
Introduction
Ethanol has emerged as a crucial player in the realm of renewable energy, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. Its significance lies in its ability to address the pressing challenges of energy security and environmental sustainability. This article explores the historical background, key concepts, production, benefits, challenges, case studies, current trends, controversies, and future outlook of ethanol as a renewable fuel source.
Historical Background
Ethanol has a rich history as a renewable fuel source, with evidence of its usage dating back centuries. Early civilizations harnessed its potential for various purposes. However, it was during the oil crises of the 1970s that ethanol gained widespread attention as a viable alternative to petroleum-based fuels. Since then, significant milestones have been achieved in ethanol production and consumption.
Key Concepts and Definitions
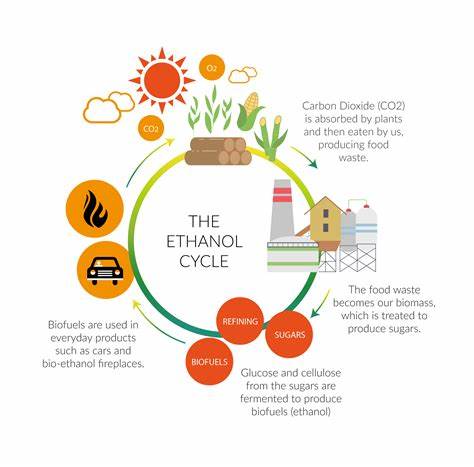
To fully grasp the potential of ethanol as a renewable fuel source, it is essential to define and understand its key concepts. Ethanol, with its molecular formula C2H5OH, is a biofuel derived from organic matter, such as corn, sugarcane, or cellulosic materials. It is classified into two generations: first-generation ethanol, produced from food crops, and second-generation ethanol, derived from non-food biomass. Additionally, the concept of carbon neutrality is integral to ethanol, as it refers to the net-zero carbon emissions resulting from its production and use.

Production of Ethanol as a Renewable Fuel Source
The production of ethanol involves different feedstocks, including corn, sugarcane, and cellulosic materials. Corn-based ethanol has been the predominant feedstock due to its abundance and high starch content. The production process includes fermentation, where enzymes convert the feedstock’s sugars into ethanol, followed by distillation to purify the ethanol. This process results in a clean and renewable fuel source.
Benefits and Advantages of Ethanol
Ethanol offers numerous environmental benefits. Its combustion produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, contributing to the reduction of global warming. Additionally, ethanol has the potential to reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy security. Moreover, ethanol production supports rural development and agriculture, creating economic opportunities for farming communities.
Challenges and Limitations of Ethanol
While ethanol offers significant advantages, it also presents challenges. One major concern is the food vs. fuel debate, as the use of food crops for ethanol production can affect food prices. Furthermore, ethanol production can impact land use and biodiversity, leading to deforestation and habitat loss. Scaling up ethanol production also requires substantial infrastructure investments, posing logistical challenges.

Case Studies or Examples
Several countries and regions have successfully implemented ethanol as a renewable fuel source. Brazil stands out as a prominent example, with its extensive use of sugarcane-based ethanol. The outcomes have been remarkable, with reduced carbon emissions and increased energy independence. Other countries, such as the United States and European nations, have also made progress in ethanol adoption, showcasing the versatility and effectiveness of this renewable fuel.
Current Trends or Developments
The ethanol industry is witnessing exciting trends and developments. Technological advancements have improved ethanol production efficiency, enabling higher yields and lower costs. Research findings continue to contribute to the optimization of production processes and the exploration of alternative feedstocks. Moreover, government policies and regulations play a pivotal role in shaping the ethanol market, providing incentives and promoting its adoption.
Challenges or Controversies
Ethanol production is not without controversies. Environmental and social impacts, such as increased water usage and potential displacement of food crops, have raised concerns. Differing viewpoints exist regarding the sustainability and effectiveness of ethanol as a renewable fuel source. Additionally, there are challenges in implementing and promoting ethanol as a mainstream fuel, including a lack of infrastructure and resistance from vested interests.
Future Outlook
The future of ethanol as a renewable fuel source is promising. Advancements in production technologies, such as cellulosic ethanol and advanced fermentation techniques, hold immense potential for enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. Ethanol will continue to play a significant role in the transition towards a low-carbon and sustainable energy future, contributing to global efforts to combat climate change.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ethanol has emerged as a renewable fuel source with significant implications for energy security and environmental sustainability. Its historical background, key concepts, production processes, benefits, challenges, case studies, current trends, controversies, and future outlook all contribute to a comprehensive understanding of its potential. Ethanol offers a sustainable solution to address the world’s energy and environmental challenges, and further research and exploration are crucial to unlocking its full potential.




