Introduction
As technology continues to advance, so does the concept of smart buildings. These buildings are designed to enhance human wellbeing by incorporating innovative technologies and sustainable practices. In this article, we explore the definition of smart buildings and their importance in promoting human wellbeing. We also delve into the historical background of building design and its impact on human wellbeing, as well as the relevance of this topic in today’s society.
Historical Background
Throughout history, building design has evolved significantly, with a growing focus on human wellbeing. From ancient Roman bathhouses to Renaissance palaces, architects have always sought to create environments that enhance the quality of life for occupants. We will examine historical examples of buildings designed with human wellbeing in mind, showcasing how this concept has shaped architectural practices over the years.
Key Concepts and Definitions
To fully understand the importance of smart buildings for human wellbeing, it is essential to explore the key concepts and definitions associated with this topic. We will define smart buildings and discuss their features, as well as delve into the concept of human wellbeing and its various components. Additionally, we will examine the design principles that promote human wellbeing in buildings.
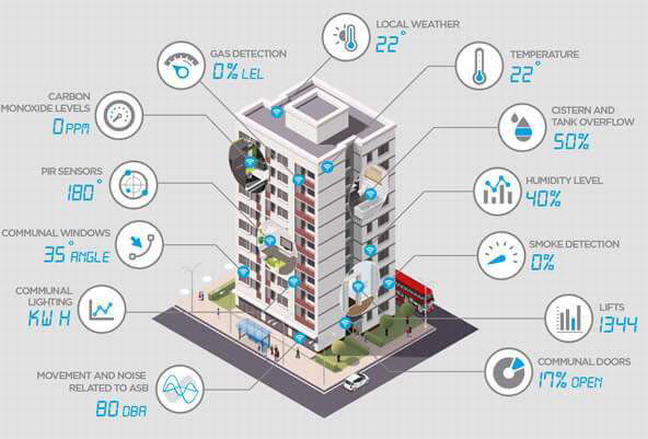
Main Discussion Points
Biophilic Design and Its Impact on Human Wellbeing
Biophilic design is a concept that emphasizes the integration of nature elements in building design. By incorporating natural light, green spaces, and natural materials, biophilic design aims to enhance human health and wellbeing. We will explore the definition and principles of biophilic design, discuss the benefits of incorporating nature elements in smart buildings, and provide examples and case studies showcasing successful biophilic design.
Indoor Environmental Quality and Its Effects on Human Wellbeing
Indoor environmental quality plays a crucial role in human wellbeing. Factors such as indoor air quality, lighting, and acoustics can significantly impact occupants’ comfort and health. We will emphasize the importance of these factors, discuss strategies for improving indoor environmental quality in smart buildings, and provide case studies highlighting successful implementation of measures to enhance indoor environmental quality.
Technological Advancements and Their Role in Promoting Human Wellbeing
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT), sensors, and artificial intelligence (AI) in smart buildings has revolutionized the way we design and experience built environments. Technology can enhance comfort, safety, and efficiency in buildings, ultimately promoting human wellbeing. We will explore how these advancements have shaped smart building design, discuss their benefits, and provide examples of innovative technologies used for promoting human wellbeing.

Case Studies or Examples
The Edge Building in Amsterdam
The Edge building in Amsterdam is a prime example of a smart building designed with human wellbeing in mind. We will provide an overview of the building and its smart design features, showcasing how it has positively impacted employee productivity and wellbeing.
The WELL Living Lab in Rochester, USA
The WELL Living Lab is a research facility dedicated to studying the impact of built environments on human wellbeing. We will describe the lab and its focus on human wellbeing, highlighting findings from studies conducted at the facility.
Current Trends or Developments
Integration of Health and Wellness Certifications in Building Standards
Health and wellness certifications are becoming increasingly integrated into building standards, emphasizing the importance of human wellbeing in design practices. We will discuss the significance of these certifications and their impact on smart building design.
Use of Data Analytics and Machine Learning for Optimizing Human Wellbeing
Data analytics and machine learning technologies have the potential to optimize human wellbeing in buildings. We will explore how these technologies can be utilized to improve the design and operation of smart buildings, ultimately enhancing occupants’ quality of life.
Adoption of Smart Technologies in Residential Buildings
Smart technologies are not limited to commercial buildings; they are also being adopted in residential buildings to improve the quality of life for residents. We will discuss how the integration of smart technologies in residential buildings promotes human wellbeing and accessibility.
Challenges or Controversies
Privacy Concerns Related to Data Collection in Smart Buildings
As smart buildings collect vast amounts of data, concerns arise regarding privacy and data security. We will delve into these concerns and discuss potential solutions to address them.
Balancing Energy Efficiency with Human Comfort and Wellbeing
While energy efficiency is essential for sustainable building design, it must be balanced with occupants’ comfort and wellbeing. We will explore the challenges architects face in striking this balance and discuss strategies for achieving both energy efficiency and human comfort.
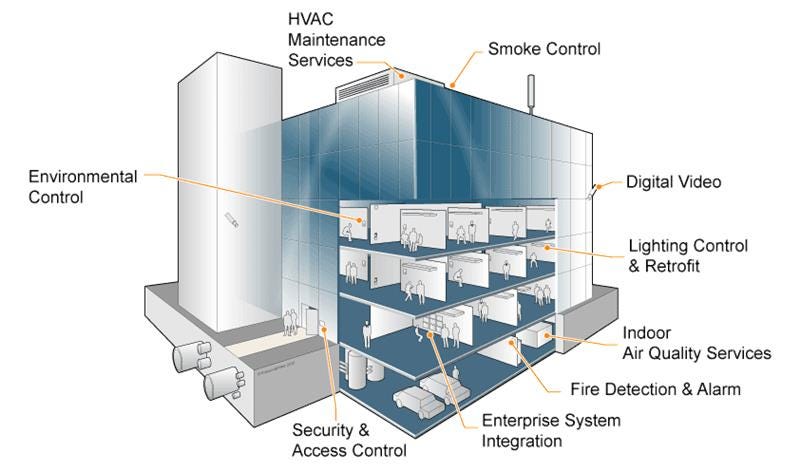
Cost Implications and Affordability of Designing Smart Buildings
Designing smart buildings for human wellbeing may come with additional costs. We will examine the cost implications of implementing smart technologies and sustainable practices and discuss the affordability of designing smart buildings.
Future Outlook
Potential Advancements in Smart Building Technologies for Enhancing Human Wellbeing
The future holds exciting possibilities for smart building technologies. We will explore potential advancements, such as augmented reality and advanced sensor technologies, that have the potential to further enhance human wellbeing in buildings.
Growing Importance of Sustainability and Resilience in Smart Building Design
Sustainability and resilience are becoming increasingly crucial in smart building design. We will discuss the growing importance of these concepts and how they can contribute to human wellbeing in the built environment.
Impact of Changing Work and Lifestyle Patterns on the Design of Future Smart Buildings
With evolving work and lifestyle patterns, the design of future smart buildings must adapt to meet the changing needs of occupants. We will explore how these patterns influence building design and discuss potential design solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, designing smart buildings that prioritize human wellbeing is of utmost importance. By incorporating innovative technologies, sustainable practices, and design principles that promote human health and comfort, we can create built environments that enhance the quality of life for occupants.




