
Vertical Farming: Revolutionizing Modern Agriculture
Introduction
Vertical farming has emerged as a revolutionary concept in modern agriculture, offering a solution to the challenges posed by traditional farming methods. This innovative approach involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers, utilizing artificial lighting and hydroponics or aeroponics systems. The benefits of vertical farming are numerous, including increased crop yields, reduced water usage, and year-round production. In this article, we will explore the historical background, key concepts, main discussion points, case studies, current trends, challenges, and future outlook of vertical farming.
Historical Background
The concept of vertical farming dates back to the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. However, it was during the 20th century that the idea gained traction as a response to the limitations of traditional farming methods. With the rise in urbanization and the need for sustainable food production in densely populated areas, vertical farming became increasingly relevant. Over the years, advancements in technology and agricultural practices have propelled the evolution of vertical farming into the innovative system we see today.
Key Concepts and Definitions
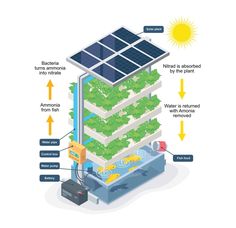
Vertical farming involves the cultivation of crops in vertically stacked layers, using methods such as hydroponics and aeroponics. Hydroponics is a soil-less method that relies on a nutrient-rich water solution to deliver essential nutrients to the plants. This method maximizes water efficiency and eliminates the need for traditional soil-based farming. Aeroponics involves growing plants in an air or mist environment, with their roots suspended in the air. This approach allows for enhanced oxygenation and nutrient absorption, resulting in accelerated plant growth.
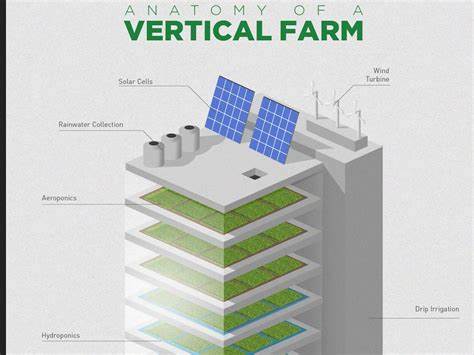
Artificial lighting plays a crucial role in vertical farming, as it ensures that plants receive the necessary light spectrum for optimal growth. LED lights are commonly used due to their energy efficiency and ability to emit specific wavelengths required by the plants. Automation is another essential component of vertical farming, enabling precise control over environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and pH levels. This level of control ensures that crops receive the ideal conditions for growth, regardless of external factors.
Main Discussion Points
Point: Planning and Design of a Vertical Farm
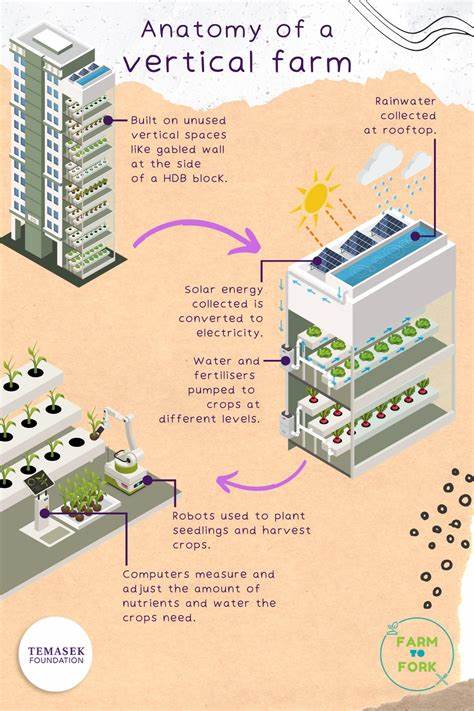
When selecting a location for a vertical farm, several factors need to be considered. These include proximity to markets, availability of resources such as water and electricity, and the potential for expansion. Designing an efficient layout is crucial to maximize space utilization. Vertical farms often employ techniques such as vertical stacking and rotating racks to optimize the use of available space. Additionally, selecting the appropriate crops is vital, considering factors such as profitability, market demand, and suitability to vertical farming conditions.
Point: Construction and Infrastructure
Constructing a vertical farm involves several steps and materials. The structure needs to be sturdy, able to support the weight of multiple layers and withstand environmental conditions. Proper insulation, ventilation, and climate control systems are crucial to maintaining optimal growing conditions within the vertical farm. Additionally, hydroponic or aeroponic systems need to be procured and set up, ensuring that the plants receive the necessary nutrients and water.
Point: Operational Management and Maintenance
Managing a vertical farm requires daily activities to ensure the well-being of the crops. This includes monitoring environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and pH levels, and making adjustments as needed. Regular maintenance of the systems, including cleaning and troubleshooting, is essential to prevent issues that could affect crop health and productivity.
Point: Harvesting, Packaging, and Distribution
Harvesting crops in a vertical farm requires careful consideration of techniques and timing. It is important to ensure that crops are harvested at their peak freshness and nutritional value. Proper packaging and labeling are essential for market readiness, as vertical farm produce often targets consumers looking for locally grown, sustainable options. Distribution options may include direct-to-consumer sales through farmers’ markets or partnerships with local grocery stores and restaurants.
Case Studies or Examples
Various successful vertical farms have made a significant impact in the agricultural industry. For instance, Gotham Greens, a New York-based vertical farming company, operates rooftop greenhouse farms that supply fresh produce to local markets. Another example is Plenty, a vertical farming startup that utilizes robotics and artificial intelligence to achieve high crop yields. These case studies showcase the feasibility and scalability of vertical farming, providing inspiration for aspiring vertical farmers.
Current Trends or Developments
Vertical farming technologies and practices continue to evolve rapidly. Recent trends include the integration of smart farming technologies, such as sensors and data analytics, to optimize resource usage and crop growth. The use of renewable energy sources, such as solar power, is also gaining traction, further enhancing the sustainability of vertical farming systems. Ongoing research and advancements in lighting technology, automation, and plant genetics promise to drive further innovation in the field.
Challenges or Controversies
Setting up and operating a vertical farm comes with its fair share of challenges. These may include high upfront costs, complexities in system design and management, and the need for specialized knowledge and skills. Additionally, controversy surrounds the use of artificial lighting and the carbon footprint associated with vertical farming. Critics argue that the energy consumption of vertical farms could outweigh the environmental benefits, making it necessary to find a balance between efficiency and sustainability.
Future Outlook
The future of vertical farming is promising, with the potential to address critical issues such as food security and sustainability. As technology continues to advance, vertical farming is expected to become more efficient, cost-effective, and accessible. Emerging concepts, such as vertical farming in urban skyscrapers and integration with renewable energy sources, hold great potential for transforming agriculture on a global scale. The continued collaboration between researchers, entrepreneurs, and policymakers will play a crucial role in shaping the future of vertical farming.
Conclusion
Vertical farming presents a revolutionary approach to modern agriculture, offering numerous benefits and solutions to traditional farming challenges. By utilizing vertical stacking, hydroponics or aeroponics systems, artificial lighting, and automation, vertical farms can achieve high crop yields, conserve water, and operate year-round. While there are challenges and controversies surrounding this concept, ongoing advancements and research promise a bright future for vertical farming. With its potential to address food security and sustainability, vertical farming stands as a significant force in shaping the future of agriculture.
References
Despommier, D. (2010). The vertical farm: feeding the world in the 21st century. Macmillan.
Goddek, S., Joyce, A., Kotzen, B., & Burnell, G. (2018). Aquaponics and hydroponics: A comparison in terms of sustainability. Sustainability, 10(12), 4368.
Halls, S. (2021). Vertical farming and urban agriculture: Making strides in sustainable food production. In Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Agriculture and Food, 174(2), 63-70.
Kumar, R., Priyadarshi, A., & Singh, D. (2020). Vertical farming: A sustainable approach to urban agriculture. In Urban Agriculture and Sustainable Cities (pp. 79-94). Springer.




