
Introduction
The topic of smart buildings and sustainable development goals has gained significant attention in recent years. As the world grapples with the detrimental effects of climate change and the need for more sustainable practices, the integration of smart buildings into the equation has emerged as a potential solution. This article aims to explore the synergy between smart buildings and sustainable development goals, highlighting their relevance and importance in achieving a more sustainable future.
Historical Background
Smart buildings have a rich history that dates back several decades. Initially, these buildings focused on incorporating advanced technologies for automation and control systems. However, with the growing concerns about environmental sustainability, the concept of smart buildings evolved to encompass energy efficiency, resource conservation, and occupant well-being. In parallel, sustainable development goals were introduced as a framework to guide global efforts towards a more sustainable future. The development and integration of smart buildings with sustainable development goals mark a significant milestone in the pursuit of sustainable development.
Key Concepts and Definitions
To understand the potential synergy between smart buildings and sustainable development goals, it is essential to define the key concepts involved. Smart buildings are structures equipped with advanced technologies that enable efficient and automated control of various systems, including lighting, HVAC, and security. Sustainable development goals, on the other hand, are a set of global objectives established by the United Nations to address social, economic, and environmental challenges. The integration of these two concepts holds the promise of achieving sustainable development through the utilization of smart building technologies.

Main Discussion Points
Point – Benefits of smart buildings in achieving sustainable development goals
Smart buildings offer numerous benefits in the context of sustainable development goals. Firstly, they contribute to energy efficiency and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. Through advanced automation and control systems, smart buildings optimize energy consumption, resulting in significant energy savings. Additionally, smart buildings promote resource conservation and waste reduction by monitoring and managing resource usage. Lastly, smart buildings have a positive impact on occupant health and well-being. By ensuring optimal indoor air quality, temperature, and lighting, smart buildings create healthier and more comfortable living and working environments.
Point – Challenges and considerations in integrating smart buildings with sustainable development goals
While the integration of smart buildings and sustainable development goals presents numerous opportunities, it also brings challenges. Technical and infrastructure requirements pose a significant challenge, as retrofitting existing buildings with smart technologies can be complex and costly. Additionally, the economic barriers and financial implications of adopting smart buildings can hinder their widespread implementation. To overcome these challenges, policy and regulatory frameworks are necessary to encourage and support the integration of smart buildings and sustainable development goals.
Point – Role of partnerships and collaborations in achieving synergy
Partnerships and collaborations play a vital role in achieving synergy between smart buildings and sustainable development goals. Successful collaborations between governments, private sectors, and communities have demonstrated the efficacy of implementing smart building solutions. Sharing knowledge and engaging stakeholders are crucial for maximizing the benefits of smart buildings for sustainable development. By fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing, the implementation of smart buildings can be accelerated, leading to more sustainable outcomes.
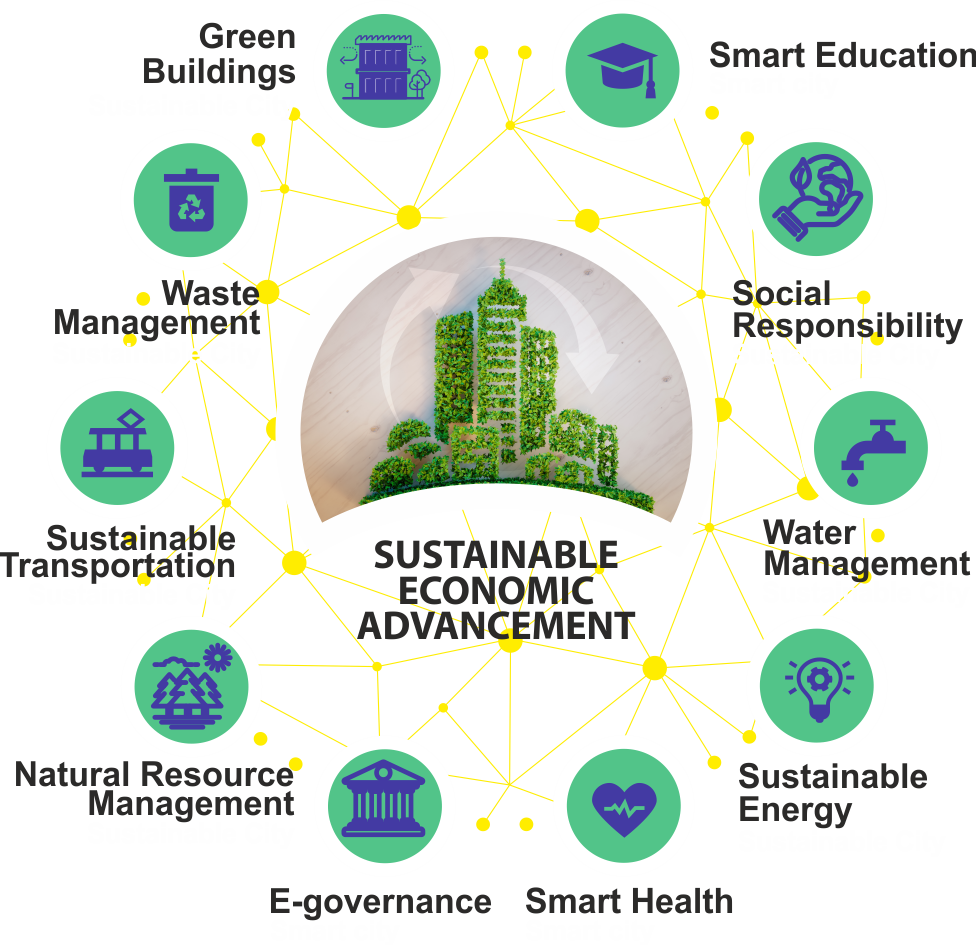
Case Studies or Examples
Real-world examples serve as testament to the synergy between smart buildings and sustainable development goals. One notable example is The Edge, a smart building in Amsterdam. This building utilizes advanced technologies to optimize energy consumption, resulting in energy savings of up to 70%. Another example is the Sidewalk Labs project in Toronto, which aims to create a sustainable neighborhood utilizing smart building technologies. These case studies demonstrate the potential and effectiveness of integrating smart buildings with sustainable development goals.
Current Trends or Developments
In recent years, there have been significant advancements and trends in smart building technologies. The rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and sensors has enabled greater connectivity and data collection within buildings. This data-driven approach allows for more precise control and optimization of various systems, leading to increased energy efficiency and resource conservation. Furthermore, research findings and innovations continue to contribute to the integration of smart buildings and sustainable development goals, further enhancing their synergy.
Challenges or Controversies
While the integration of smart buildings and sustainable development goals presents immense potential, it is not without challenges and controversies. One of the primary challenges is the upfront cost of implementing smart building technologies, which can be prohibitive for some stakeholders. Additionally, concerns about data privacy and security surrounding the use of IoT devices in smart buildings have sparked debates within the field. Addressing these challenges and controversies is crucial for the successful implementation of smart buildings in pursuit of sustainable development.
Future Outlook
The future of smart buildings and sustainable development goals holds immense promise. As technology continues to advance, emerging technologies and strategies will further enhance the synergy between these two concepts. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into smart building systems will enable even greater optimization and efficiency. Additionally, strategies such as decentralized energy generation and the utilization of renewable energy sources will transform the way smart buildings contribute to sustainable development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of smart buildings and sustainable development goals offers a synergy that can lead us towards a more sustainable future. The benefits of smart buildings in achieving energy efficiency, resource conservation, and occupant well-being are undeniable. However, challenges related to cost, infrastructure, and regulations must be addressed. By fostering partnerships and collaborations, sharing knowledge, and embracing emerging technologies, we can maximize the potential of smart buildings to contribute to sustainable development goals.
References
Smart Buildings Council. (2021). About Smart Buildings. Retrieved from https://www.smartbuildingscouncil.org/about
United Nations. (2021). Sustainable Development Goals. Retrieved from https://sdgs.un.org/goals




