
Introduction
Biological Wastewater Treatment Methods: An Eco-Friendly Approach
In today’s world, the importance of effective wastewater treatment methods cannot be overstated. With the increasing global population and industrialization, the need for sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions is paramount. Biological wastewater treatment methods have emerged as a viable and efficient approach to address this challenge. This article aims to explore the various aspects of biological wastewater treatment, from its historical background to current trends and developments, as well as challenges and future prospects.
Historical Background
Wastewater treatment methods have a long history, with civilizations recognizing the need to manage and treat wastewater for centuries. From simple sedimentation processes used by ancient Egyptians to the more complex filtration systems of the Roman Empire, wastewater treatment methods have evolved significantly over time. However, it was not until the 19th century that biological wastewater treatment methods began to gain recognition and adoption.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Biological wastewater treatment methods rely on the activity of microorganisms to break down organic matter and pollutants present in wastewater. These microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, play a crucial role in the treatment process by converting harmful substances into less harmful forms. Understanding key terms and concepts associated with biological wastewater treatment, such as aerobic and anaerobic processes, activated sludge, biofilm, and more, is vital to comprehending the functioning of different treatment methods.
Main Discussion Points
Activated Sludge Process: Nature’s Cleaning Symphony
The activated sludge process is a widely used biological wastewater treatment method. It involves introducing wastewater to a mixture of microorganisms, referred to as activated sludge, in an aerated tank. The microorganisms break down organic matter through respiration, resulting in clean effluent. This process is highly efficient, cost-effective, and allows for the removal of various pollutants. However, it does have limitations, such as the need for extensive infrastructure and the potential for sludge bulking.
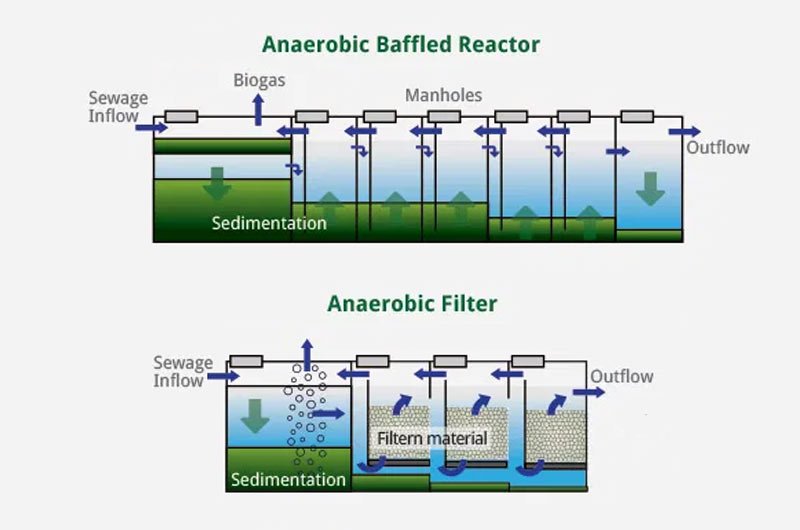
Trickling Filter System: Nature’s Filtration Marvel
Trickling filter systems utilize a bed of rocks or synthetic media to support a biofilm of microorganisms. Wastewater is distributed over the media, and as it trickles down, the microorganisms in the biofilm consume the organic matter. This method is known for its simplicity and low energy requirements. However, its effectiveness can be influenced by factors such as temperature, loading rates, and media clogging. Despite these limitations, trickling filter systems remain a popular choice for wastewater treatment in certain scenarios.
Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) Process: The Art of Timing
The sequencing batch reactor (SBR) process involves treating wastewater in a single tank, sequentially carrying out different treatment stages. These stages include filling, reacting, settling, decanting, and idle periods. The unique design and flexibility of SBR systems allow for efficient nutrient removal, reduced sludge production, and simplified operation. However, challenges such as controlling the timing and optimizing the process can impact its performance.
Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Technology: The Cutting Edge of Wastewater Treatment
Membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology combines biological treatment with membrane filtration to achieve superior effluent quality. The system utilizes a membrane barrier to separate the treated water from the biomass, resulting in a more efficient and compact process. MBR systems offer advantages such as high removal efficiency, small footprint, and the potential for water reuse. However, they are also associated with higher capital and operational costs, membrane fouling, and energy requirements.
Case Studies or Examples
Realizing the Potential: Successful Biological Wastewater Treatment Projects
Real-world examples demonstrate the efficacy and benefits of biological wastewater treatment methods. One such example is the Stockholm Värtan Wastewater Treatment Plant in Sweden. By implementing a combination of activated sludge and MBR technology, the plant achieved a remarkable reduction in nutrient levels and improved effluent quality. Another successful case study is the Hammarby Sjöstadsverket in Stockholm, where a holistic approach integrating various treatment methods resulted in a sustainable and environmentally friendly wastewater treatment solution.
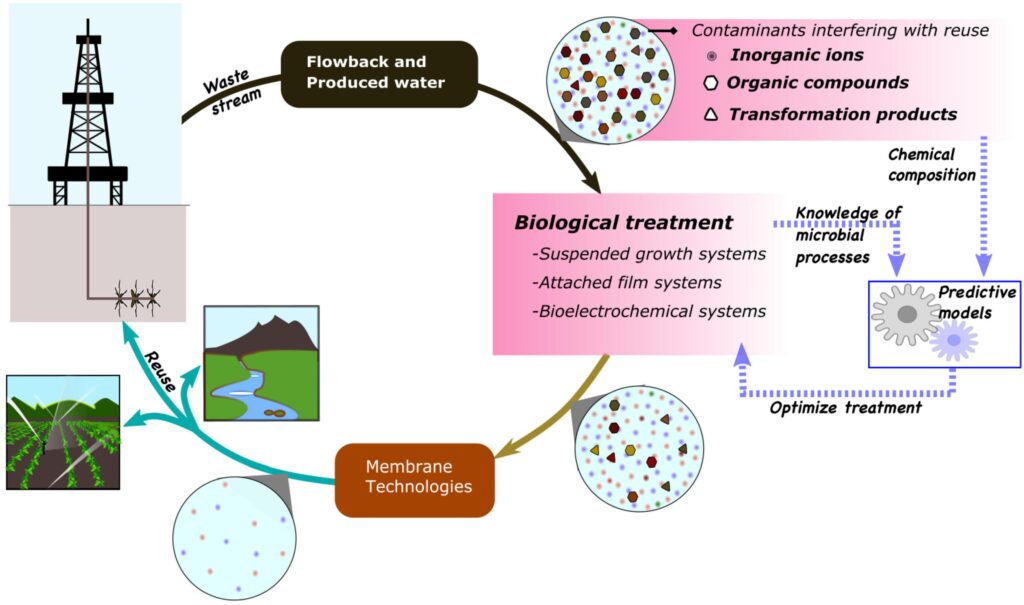
Current Trends or Developments
Glimpses of the Future: Advancements in Biological Wastewater Treatment
The field of biological wastewater treatment is constantly evolving, with researchers and innovators striving to improve efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. One notable trend is the integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and automation, to optimize treatment processes. Additionally, the exploration of new biofilm materials and the development of energy-efficient treatment systems are promising areas of ongoing research.
Challenges or Controversies
Navigating the Waters: Overcoming Challenges in Biological Wastewater Treatment
Implementing biological wastewater treatment methods is not without its challenges. Common obstacles include the variability of influent composition, the management of excess sludge, and the control of microbial populations. Controversies surrounding these methods often revolve around the trade-offs between cost, energy consumption, and environmental impact. To overcome these challenges, innovative technologies, improved process control, and interdisciplinary collaborations are needed.
Future Outlook
Towards a Sustainable Future: The Role of Biological Wastewater Treatment
The future of biological wastewater treatment holds immense potential in achieving sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions. Advancements in research and innovation will further enhance the efficiency, effectiveness, and affordability of these treatment methods. Additionally, the integration of biological wastewater treatment into broader resource recovery systems, such as anaerobic digestion and nutrient recovery, will contribute to a circular economy approach.
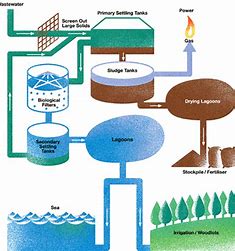
Conclusion
In conclusion, biological wastewater treatment methods offer a promising and eco-friendly approach to managing and treating wastewater. From the historical evolution to the current challenges and future prospects, this article has provided an in-depth exploration of the topic. With ongoing research and innovation, biological wastewater treatment methods will continue to play a vital role in achieving sustainable and environmentally friendly wastewater management.
References:
Smith, J. W., & Johnson, R. A. (2018). Biological Wastewater Treatment: Principles, Modelling and Design. IWA Publishing.
Henze, M., & Comeau, Y. (2008). Wastewater Treatment: Biological and Chemical Processes. Springer.




