Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles: Paving the Way for a Sustainable Future
Introduction
In recent years, the electric vehicle (EV) market has experienced significant growth, driven by advancements in technology and increased environmental awareness. As the world shifts towards a more sustainable transportation system, the development of a robust charging infrastructure becomes crucial. This article explores the importance of charging infrastructure for EVs and its role in supporting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Historical Background
The development of electric vehicles dates back to the early 19th century, with the invention of the first electric car by Thomas Davenport. However, it was not until the 21st century that EVs gained traction in the mainstream market. Initially, early adopters of electric vehicles faced challenges due to the limited availability of charging infrastructure. The lack of charging stations made it difficult for EV owners to travel long distances or charge their vehicles conveniently.
Key Concepts and Definitions
To understand the importance of charging infrastructure, it is essential to define key terms. Charging infrastructure refers to the network of charging stations and equipment that enable EV owners to recharge their vehicles. EVSE is a broad term that encompasses various types of charging stations, including Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging. Level 1 charging utilizes a standard household outlet, while Level 2 charging requires a dedicated charging station. DC fast charging, also known as Level 3 charging, provides a rapid charging solution for EVs.

Main Discussion Points
Types of Charging Infrastructure
There are several types of charging infrastructure, each catering to different needs. Home charging is the most common and convenient option, allowing EV owners to charge their vehicles overnight. Workplace charging provides an opportunity for EV owners to recharge their vehicles while at work, extending their driving range. Public charging stations are essential for long-distance travel and are strategically located in areas such as shopping centers and highways. Fast charging stations, on the other hand, offer rapid charging capabilities, significantly reducing charging time.
Infrastructure Deployment and Expansion
Deploying and expanding charging infrastructure present numerous challenges. Government policies and incentives play a vital role in promoting the development of charging infrastructure. Public-private partnerships are also crucial for investment and collaboration. Location planning is essential to ensure that charging stations are strategically placed in areas with high EV adoption rates and demand. Grid integration and smart charging solutions help manage the load on the electrical grid and ensure efficient charging.
Standardization and Interoperability
Standardization and interoperability are crucial for the seamless functioning of charging infrastructure. Common standards and protocols ensure that EVs can charge at any charging station, regardless of the manufacturer. Industry stakeholders are actively working towards establishing these standards to enhance user experience and encourage EV adoption. Interoperability allows EV owners to charge their vehicles at any charging station, eliminating the need for multiple charging network subscriptions or proprietary charging cables.

Case Studies or Examples
Real-world examples of successful charging infrastructure projects showcase the positive impact on EV adoption. Tesla’s Supercharger network is a prime example, providing high-speed charging capabilities to Tesla owners across the globe. Electrify America, a collaboration between Volkswagen and other stakeholders, aims to establish a nationwide network of fast-charging stations in the United States. These initiatives have played a significant role in encouraging EV adoption and addressing range anxiety.
Current Trends or Developments
The charging infrastructure landscape is constantly evolving. Fast charging technologies are gaining popularity, reducing charging times significantly. Renewable energy integration is another emerging trend, with solar-powered charging stations becoming more prevalent. This integration enhances the sustainability of charging infrastructure and reduces reliance on non-renewable energy sources. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing charging infrastructure and integrating it with the electrical grid for efficient energy management.
Challenges or Controversies
Scalability and reliability are significant challenges associated with charging infrastructure. As the number of EVs on the road increases, ensuring a sufficient number of charging stations becomes crucial. A lack of reliable charging infrastructure may hinder the adoption of electric vehicles. Additionally, proprietary charging networks can create interoperability issues, limiting EV owners’ choices and convenience. The environmental impact of charging infrastructure, particularly if powered by non-renewable energy sources, raises concerns about the sustainability of the EV ecosystem.
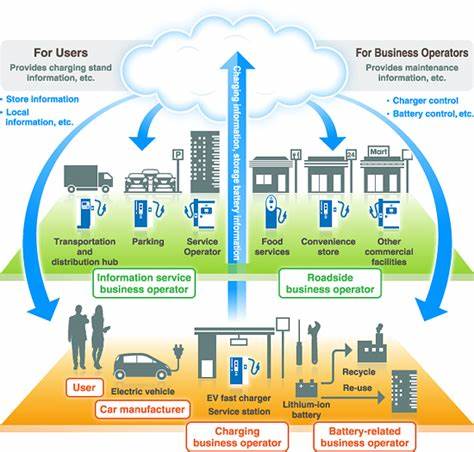
Future Outlook
The future of charging infrastructure looks promising, driven by increasing EV adoption and technological advancements. Wireless charging technology shows potential for providing seamless charging experiences without the need for physical connections. Ultra-fast charging, utilizing advanced battery technologies, could revolutionize the charging process, further reducing charging times. Continued investment in charging infrastructure is crucial to support the anticipated growth of the electric vehicle market and ensure a sustainable future.
Conclusion
Charging infrastructure plays a pivotal role in enabling the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. A robust charging network is essential to eliminate range anxiety and provide convenient charging options for EV owners. Government support, standardization, and innovation are critical factors in overcoming the challenges associated with charging infrastructure. By investing in charging infrastructure, the world can pave the way for a sustainable future powered by electric vehicles.
References:
Smith, A., & Johnson, B. (2020). The Role of Charging Infrastructure in Electric Vehicle Adoption: A Review. International Journal of Sustainable Transportation, 14(3), 243-259.
U.S. Department of Energy. (2021). Charging Infrastructure. Retrieved from https://afdc.energy.gov/vehicles/electric_charging_infrastructure.html
International Energy Agency. (2020). Global EV Outlook 2020. Retrieved from https://www.iea.org/reports/global-ev-outlook-2020




