustainability
Introduction
The field of ocean energy is rapidly developing and holds great promise for promoting environmental responsibility. As the world grapples with climate change and the need to transition away from fossil fuels, exploring alternative sources of renewable energy becomes increasingly crucial. The vast potential of the world’s oceans to generate clean and sustainable power makes ocean energy an exciting avenue to explore. This article will delve into the historical background, discuss key concepts, explore case studies, analyze current trends, address challenges and controversies, discuss the future outlook, and highlight the significance of ocean energy in promoting environmental responsibility.
Historical Background
The development of ocean energy technologies dates back several decades. In the mid-20th century, researchers began exploring the potential of waves, tides, and temperature differences in the ocean to generate electricity. Over time, advancements in engineering and technology have led to the creation of various devices and systems capable of harnessing ocean energy. Notable milestones include the installation of the world’s first commercial wave energy farm in Portugal in 2008 and the deployment of the first grid-connected tidal energy turbine off the coast of Northern Ireland in 2008.
Key Concepts and Definitions
To fully understand ocean energy and its implications, it is important to define key terms such as ocean energy, renewable energy, and environmental responsibility. Ocean energy refers to the energy harnessed from the motion of waves, the rise and fall of tides, and the temperature differences in the ocean. Renewable energy, on the other hand, is energy derived from sources that are naturally replenished, such as sunlight, wind, and ocean energy. Environmental responsibility encompasses the actions and practices taken to minimize harmful impacts on the environment and promote sustainability.
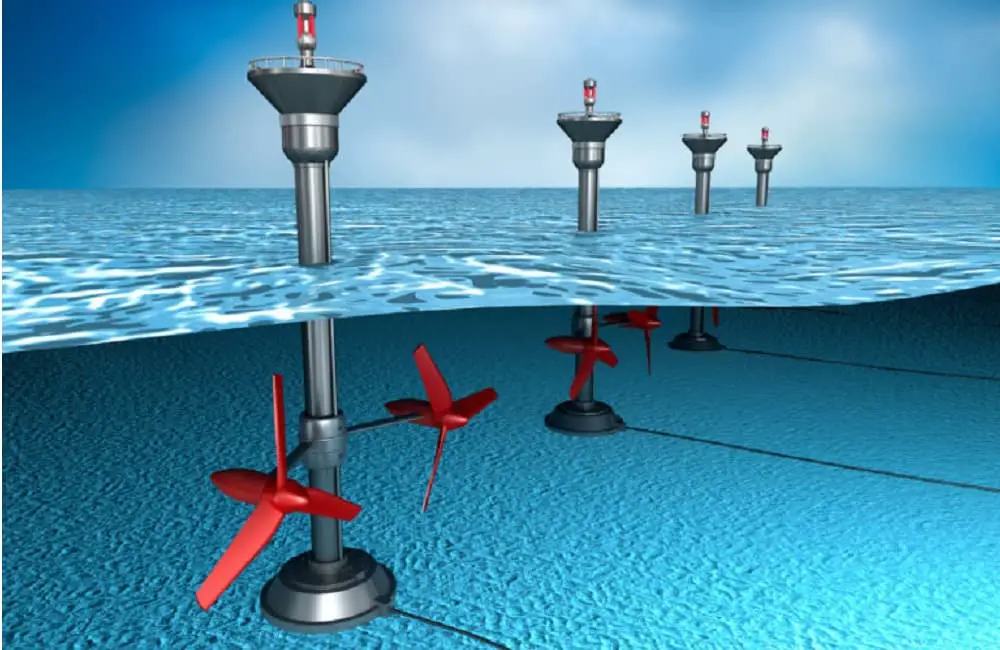
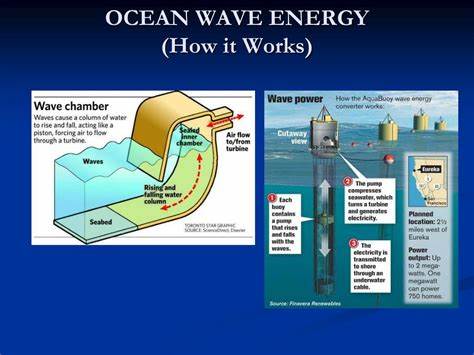
Different types of ocean energy technologies exist, including tidal, wave, and thermal. Tidal energy is generated by harnessing the kinetic energy of tidal currents, while wave energy utilizes the motion of waves to produce electricity. Thermal energy, also known as ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC), captures the temperature difference between warm surface waters and cold deep waters to generate power.
Main Discussion Points
The potential of ocean energy to reduce dependency on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
Ocean energy has the potential to provide a clean, renewable source of power that can help reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. By tapping into the immense energy of the ocean, we can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change. Unlike fossil fuels, ocean energy does not contribute to air pollution or emit harmful greenhouse gases. Additionally, the ocean’s energy potential is virtually limitless, making it a promising alternative to fossil fuels.

Replacing traditional energy sources with ocean energy offers significant environmental benefits. It reduces carbon emissions, decreases reliance on finite resources, and helps preserve ecosystems vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. By embracing ocean energy, we can create a more sustainable and resilient future for generations to come.
The challenges and opportunities of harnessing ocean energy.
While ocean energy holds tremendous potential, there are challenges to overcome in harnessing it effectively. Technical and logistical challenges include designing and deploying robust devices capable of withstanding harsh marine environments. Additionally, the installation and maintenance of ocean energy infrastructure can be complex and costly. However, with advancements in technology and ongoing research, these challenges can be addressed.
Despite the challenges, there are significant economic and social opportunities associated with ocean energy projects. Developing a thriving ocean energy industry can create job opportunities, stimulate local economies, and drive innovation. It can also enhance energy security by diversifying our energy sources and reducing dependence on imported fuels.
The role of government policies and regulations in promoting ocean energy.
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in promoting the development of ocean energy. Existing policies and incentives aim to support renewable energy projects, including those in the ocean energy sector. These policies include feed-in tariffs, tax credits, and grants that encourage investment in ocean energy technologies. However, to drive further progress, consistent and supportive regulations are needed. Clear guidelines and streamlined approval processes can facilitate the deployment of ocean energy projects while ensuring environmental protection and stakeholder engagement.
Case Studies or Examples
Real-world examples of successful ocean energy projects provide valuable insights into the environmental and economic impacts of this technology. The MeyGen tidal energy project in Scotland, for instance, has successfully deployed multiple tidal turbines and demonstrated the feasibility of large-scale tidal energy generation. This project not only provides clean electricity to thousands of homes but also creates jobs and stimulates economic growth in the region.
Another notable example is the Wave Hub project in Cornwall, England, which serves as a testing facility for various wave energy devices. By providing a platform for developers to trial their technologies, the project contributes to the advancement of wave energy and the growth of the industry.
These case studies highlight the potential of ocean energy to transform the energy landscape while minimizing environmental impacts and generating economic benefits.
Current Trends or Developments
Ongoing research and development efforts continue to drive advancements in ocean energy technologies. Innovations such as improved turbine designs, enhanced wave energy converters, and optimized control systems are being pursued to increase efficiency and reliability. In addition, collaborative initiatives between industry, academia, and governments are driving the commercialization and scaling up of ocean energy projects. For example, the European Marine Energy Centre is facilitating the testing and demonstration of wave and tidal energy devices, accelerating the progress of this sector.
Challenges or Controversies
The environmental impact of ocean energy technologies is a significant consideration. Potential challenges include the disturbance of marine ecosystems, the potential for underwater noise pollution, and the risk of collision with marine life. However, proper assessment, planning, and mitigation measures can minimize these impacts and ensure the sustainable development of ocean energy.
Controversies surround the potential disruption to marine ecosystems and the effectiveness and feasibility of ocean energy. Some argue that the potential benefits of ocean energy outweigh the risks, while others raise concerns about the long-term impacts on marine ecosystems and the viability of ocean energy as a reliable energy source. Further research and ongoing monitoring are needed to address these concerns and inform decision-making.
Future Outlook
The future of ocean energy looks promising. With continued advancements in technology and increasing global recognition of the need for renewable energy, ocean energy is poised to play a significant role in achieving global sustainability goals. As economies strive to reduce carbon emissions and transition to clean energy sources, ocean energy can provide a reliable and sustainable solution.
Advancements in technology and scalability are expected in the coming years. Researchers and engineers are exploring innovative concepts and materials to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of ocean energy systems. As economies of scale are realized and deployment costs decrease, ocean energy has the potential to become a mainstream energy source.
Conclusion
Ocean energy represents a vast, untapped resource that holds immense potential for promoting environmental responsibility. By harnessing the power of the sea, we can reduce dependency on fossil fuels, mitigate climate change, and create a sustainable energy future. Although challenges and controversies exist, ongoing advancements, case studies, and supportive government policies are driving the growth of this industry. By embracing ocean energy, we can pave the way for a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable world.
References:
Ocean Energy Europe. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.oceanenergy-europe.eu/
European Marine Energy Centre. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.emec.org.uk/
Ocean Energy Systems. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.ocean-energy-systems.org/




