
Corporate Responsibility and Ocean Energy: Pioneering Sustainable Solutions
Introduction
Ocean energy is gaining recognition as a sustainable source of power with the potential to address climate change. As companies around the world strive to uphold corporate responsibility, adopting ocean energy is becoming increasingly important. This article will explore the significance of ocean energy within the context of corporate responsibility, shedding light on its environmental, social, and economic dimensions.
Historical Background
The development and utilization of ocean energy have a rich history. From early experiments with wave and tidal energy in the 19th century to the modern-day innovations in ocean thermal energy conversion, the journey of ocean energy has been marked by technological advancements. Alongside these developments, corporate responsibility in the renewable energy sector has evolved, reflecting society’s growing concern for environmental sustainability.
Key Concepts and Definitions
To understand the intersection of corporate responsibility and ocean energy, it is crucial to define these concepts. Corporate responsibility encompasses environmental stewardship, social impact, and economic sustainability. Ocean energy refers to the harnessing of renewable energy from the ocean, including various forms such as wave energy, tidal energy, and ocean thermal energy conversion.
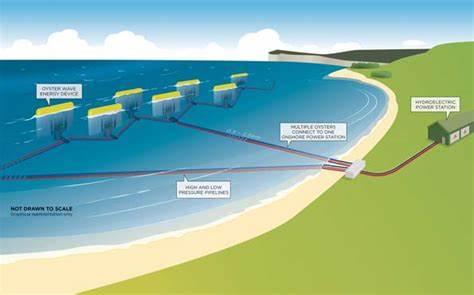
Main Discussion Points
The role of corporate responsibility in driving the adoption of ocean energy
Companies are increasingly integrating ocean energy into their sustainability strategies. By embracing this renewable energy source, they demonstrate their commitment to reducing carbon footprints and transitioning to cleaner technologies. The motivations for corporate engagement in ocean energy initiatives include meeting renewable energy targets, enhancing brand reputation, and contributing to global efforts in combatting climate change.
Environmental benefits and impacts of ocean energy
Ocean energy holds significant potential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. By harnessing the power of waves, tides, and temperature differences, this renewable energy source can replace fossil fuel-based electricity generation. However, the deployment and operation of ocean energy technologies may have some environmental impacts, such as noise disturbance, habitat alteration, and effects on marine ecosystems. Addressing these concerns is crucial to ensure the long-term sustainability of ocean energy projects.
Social and economic considerations of ocean energy
Ocean energy projects can bring various socio-economic benefits to coastal communities. By providing clean and reliable energy, these projects can enhance energy security, create job opportunities, and stimulate local economic development. However, challenges related to project financing, infrastructure requirements, and stakeholder engagement need to be carefully navigated to maximize the positive impacts of ocean energy on society.
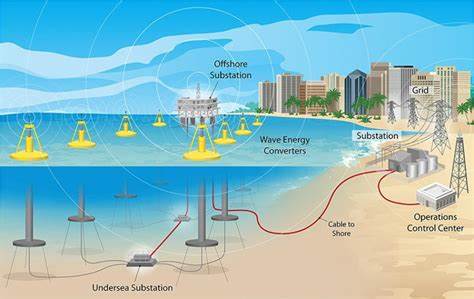
Case Studies or Examples
Notable companies and organizations have embraced ocean energy, showcasing corporate responsibility in action. One such example is Orsted, a global leader in offshore wind energy, which has expanded its portfolio to include wave and tidal energy projects. Orsted’s commitment to corporate responsibility is evident in its efforts to minimize the environmental impacts of its projects and engage with local communities. Additionally, the European Marine Energy Centre (EMEC) has facilitated successful ocean energy projects, demonstrating the potential of this renewable energy source to contribute to sustainability goals.
Current Trends or Developments
Advancements in ocean energy technologies are revolutionizing the field and influencing corporate responsibility. Innovations such as floating offshore wind turbines and improved wave energy converters are expanding the possibilities for harnessing clean energy from the ocean. Furthermore, research findings on the environmental benefits and socio-economic impacts of ocean energy are shaping the strategies of companies and policymakers alike, reinforcing the importance of corporate responsibility in this sector.
Challenges or Controversies
Ocean energy projects are not without challenges and controversies. Environmental concerns, such as the potential impacts on marine life and ecosystems, need to be carefully assessed and mitigated. Additionally, differing viewpoints exist regarding the economic viability and scalability of ocean energy. Some argue that the costs of developing ocean energy technologies are prohibitive, while others believe that with continued innovation and supportive policies, this renewable energy source can become economically competitive and widely adopted.

Future Outlook
The future of ocean energy looks promising, with the potential to become a mainstream energy source. As advancements in technology continue to drive down costs and improve efficiency, ocean energy has the capacity to play a significant role in the global energy transition. Innovations in energy storage and grid integration will further enhance the reliability and scalability of ocean energy projects. Policy changes that incentivize and support corporate responsibility in the ocean energy sector will be pivotal in driving its growth and mainstream adoption.
Conclusion
Corporate responsibility and ocean energy are intertwined in the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions. By embracing ocean energy, companies can demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship, social impact, and economic sustainability. However, it is crucial to address environmental concerns and navigate the challenges associated with ocean energy projects. Continued collaboration and commitment to sustainable energy solutions are essential in maximizing the potential of ocean energy and achieving corporate responsibility goals.
References
Smith, B. Ocean energy: current status and future perspectives. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016.
European Marine Energy Centre. (2021). Retrieved from https://www.emec.org.uk/
Orsted. (2021). Retrieved from https://orsted.com/




