
Introduction
Ocean energy has emerged as a promising renewable energy source, harnessing the power of waves, tides, and currents to generate electricity. With its vast potential, it offers a sustainable solution to meet our growing energy demands while reducing reliance on fossil fuels. However, as we embrace this alternative, it is crucial to address the environmental concerns associated with ocean energy projects.
Historical Background
The development and utilization of ocean energy can be traced back to centuries ago, with early civilizations using tidal mills to grind grains. Over time, advancements in technology have led to the exploration of various forms of ocean energy, including wave energy converters and tidal turbines. As we have progressed, so have our concerns for the environment, prompting the need to understand and mitigate the potential impacts of ocean energy projects.
Key Concepts and Definitions
To fully grasp the significance of ocean energy and its environmental implications, it is important to define its various forms. Ocean energy encompasses wave energy, which harnesses the power of ocean waves, tidal energy, which utilizes the rise and fall of tides, and current energy, which capitalizes on the flow of ocean currents. Alongside these forms, it is essential to comprehend the environmental concerns related to ocean energy, such as the effects on marine ecosystems, biodiversity, and ecosystem services.
Main Discussion Points
Environmental impacts of ocean energy projects
Ocean energy projects can have a range of environmental impacts. Firstly, they can affect marine wildlife and habitats, potentially disrupting feeding and migration patterns. Secondly, noise pollution from the installation and operation of devices can have adverse effects on marine mammals, such as disturbance and stress. Lastly, physical and visual impacts on coastal areas can alter the natural landscape and potentially affect tourism and recreational activities.

Strategies for mitigating environmental concerns
To minimize environmental impacts, careful site selection and project design are crucial. By considering factors such as marine wildlife distributions and migratory routes, projects can be designed to avoid sensitive areas. Additionally, conducting thorough environmental impact assessments and implementing effective monitoring programs can aid in identifying and mitigating potential risks. Furthermore, collaboration and engagement with stakeholders, including local communities and environmental organizations, can help ensure that concerns are addressed and mitigation measures are implemented.
Case Studies or Examples
Orkney Islands, Scotland – Successfully integrating wave and tidal energy
The Orkney Islands in Scotland serve as a prime example of successfully integrating wave and tidal energy while minimizing environmental impact. Through meticulous site selection and project planning, developers have managed to avoid sensitive areas and reduce potential harm to marine wildlife. This case demonstrates the importance of proactive decision-making and considering environmental factors from the outset.
Bay of Fundy, Canada – Addressing concerns of marine wildlife
In the Bay of Fundy, Canada, strategic project planning has been instrumental in addressing concerns related to marine wildlife. By conducting extensive research on species abundance and behavior, developers have been able to implement measures to avoid critical habitats and migration routes. This case exemplifies the significance of thorough scientific assessments in guiding project design and minimizing impacts.
Current Trends or Developments
Advancements in ocean energy technology continue to drive the industry forward. Researchers and developers are constantly striving to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of devices, leading to increased energy generation and reduced environmental impacts. Moreover, recent research findings shed light on the potential effects of ocean energy projects on marine ecosystems, aiding in the development of effective mitigation measures and best practices.
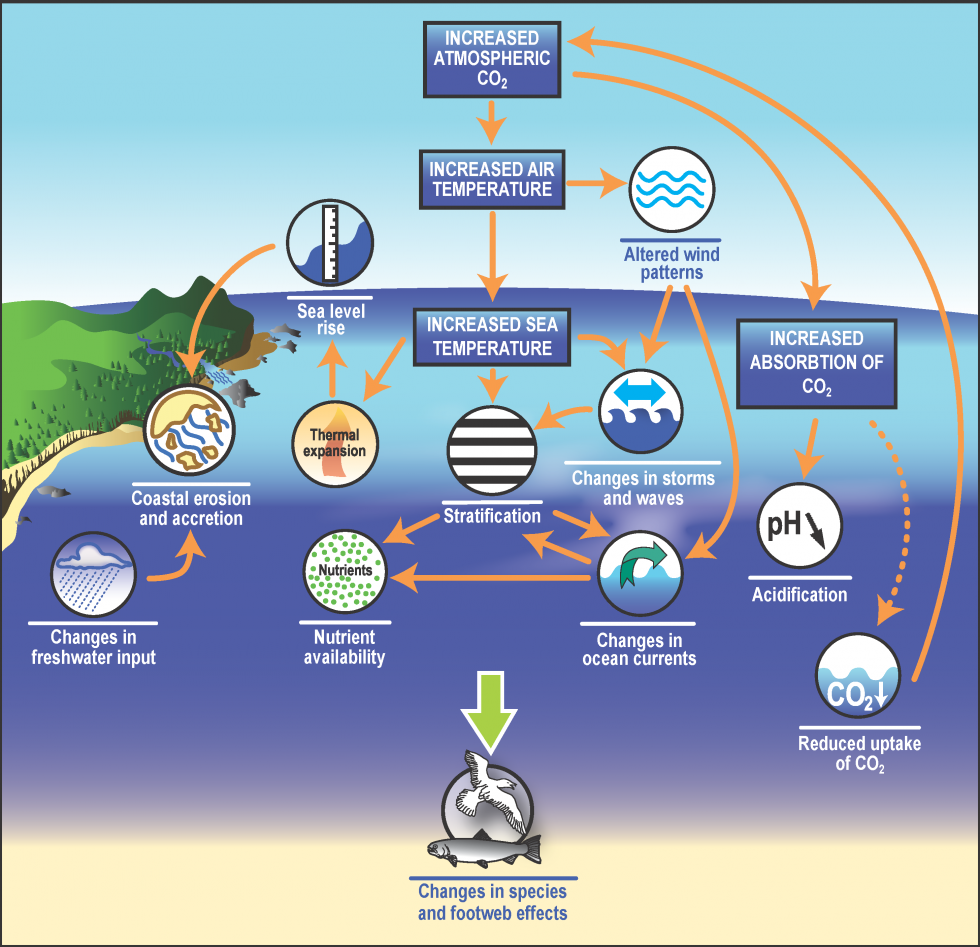
Challenges or Controversies
Debate surrounds the potential long-term effects of ocean energy on marine ecosystems. While the industry aims to minimize impacts, there is a need for ongoing research and monitoring to fully understand the consequences of large-scale deployment. Additionally, there can be conflicts between renewable energy goals and conservation priorities, highlighting the importance of finding a balance between sustainable energy production and environmental protection.
Future Outlook
The future of ocean energy holds great promise. Technological advancements are expected to further reduce environmental impacts, making it an even more viable and sustainable energy source. Furthermore, integration of ocean energy with other renewable sources, such as wind and solar, can create a comprehensive and resilient energy system. Continued research and monitoring will play a vital role in ensuring the responsible development and deployment of ocean energy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ocean energy offers a valuable renewable energy source that can help mitigate climate change and reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. However, it is imperative to address and mitigate the environmental concerns associated with ocean energy projects. By employing strategic project planning, thorough environmental assessments, and stakeholder engagement, we can harness the power of the oceans while preserving their delicate ecosystems.




