Introduction
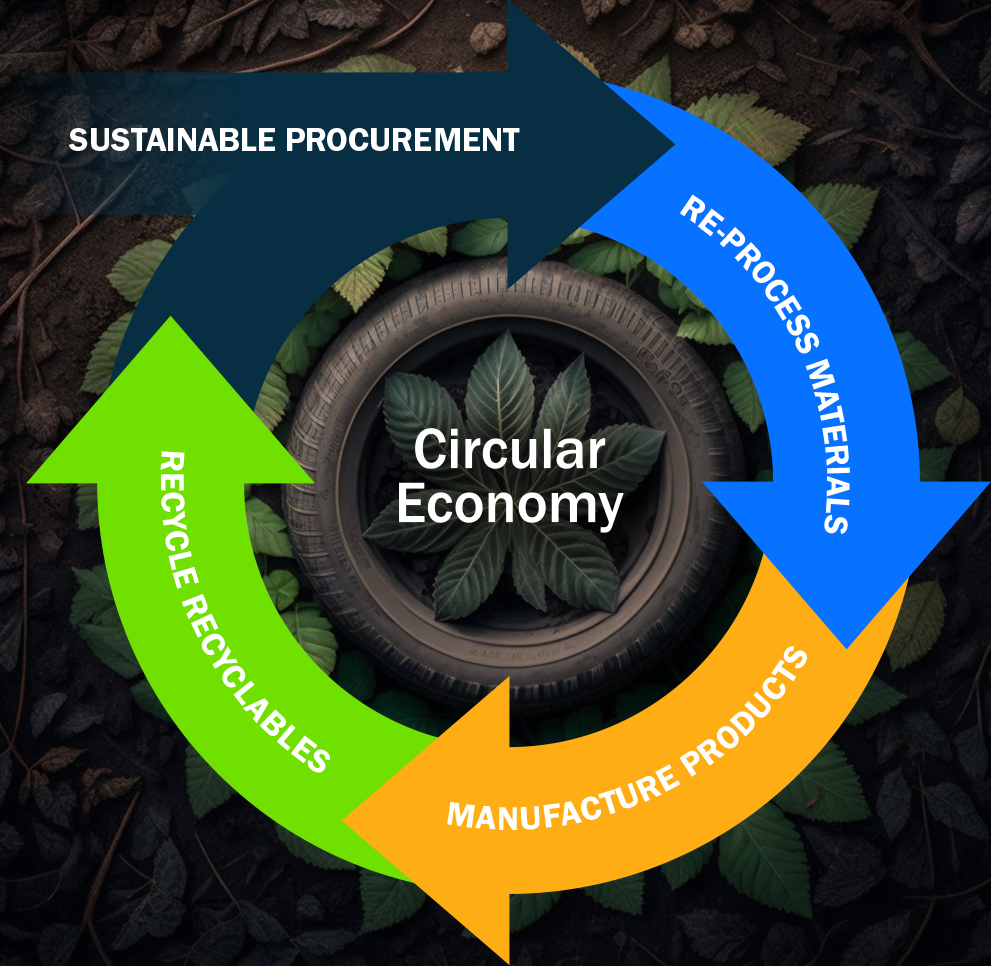
The concept of the circular economy aims to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency. It is a system that strives to close the loop by ensuring that products and materials are used, reused, and recycled to their fullest potential. Waste-to-Energy (WtE) plays a crucial role in this revolution by transforming waste into valuable resources, contributing to a sustainable and circular economy.
Historical Background
The idea of a circular economy is not a new concept. It dates back to the early 20th century when sustainability pioneers recognized the importance of minimizing waste and promoting resource efficiency. Over time, the concept evolved with advancements in technology and a deeper understanding of environmental challenges. Concurrently, WtE technologies developed as a response to the growing need for efficient waste management solutions.
Key Concepts and Definitions
The circular economy is a system that aims to decouple economic growth from resource consumption. It is guided by principles such as designing out waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. WtE involves the conversion of waste materials into usable forms of energy, such as electricity, heat, or fuel, through various processes. This integration of WtE into the circular economy ensures that waste is not only managed but also utilized as a valuable resource.

Main Discussion Points
WtE as a solution for waste management
Traditional waste management methods face numerous challenges, including limited landfill space, pollution, and health risks. WtE technologies offer a sustainable alternative by converting waste into valuable resources. Through processes like incineration, anaerobic digestion, and gasification, WtE not only reduces the volume of waste but also extracts energy and materials from it.
Environmental benefits of WtE in the circular economy
WtE processes contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy sources. Moreover, WtE reduces the reliance on landfilling, which emits harmful gases and contributes to groundwater contamination. Additionally, WtE systems provide opportunities for resource recovery and recycling, further reducing the environmental impact of waste.
Economic and social benefits of WtE in the circular economy
The WtE sector presents significant economic opportunities, including job creation and revenue generation. As the demand for sustainable waste management solutions grows, the WtE industry can play a vital role in providing employment opportunities. Furthermore, WtE technologies contribute to energy generation and security, reducing reliance on non-renewable sources. This fosters economic resilience and stability.

Case Studies or Examples
Successful WtE projects around the world demonstrate the effectiveness of integrating WtE into the circular economy. For instance, the city of Copenhagen, Denmark, operates an efficient WtE plant that converts waste into electricity and district heating. In China, the Shenzhen East Waste-to-Energy Plant processes over 5,000 tons of waste daily, benefiting both the economy and the environment.
Current Trends or Developments
Advancements in WtE technologies continue to drive innovation in the field. For example, researchers are exploring the use of advanced gasification processes to maximize energy recovery and minimize environmental impact. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve the efficiency of anaerobic digestion, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
Challenges or Controversies
While WtE offers significant benefits, it is not without challenges and controversies. Potential environmental impacts, such as air pollution and emissions from WtE facilities, require stringent regulations and monitoring. Concerns regarding the release of harmful substances during the incineration process need to be addressed through proper waste treatment and emission control technologies. The role of WtE in the circular economy also faces differing viewpoints, with some advocating for a more comprehensive focus on waste reduction and recycling.

Future Outlook
The WtE sector is poised for growth and expansion as society increasingly embraces the circular economy. Advancements in technology and supportive policies can accelerate the adoption of WtE as a cornerstone in the circular economy. Governments and regulatory bodies have a crucial role in incentivizing and promoting WtE solutions, ensuring a sustainable and circular future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the circular economy revolution requires the integration of waste-to-energy as a cornerstone. WtE technologies offer an efficient and sustainable solution for waste management, providing environmental, economic, and social benefits. By harnessing the potential of WtE, we can pave the way towards a circular economy that maximizes resource efficiency and minimizes waste.
References:
- Ellen MacArthur Foundation. (n.d.). Circular Economy. Retrieved from https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/circular-economy/concept
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (n.d.). Waste-to-Energy. Retrieved from https://www.epa.gov/energy/waste-energy-technical-assistance-partnership
- European Commission. (2015). European Union Waste Framework Directive. Retrieved from https://ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/framework/
- World Bank. (2018). What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050. Retrieved from https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/30317




