
Introduction
The topic of building resilience against pandemics through wastewater monitoring is crucial in the context of pandemic preparedness and response. With the ongoing global health crisis caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, it is evident that early detection and effective surveillance systems are essential in mitigating the spread of infectious diseases. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the role of wastewater monitoring in pandemic preparedness and response, along with its historical background, key concepts and definitions, main discussion points, case studies, current trends, challenges, future outlook, and a conclusion summarizing the key takeaways.
Historical Background
Wastewater monitoring has evolved as an essential tool in public health and disease surveillance over the years. Historical examples demonstrate the use of wastewater monitoring to detect and respond to pandemics or disease outbreaks. Monitoring wastewater for the presence of pathogens and genetic markers has helped in identifying the source of infections and developing effective public health interventions.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Wastewater monitoring refers to the systematic collection and analysis of wastewater samples to detect and track the presence of pathogens, genetic markers, and other indicators of infectious diseases. It plays a pivotal role in pandemic preparedness and response by providing valuable insights into the prevalence and spread of diseases within a community. Key terms and concepts related to wastewater monitoring include viral shedding, genetic markers, and quantitative PCR, which enable scientists and public health officials to analyze and interpret the data obtained from wastewater samples.
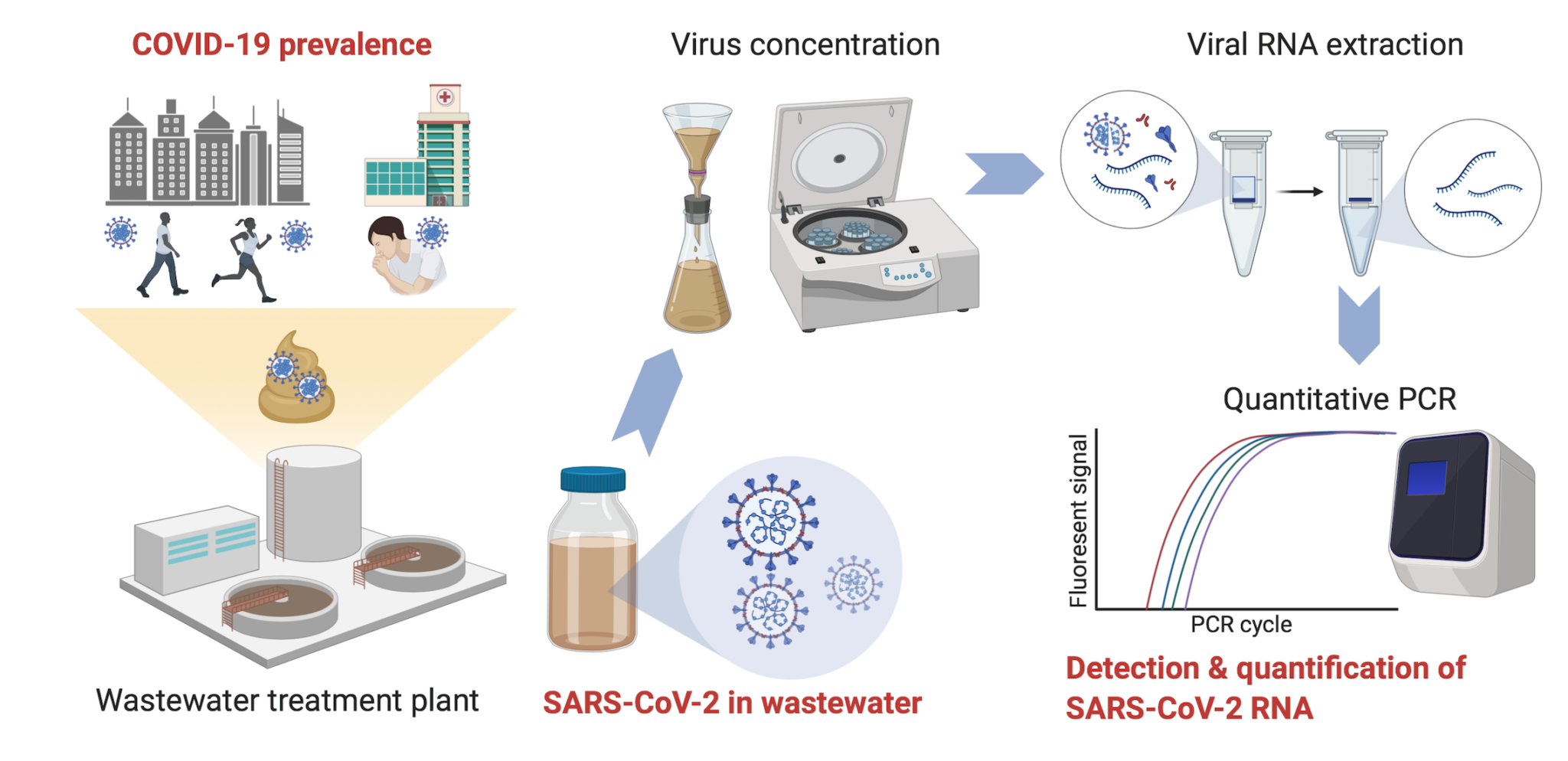
Main Discussion Points
Importance of Wastewater Monitoring in Early Detection
Wastewater monitoring serves as an early warning system for detecting the presence of a pandemic or disease outbreak in a community. By analyzing wastewater samples, scientists can identify genetic markers or viral shedding patterns associated with specific diseases. This early detection significantly aids in implementing timely public health interventions to prevent further spread. Compared to traditional surveillance methods, wastewater monitoring provides a cost-effective and non-invasive approach for early detection, making it an invaluable tool in pandemic preparedness.
Use of Wastewater Monitoring for Public Health Decision Making
Wastewater monitoring data plays a vital role in informing public health interventions and resource allocation. By tracking the presence and concentration of pathogens in wastewater, public health officials can identify hotspots and track the spread of the virus within a community. This information helps prioritize testing, allocate healthcare resources, and implement targeted interventions to control the spread. Real-world examples have shown how wastewater monitoring data influenced public health decisions, leading to improved pandemic response strategies.
Collaborative Approaches in Wastewater Monitoring
Collaboration between researchers, public health agencies, and wastewater treatment plants is essential for the success of wastewater monitoring programs. Establishing collaborative networks enables the sharing of knowledge, expertise, and resources, thereby facilitating efficient and effective surveillance. However, challenges such as data sharing, standardization, and coordination among multiple stakeholders need to be addressed. Successful collaborative approaches in wastewater monitoring have been implemented, showcasing the benefits of such partnerships in pandemic preparedness and response.

Case Studies or Examples
Case study: The use of wastewater monitoring in detecting the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in a community has been instrumental in identifying outbreaks and implementing targeted interventions.
Case study: Wastewater monitoring has proven to be a valuable tool in monitoring vaccine effectiveness and tracking virus mutations, aiding in vaccine development and deployment strategies.
Case study: Wastewater monitoring has been successfully employed in controlling the spread of other infectious diseases, such as poliovirus, by identifying areas with active transmission.
Current Trends or Developments
Recent advancements in wastewater monitoring technologies and methodologies have improved the efficiency and accuracy of data collection and analysis. Ongoing research and studies in the field continue to explore new avenues for utilizing wastewater monitoring in pandemic preparedness. Recent findings and trends highlight the potential of wastewater monitoring as a key component of global surveillance systems.
Challenges or Controversies
Implementing wastewater monitoring programs faces challenges such as the need for standardized protocols, data sharing mechanisms, and coordination among various stakeholders. Privacy concerns and ethical considerations regarding the collection and use of wastewater data also exist. Differing viewpoints on the effectiveness and reliability of wastewater monitoring as a surveillance tool add to the controversies surrounding its widespread adoption.

Future Outlook
The future of wastewater monitoring for pandemic resilience holds immense potential. Advancements in technology and integration with global surveillance systems can enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of wastewater monitoring. However, challenges in standardization, data sharing, and collaboration need to be addressed. The integration of wastewater monitoring into global surveillance systems can provide an early warning system for detecting and responding to future pandemics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the importance of building resilience against pandemics through wastewater monitoring cannot be overstated. Early detection, informed decision-making, and collaborative approaches are key in utilizing wastewater monitoring as a powerful tool in pandemic preparedness and response. As advancements continue to be made and challenges are overcome, wastewater monitoring has the potential to significantly contribute to global public health and the prevention of future pandemics.




