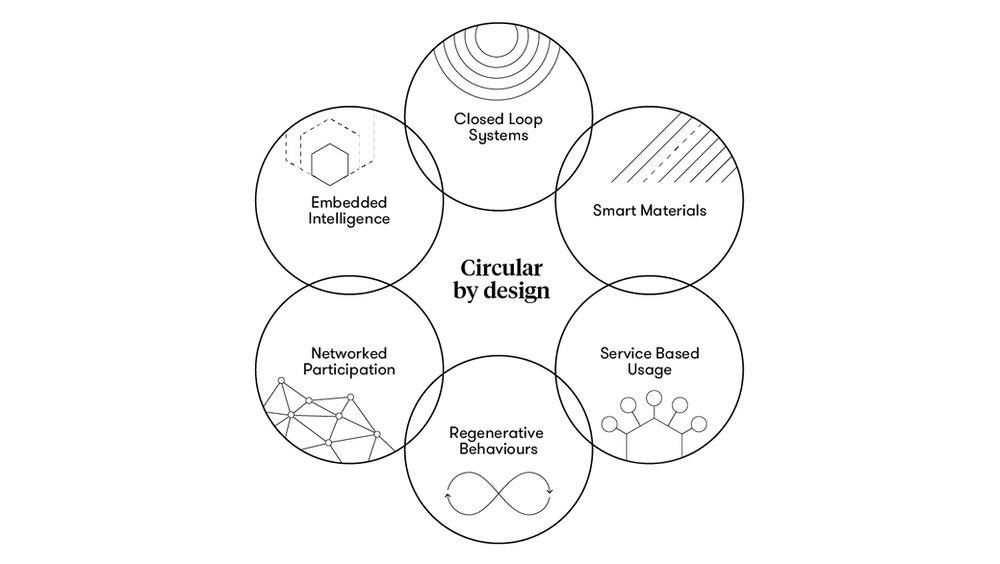
Circular Design Principles in Product Development: Creating a Sustainable Future
Introduction
Circular design principles in product development have gained significant attention due to their potential to create a sustainable future. This article introduces the concept of circular design principles and discusses their relevance and importance in today’s society.
Historical Background
The development of circular design principles can be traced back to several key milestones and events. There has been a growing recognition of the need to shift away from the linear “take-make-dispose” model. This section provides a brief history of the evolution of circular design principles, highlighting the turning points in their development.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Circular design principles encompass various key terms and concepts that are crucial to understanding their implementation. This section defines circular design principles in product development and explains concepts such as:
Cradle to Cradle Design: Designing products with the intention of creating a closed-loop system where materials can be endlessly recycled or reused.
Extended Producer Responsibility: Holding producers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including proper disposal and recycling.
Material Flow Management: Efficiently managing the flow of materials throughout the product lifecycle to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization.
Life Cycle Assessment: Evaluating the environmental impacts of a product throughout its entire lifecycle, from extraction of raw materials to disposal.
Closed-loop Systems: Creating systems where resources are continuously circulated and reused, minimizing waste and the need for new resources.
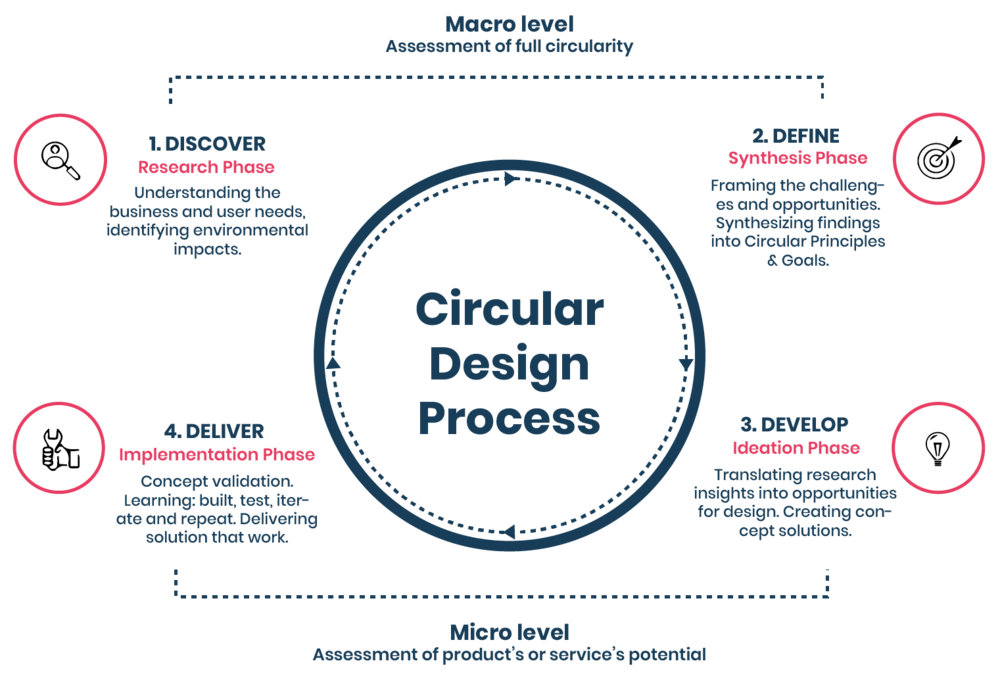
Main Discussion Points
Point: Designing for Durability and Longevity
Designing products that are built to last is a fundamental aspect of circular design principles. Creating durable and long-lasting products is crucial for reducing waste and resource consumption. This section explores the importance of designing for durability, discusses strategies for achieving longevity, and highlights the benefits associated with this approach.
Point: Implementing Recycling and Reuse Strategies
Incorporating recycling and reuse strategies into the product development process is essential for achieving circularity. This section emphasizes the importance of integrating recycling and reuse from the initial design phase and discusses strategies such as:
Remanufacturing: Rebuilding products to their original specifications, extending their useful life.
Repair and Maintenance Programs: Encouraging and facilitating the repair and maintenance of products to extend their lifespan.
Material Recovery and Recycling Initiatives: Implementing systems to recover and recycle materials at the end of a product’s life.
Point: Adopting Circular Business Models
Circular business models play a pivotal role in driving circular design principles in product development. This section delves into the concept of circular business models and explores different approaches, including:
Product as a Service: Shifting from selling products to providing services, where the manufacturer retains ownership and responsibility for the product.
Sharing Economy Platforms: Facilitating the sharing or renting of products among consumers, maximizing utilization and reducing the need for new production.
Closed-loop Supply Chains: Designing supply chains that prioritize the reuse and recycling of materials, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact.
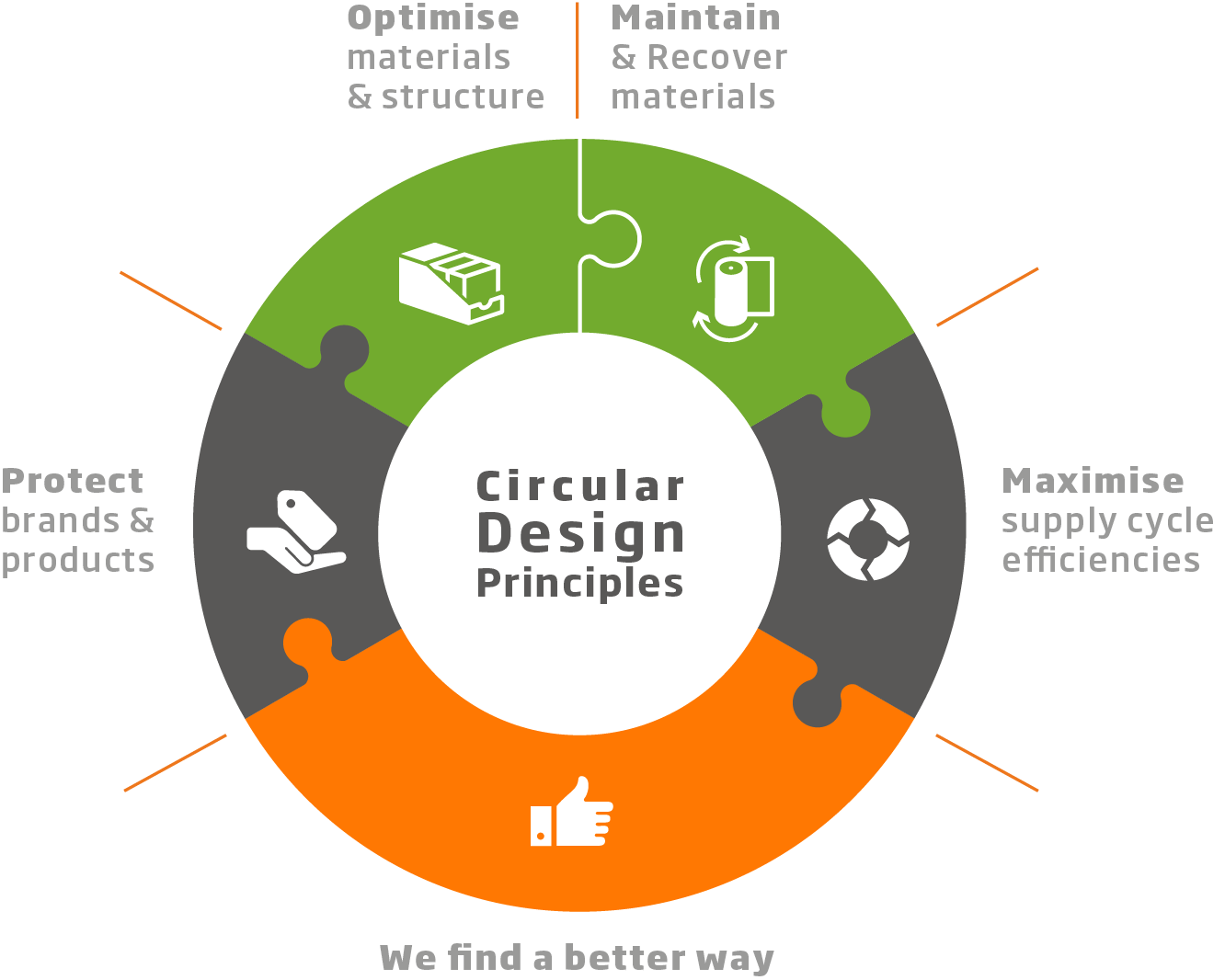
Case Studies or Examples
Real-world case studies and examples serve as powerful demonstrations of successful implementation of circular design principles. This section provides a collection of case studies that showcase the positive impact of circular design principles in product development. These examples highlight the outcomes and benefits derived from embracing circularity.
Current Trends or Developments
The field of circular design principles is constantly evolving. This section discusses recent trends and developments in this area, focusing on innovative approaches and technologies being utilized. It highlights how these advancements contribute to the continued progress of circular design principles in product development.
Challenges or Controversies
Implementing circular design principles is not without its challenges. This section addresses the common obstacles faced in integrating circularity into product development. It also explores controversies or differing viewpoints surrounding the topic. Suggestions and potential solutions to overcome these challenges are discussed to encourage further progress.
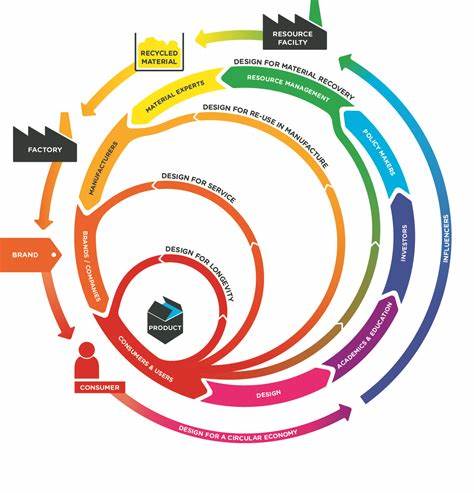
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, circular design principles have a promising future. This section speculates on the potential implications and directions of these principles in product development. It discusses potential advancements and changes that may occur, highlighting the transformative impact they can have on industries and society as a whole.
Conclusion
In summary, circular design principles provide a framework for creating sustainable and circular products. This article has explored the concept, historical background, key concepts, and main discussion points associated with circular design principles in product development. It emphasizes the significance of implementing circularity and encourages further exploration and adoption of these principles.




