
Sustainable Energy Transition: A Comprehensive Blueprint for a Sustainable Future
Introduction
In today’s rapidly changing world, the transition to sustainable energy has become an urgent and critical topic of discussion. The need to shift from traditional energy sources, which contribute to climate change and environmental degradation, to more sustainable alternatives has never been more paramount. This article aims to provide a thorough and comprehensive overview of sustainable energy transition and the significant role that thought leaders play in driving this crucial change.
Historical Background
To fully comprehend the significance of sustainable energy transition, it is essential to examine the historical context of energy consumption patterns and their environmental impacts. For many years, the world has heavily relied on fossil fuels, resulting in detrimental greenhouse gas emissions and other adverse effects on the environment. However, over time, the concept of sustainable energy has evolved, and initiatives to promote renewable energy sources have gained significant momentum.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Before diving into the main discussion points, it is crucial to establish a clear understanding of sustainable energy and the concept of energy transition. Sustainable energy refers to energy sources that are renewable, environmentally friendly, and economically viable. Energy transition, on the other hand, entails a gradual shift from conventional energy sources to sustainable alternatives. Thought leaders play a pivotal role in driving this transition by advocating for change and influencing decision-makers.
Main Discussion Points
Point: The Role of Policy and Regulations in Sustainable Energy Transition
Government policies supporting renewable energy have proven to be instrumental in driving the transition towards sustainable energy. These policies provide incentives, subsidies, and regulations that encourage the adoption of clean energy sources. Additionally, international agreements and commitments, such as the Paris Agreement, have further accelerated the transition by fostering global cooperation.
However, despite the progress made, policy barriers and challenges still exist. Certain governments may be hesitant to implement renewable energy policies due to various reasons, including political and economic factors. Overcoming these barriers and addressing the challenges is crucial for the successful transition to sustainable energy.
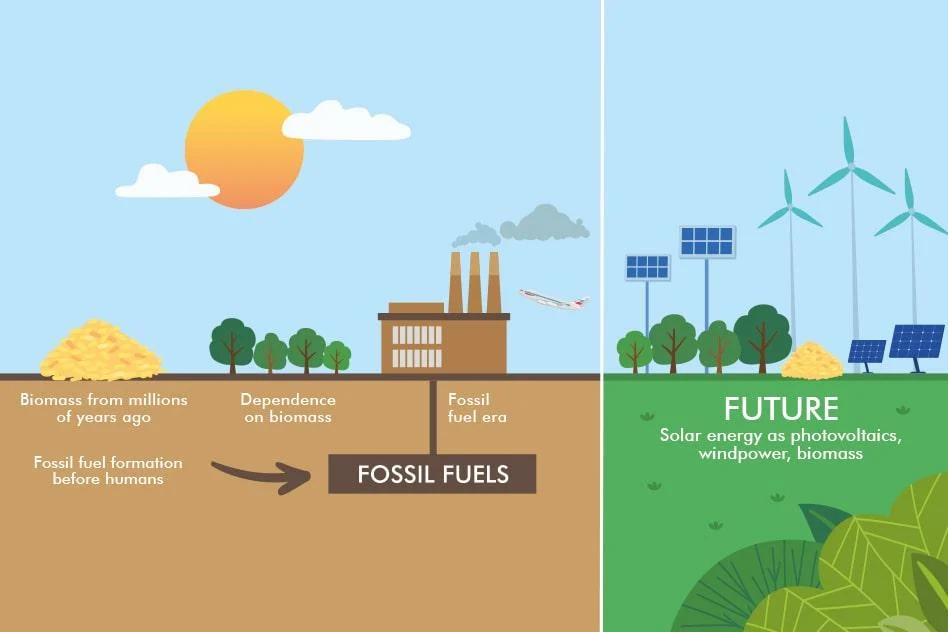
Point: Technology Innovations and Advancements in Sustainable Energy
Renewable energy technologies have made remarkable advancements in recent years. Solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power are among the key sources that have gained widespread adoption. Additionally, energy storage and grid integration have become vital components of sustainable energy systems, ensuring reliability and stability.
Furthermore, emerging technologies, such as advanced energy management systems and smart grids, have the potential to revolutionize the energy sector. These advancements can drive the transition towards a more sustainable and efficient energy future.
Point: Financing and Investment Strategies for Sustainable Energy Transition
Clean energy financing mechanisms, including green bonds and carbon markets, have played a crucial role in attracting capital for sustainable energy projects. Private sector investments and impact investment have also been instrumental in driving the transition by providing financial support for renewable energy initiatives.
However, challenges and opportunities exist in attracting capital for sustainable energy projects. Despite the growing interest in sustainable investments, the availability of capital remains a challenge. Developing innovative financing strategies and addressing investment barriers are essential for accelerating the transition.
Case Studies or Examples
Case Study: Successful Sustainable Energy Transition in a Specific Country or Region
One notable example of a successful sustainable energy transition is Denmark. The country has made significant strides in transitioning to renewable energy sources, particularly wind power. Through strong government support, favorable policies, and collaboration with industry stakeholders, Denmark has achieved impressive renewable energy penetration and has become a global leader in sustainable energy.
Case Study: Innovative Projects or Initiatives Driving the Transition
The Solar Impulse project serves as a prime example of an innovative initiative driving the sustainable energy transition. The project involved a solar-powered aircraft that completed a round-the-world flight, highlighting the potential of renewable energy technologies. It showcased the importance of innovation and the need for sustainable alternatives in the transportation sector.
Case Study: Lessons Learned from Failed Attempts at Sustainable Energy Transition
Germany’s transition to renewable energy, known as the Energiewende, provides valuable lessons on the challenges of sustainable energy transition. While the country has made significant progress, there have been issues related to grid stability, high costs, and public acceptance. These challenges emphasize the importance of comprehensive planning, stakeholder engagement, and addressing potential drawbacks.
Current Trends or Developments
Recent trends and research findings indicate a promising future for sustainable energy transition. The increasing adoption of electric vehicles, the emergence of community-based renewable energy projects, and the integration of artificial intelligence in energy systems are among the key developments shaping the transition.
Furthermore, global sustainable energy targets, such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and the International Renewable Energy Agency’s targets, guide and monitor progress in achieving a sustainable energy future.
Challenges or Controversies
Addressing public resistance and skepticism towards sustainable energy poses a significant challenge. Misinformation and misconceptions surrounding renewable energy technologies can hinder progress. Education, awareness campaigns, and effective communication strategies are vital in overcoming these challenges and building public support.
Certain renewable energy technologies, such as wind turbines and solar farms, have also faced controversies. Concerns related to visual impacts, noise pollution, and potential harm to wildlife have sparked debates. Balancing the benefits of renewable energy with the concerns of local communities is crucial for successful implementation.

Future Outlook
The future of sustainable energy transition holds immense potential. Breakthroughs in technology and policy are expected to drive further progress. Advancements in energy storage, smart grids, and renewable energy generation technologies are anticipated to make sustainable energy more accessible and reliable.
However, anticipated challenges such as the need for infrastructure enhancements, regulatory frameworks, and financing mechanisms must be addressed to ensure a smooth transition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sustainable energy transition is a critical pathway to combat climate change and achieve a more sustainable future. Thought leaders play a vital role in driving this transition by advocating for change and influencing policy decisions. By understanding the historical background, key concepts, main discussion points, case studies, current trends, challenges, and future outlook, individuals and organizations can actively contribute to this global endeavor.
References:
International Energy Agency. (2021). World Energy Outlook 2020.
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-energy/
International Renewable Energy Agency. (2021). Global Renewables Outlook: Energy Transformation 2050.




