Building Management Systems (BMS): Revolutionizing Modern Building Management
Introduction
Building Management Systems (BMS) play a crucial role in modern building management, offering advanced automation and optimization capabilities. This article explores the historical background, key concepts, and main discussion points surrounding BMS. Additionally, it delves into case studies, current trends, challenges, and future outlook for BMS implementation.
Historical Background
BMS has its roots in the evolution of building automation. Over the years, advancements in technology have paved the way for the development of sophisticated BMS. Early examples of BMS can be traced back to the 1970s, where basic control systems were used to regulate temperature and energy usage. With the advent of computer technology, BMS significantly improved, integrating various building systems for seamless operation.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Building Management System (BMS) definition and components
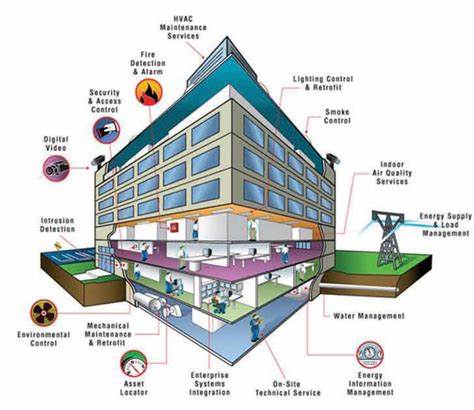
A BMS refers to a centralized system that monitors, controls, and optimizes various building systems, such as HVAC, lighting, and security. It comprises sensors, actuators, and controllers that gather data and initiate actions to ensure efficient building operation.
Difference between BMS and HVAC systems
Although BMS and HVAC systems are closely related, they serve different purposes. BMS focuses on the centralized control and optimization of multiple building systems, while HVAC systems specifically deal with heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.
Integration of BMS with other building systems
BMS enables seamless integration with other building systems, such as lighting and security. This integration facilitates data analysis and automation processes, leading to enhanced building performance and energy efficiency.
Importance of data analysis and automation in BMS
Data analysis plays a crucial role in BMS as it enables informed decision-making, predictive maintenance, and fault detection. Automation processes allow for real-time monitoring, alerts, and optimization, ensuring optimal building performance.

Main Discussion Points
Components and functionality of BMS
The core components of BMS include sensors, actuators, and controllers. These components work together to monitor various parameters, control building systems, and optimize energy usage. Centralized building management through BMS streamlines operations, reduces costs, and improves efficiency.
Energy efficiency and sustainability with BMS
BMS plays a vital role in reducing energy consumption and carbon footprint. It optimizes HVAC systems, utilizing energy efficiently, and integrates renewable energy sources. This leads to significant energy savings and promotes sustainability in buildings.
Security and safety features of BMS
BMS ensures the seamless monitoring and control of building security systems. It integrates fire safety and emergency response systems, providing real-time monitoring and alerts for potential risks or incidents. This enhances the safety and security of occupants.
Case Studies or Examples
Case study: Implementation of BMS in a commercial office building
The implementation of BMS in a commercial office building resulted in improved energy management and enhanced comfort for occupants. BMS optimized HVAC systems, reduced energy consumption, and provided real-time analytics for efficient building operation.
Case study: BMS utilization in a hospital for energy efficiency and patient comfort
In a hospital setting, BMS played a crucial role in optimizing energy usage while maintaining the comfort of patients and staff. Integration of BMS with HVAC systems ensured efficient temperature control, reducing energy costs and improving patient experience.
Case study: BMS integration in a smart city project for enhanced sustainability
BMS integration in a smart city project facilitated the centralized management of various building systems. This streamlined operations, reduced energy consumption, and promoted sustainable practices, contributing to the overall development of the smart city.
Current Trends or Developments
Internet of Things (IoT) and its impact on BMS
The integration of IoT with BMS enables the exchange of data between various devices and systems, enhancing building automation and efficiency. IoT empowers BMS to collect and analyze real-time data, leading to intelligent decision-making and predictive maintenance.
Big data analytics and cloud computing in BMS
Big data analytics and cloud computing have revolutionized BMS by providing powerful data analysis and storage capabilities. This allows for efficient management of vast amounts of data, enabling advanced analytics and optimization processes.
Advancements in predictive maintenance and fault detection using BMS data
BMS data is being utilized to implement predictive maintenance strategies and detect faults before they cause significant disruptions. This proactive approach ensures the smooth operation of building systems and reduces maintenance costs.
Challenges or Controversies
Privacy concerns related to data collection and management in BMS
The collection and management of data in BMS raise privacy concerns. Proper protocols and security measures must be in place to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
Compatibility and interoperability challenges with different building systems
Integration of various building systems within BMS can be challenging due to compatibility issues. Standardization efforts and technological advancements are necessary to seamlessly integrate different systems and devices.
Cost considerations and return on investment for BMS implementation
Implementing BMS can come with significant upfront costs. However, the long-term benefits, such as energy savings, improved efficiency, and enhanced occupant comfort, often outweigh the initial investment.
Future Outlook
Potential advancements in BMS technology
The future of BMS holds promising advancements, including increased connectivity, enhanced automation, and improved integration capabilities. These advancements will further optimize building management and improve energy efficiency.
Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in BMS
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are expected to play a crucial role in BMS. These technologies will enable BMS to learn from data, make intelligent decisions, and adapt to changing conditions for optimal building performance.
Emerging trends in smart buildings and their impact on BMS
The rise of smart buildings presents new opportunities and challenges for BMS. The integration of BMS with smart building technologies will enable advanced automation, data-driven decision-making, and a more sustainable built environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Building Management Systems are integral to modern building management. Through centralized control, optimization, and integration of various building systems, BMS improves energy efficiency, enhances security, and promotes sustainability. As technology continues to advance, further exploration and implementation of BMS are vital for the development of smart and sustainable buildings.




