
Hydroponics, Aeroponics, and Aquaponics: Revolutionizing Agriculture for Sustainable Food Production
Introduction
Innovative cultivation methods such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics are gaining significant attention in the field of agriculture. These soilless cultivation techniques offer numerous advantages, including increased crop yields, efficient nutrient management, and reduced environmental impact. This article explores the historical background, key concepts and definitions, main discussion points, case studies, current trends, challenges, future outlook, and the significance of these alternative agricultural practices.
Historical Background
Hydroponics, the practice of growing plants in nutrient-rich water without soil, has ancient origins dating back to the Hanging Gardens of Babylon. However, it wasn’t until the 19th century that scientists began to experiment with hydroponic techniques for commercial purposes.
Aeroponics, a variation of hydroponics, was developed in the 20th century. It involves the use of mist or fog to deliver nutrients directly to the plant roots, resulting in faster growth and increased nutrient absorption.
In recent years, aquaponics has emerged as a sustainable cultivation method that combines hydroponics with aquaculture. This integrated system utilizes the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants, where fish waste provides nutrients for the plants, and the plants filter the water for the fish.
Key Concepts and Definitions
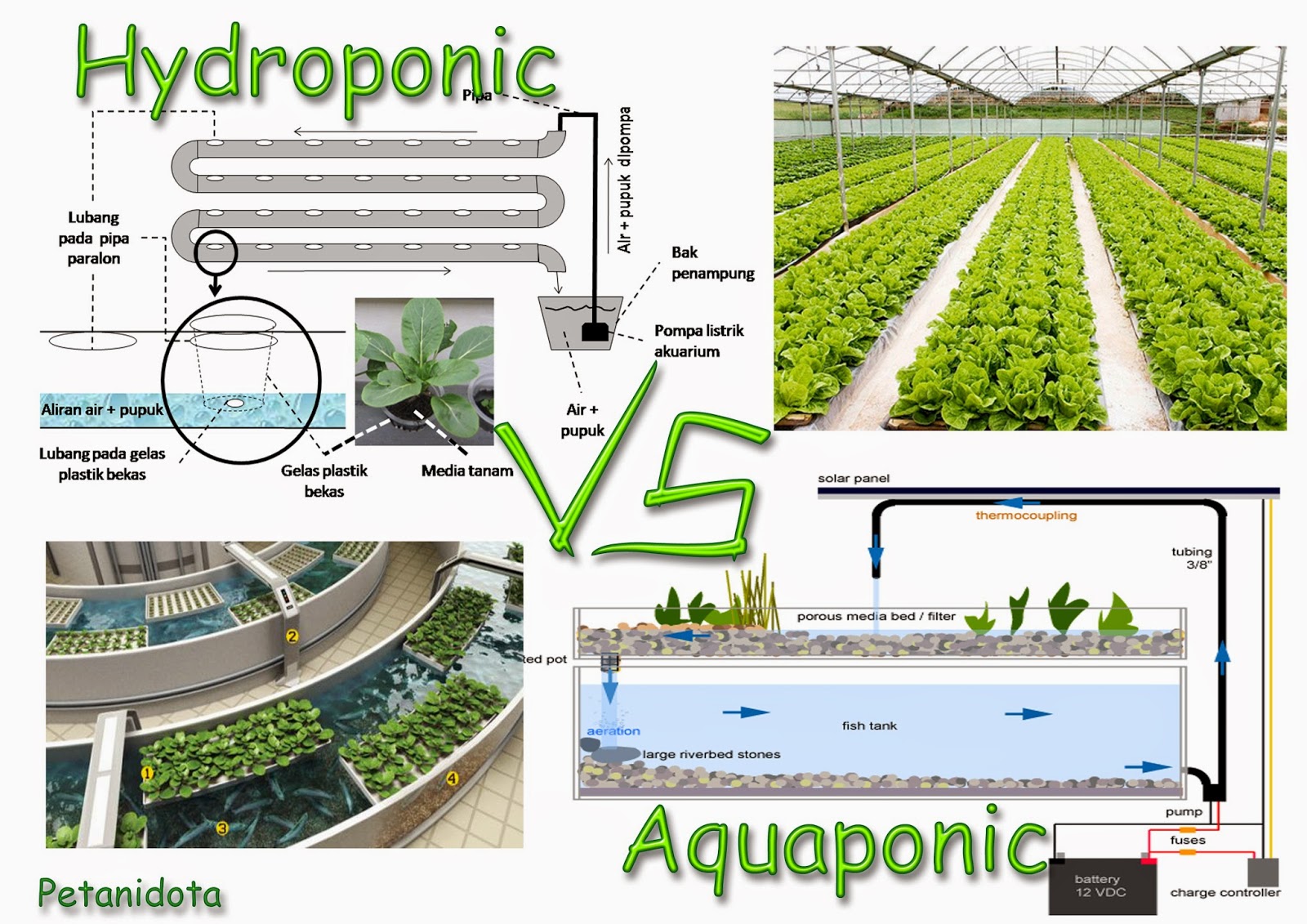
Hydroponics is a cultivation method that relies on nutrient-rich water as a growing medium. Nutrients are dissolved in the water and delivered directly to the plant roots, allowing for optimal nutrient absorption. There are various types of hydroponic systems, including the nutrient film technique, deep water culture, and others.
Aeroponics utilizes mist or fog to deliver nutrients to the plant roots. The absence of a growing medium allows for increased oxygenation and faster growth rates. Despite its benefits, aeroponic systems can be challenging to maintain due to the need for precise control of environmental factors.
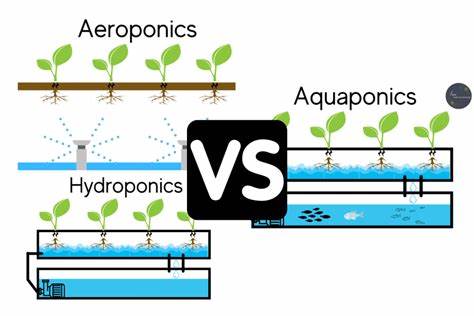
Aquaponics combines hydroponics and aquaculture to create a symbiotic ecosystem. The waste produced by fish serves as a nutrient source for plants, while the plants filter the water for the fish. This closed-loop system maximizes nutrient recycling and minimizes waste.
Main Discussion Points
Comparison of growth rates and yields in hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics has been extensively studied. Research has shown that these methods can significantly increase crop yields compared to traditional soil-based cultivation. However, each method has its advantages and disadvantages in terms of growth speed and yield potential.
Nutrient management and environmental impact are crucial aspects to consider. Hydroponics and aeroponics allow for precise control of nutrient delivery, minimizing waste and nutrient deficiencies. Aquaponics takes it a step further by utilizing fish waste as a nutrient source. However, the environmental impact, including water usage and energy consumption, varies for each method.
System complexity and scalability differ among hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics. Hydroponics is relatively simple to set up and can be easily scaled up. Aeroponics requires more technical expertise and investment but offers faster growth rates. Aquaponics, although more complex, provides a holistic and sustainable approach to cultivation.
Case Studies or Examples
Several successful hydroponic farms have emerged worldwide, showcasing the potential of this cultivation method. For example, Gotham Greens in New York City has implemented hydroponic systems on rooftops, efficiently utilizing urban space to produce fresh and sustainable produce.
Commercial agriculture has also adopted aeroponic systems. AeroFarms, located in Newark, New Jersey, utilizes vertical farming techniques to maximize crop yields in limited space. Their aeroponic systems have demonstrated significant advancements in the field of sustainable agriculture.
Aquaponic projects have made a positive impact on local communities. The GrowHaus in Denver, Colorado, is a nonprofit organization that operates an aquaponic farm to provide fresh produce and educational programs to underserved neighborhoods.
Current Trends or Developments
Recent advancements in hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics technology have led to increased efficiency and productivity. For instance, the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) devices allows for remote monitoring and control of environmental factors, optimizing plant growth.
Research findings on nutrient optimization and plant growth in soilless systems continue to expand our understanding of these cultivation methods. Scientists are exploring the effects of different nutrient compositions, lighting systems, and growth mediums to maximize crop yield and quality.
Urban and vertical farming have seen a surge in popularity, leading to increased adoption of hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics. These methods offer the potential to produce fresh, nutritious food in urban areas with limited access to traditional farmland.
Challenges or Controversies
Disease and pest management pose challenges in soilless cultivation. Without the natural microbial activity found in soil, plant pathogens and pests can spread rapidly. However, advancements in integrated pest management and disease prevention strategies are mitigating these challenges.
The use of synthetic nutrients in hydroponics has raised controversy. Some argue that synthetic nutrients may not provide the same nutritional value as those derived from natural sources. However, proponents argue that synthetic nutrients can be precisely formulated to meet plant requirements.
Ethical concerns regarding the welfare of fish in aquaponic systems have been raised. Critics argue that keeping fish in confined spaces may compromise their well-being. However, aquaponic systems can be designed to prioritize fish welfare by providing appropriate habitat and monitoring water quality.
Future Outlook
The future applications and advancements in hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics are promising. As technology continues to evolve, these cultivation methods will become more efficient, cost-effective, and accessible to a wider range of farmers and growers.
Hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics can play a significant role in addressing food security and sustainability challenges. By maximizing crop yields, minimizing resource usage, and reducing environmental impact, these methods offer a viable solution to feed a growing global population.
Emerging technologies and innovations, such as vertical farming and the use of alternative energy sources, will further enhance the efficiency and sustainability of these cultivation methods.

Conclusion
In conclusion, hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics are revolutionizing agriculture by offering sustainable alternatives to traditional soil-based cultivation. These methods provide increased crop yields, efficient nutrient management, and reduced environmental impact. By embracing these innovative practices, we can pave the way for a more sustainable and food-secure future.
References
Smith, J. (2020). Hydroponics: A Comprehensive Guide to Hydroponics for Beginners.
Rakocy, J. E., & Bailey, D. S. (2005). Aquaponic Food Production: Raising Fish and Plants for Food and Profit.
Li, Y., & Third, K. (2020). An Introduction to Aeroponics: A Sustainable Soilless Cultivation Method for the Future. Journal of Horticultural Science & Biotechnology.




