
Introduction
The circular economy has emerged as a concept for addressing environmental challenges and promoting sustainable development. By rethinking traditional models of production and consumption, the circular economy aims to reduce waste, conserve resources, and create a more equitable and prosperous society. In this article, we will explore the importance of the circular economy in driving job creation in the green sector, its relevance in the transition to a low-carbon economy, and the background that has shaped this concept.
Historical Background
The origins of the circular economy concept can be traced back to the 1960s, with the work of economists such as Kenneth Boulding and Herman Daly. However, it was in the 1980s that the term gained prominence, thanks to the efforts of architect Walter R. Stahel and his book “The Performance Economy.” Stahel advocated for a shift from a linear model to a circular economy that prioritizes resource efficiency and waste prevention.
Key Concepts and Definitions
At its core, the circular economy is based on the principles of waste prevention, reuse, and recycling. It seeks to decouple economic growth from resource consumption and environmental degradation. The green sector refers to industries and businesses that prioritize sustainability and environmental stewardship in their operations. This includes sectors such as renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and waste management.
Job creation in the green sector is important for economic growth and social equity. It not only provides employment opportunities but also drives innovation, enhances resource efficiency, and reduces the carbon footprint of industries.
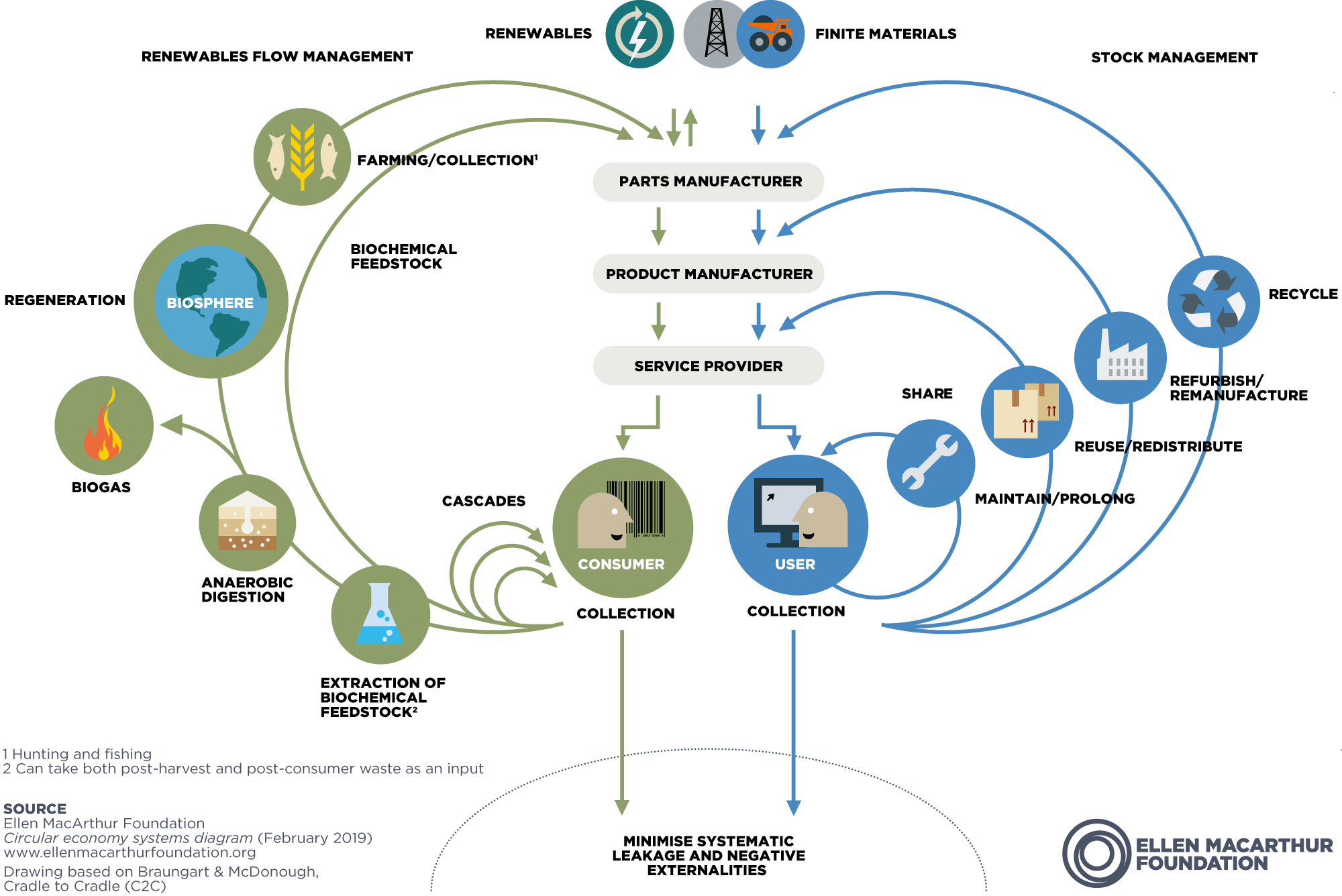
Main Discussion Points
The Economic Benefits of the Circular Economy
The circular economy presents economic opportunities. By transitioning to a more resource-efficient and circular model, businesses can create new revenue streams and tap into emerging markets. For instance, the rise of product-as-a-service models has the potential to generate new business models and employment opportunities.
Many companies and industries have embraced circular economy practices and reaped positive economic outcomes. For example, Interface, a flooring company, implemented a circular business model called “Mission Zero” and managed to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions and waste while increasing its profitability.
Environmental Benefits of the Circular Economy
The circular economy plays a crucial role in reducing resource consumption, waste generation, and pollution. By embracing practices such as recycling and remanufacturing, industries can minimize their environmental footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
The transition to a circular economy also presents significant job creation potential in sectors such as renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and waste management. These sectors not only help mitigate climate change but also create employment opportunities for individuals with diverse skill sets.
Social Benefits of Job Creation in the Green Sector
Job creation in the green sector has the potential to address social issues such as unemployment and poverty. By providing decent wages, job security, and opportunities for skills development, green jobs can enhance the well-being of individuals and communities.
It is essential to ensure that job creation in the green sector is inclusive and equitable. This means prioritizing opportunities for marginalized communities and vulnerable populations, who are often disproportionately affected by environmental degradation and the lack of economic opportunities.
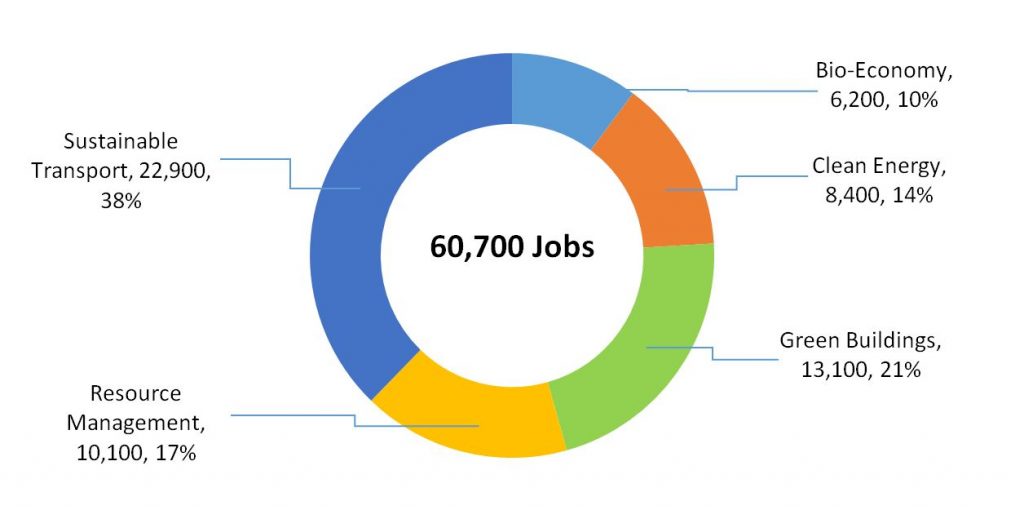
Case Studies or Examples
Several countries and regions have successfully implemented circular economy strategies and created jobs in the green sector. The Netherlands, for instance, has embraced the circular economy and has become a global leader in waste management and resource recovery. The country has created thousands of jobs in industries such as recycling, renewable energy, and sustainable construction.
Companies like Patagonia, a renowned outdoor clothing brand, have also demonstrated the potential of circular economy practices. Patagonia encourages its customers to repair and reuse their products, fostering a culture of sustainability and reducing the demand for new items.
Current Trends or Developments
Recent years have witnessed a growing adoption of circular economy practices and the expansion of the green sector. Governments, businesses, and consumers are increasingly recognizing the need for sustainable solutions and are actively seeking to integrate circularity into their operations.
Research reports and studies have provided valuable insights into the job creation potential in the green sector. For example, a study by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation estimated that the circular economy could create 18 million new jobs worldwide by 2030.
Challenges or Controversies
Implementing circular economy practices and promoting job creation in the green sector is not without its challenges. Barriers such as limited awareness, lack of financial incentives, and the complexity of supply chains can hinder the widespread adoption of circular principles.
Controversies also exist surrounding the trade-offs between economic growth and environmental sustainability. Some argue that the circular economy may not be compatible with continued economic expansion. However, proponents believe that a circular economy can enable sustainable economic growth by decoupling it from resource consumption.
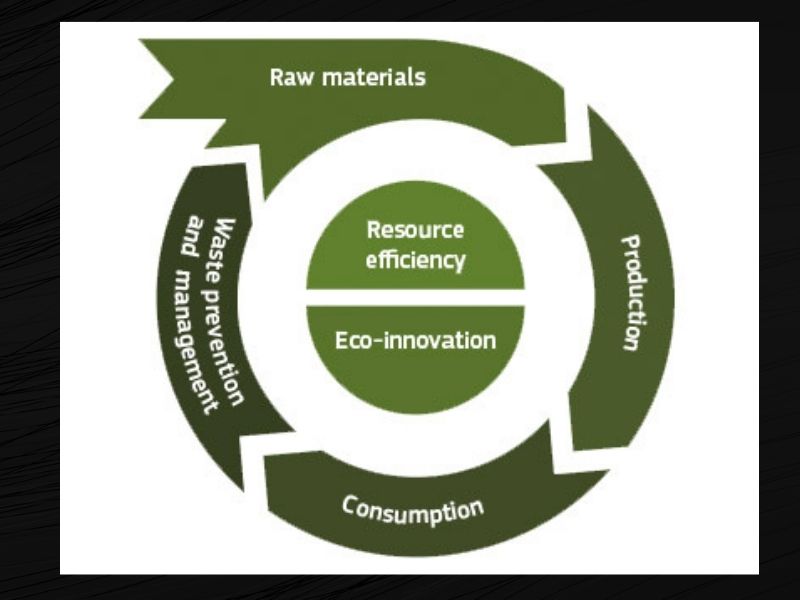
Future Outlook
The future implications of the circular economy for job creation in the green sector are promising. As technology advances and innovation continues, new opportunities for employment and economic growth will emerge. Emerging technologies such as 3D printing, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things have the potential to further enhance the circular economy and create new green jobs.
To unlock the full potential of the circular economy in creating green jobs, continued research, collaboration, and policy support are crucial. Governments, businesses, and individuals must work together to develop and implement strategies that promote circularity and enable the transition to a more sustainable and prosperous future.
Conclusion
The circular economy offers an innovative and sustainable solution to environmental challenges while driving job creation in the green sector. By rethinking traditional models of production and consumption, businesses and industries can create economic growth, reduce waste, and enhance social equity. It is imperative for governments, businesses, and individuals to embrace the circular economy and unlock its full potential in creating green jobs. Only through collective action and collaboration can we achieve sustainable development goals and secure a better future for generations to come.
References
Stahel, W. R. (2010). The Performance Economy. Palgrave Macmillan.
Ellen MacArthur Foundation. (2019). Completing the Picture: How the Circular Economy Tackles Climate Change. Retrieved from https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/assets/downloads/EMF_Circular_Economy_Climate_2019.pdf




