
The Evolution of Vertical Garden Technology: Enhancing Urban Environments and Sustainability
Introduction
Vertical garden technology has revolutionized urban landscaping by providing innovative solutions for limited space and environmental challenges. This article explores the historical background, key concepts, and advancements in this field, while also aiming to provide more comprehensive information to readers. By addressing the main discussion points, case studies, current trends, challenges, and future outlook, we can showcase the potential benefits of vertical gardens in addressing urbanization and climate change.
Historical Background
The concept of vertical gardens dates back centuries, with ancient civilizations using trellises and ivy-covered walls for aesthetic and practical purposes. However, it was not until the 20th century that vertical garden technology began to gain traction. Advancements in materials and design techniques led to the development of more sophisticated structures and systems.
Key Concepts and Definitions
A vertical garden, also known as a living wall or green facade, refers to a structure that supports plant growth vertically, utilizing both natural and artificial systems. Various types and designs of vertical gardens exist, including modular systems and hydroponic setups. These gardens require careful consideration of irrigation, lighting, and plant selection to ensure optimal growth.

Main Discussion Points
Evolution of Vertical Garden Structures
The evolution of vertical garden structures has progressed from simple trellises to complex modular systems. The use of advanced materials, lightweight panels, and modular grids has facilitated the construction of intricate and versatile vertical gardens. These structures can now be easily integrated into existing buildings and urban landscapes, transforming the way we incorporate green spaces in cities.
Evolution of Plant Selection and Maintenance
Plant selection for vertical gardens has evolved to include native species and specific plant varieties that thrive in vertical environments. This shift ensures better adaptation to local climates and reduces the need for excessive maintenance. Automation technologies, such as remote monitoring and automated irrigation systems, have also enhanced plant maintenance practices, making vertical gardens more sustainable and cost-effective.
Integration of Technology in Vertical Garden Systems
The incorporation of technology has significantly improved the efficiency, sustainability, and performance of vertical garden systems. Sensors and data analytics are now being utilized to monitor key parameters like moisture levels and plant health, optimizing resource allocation and reducing waste. These advancements have made vertical gardens more resilient and adaptable to changing environmental conditions.
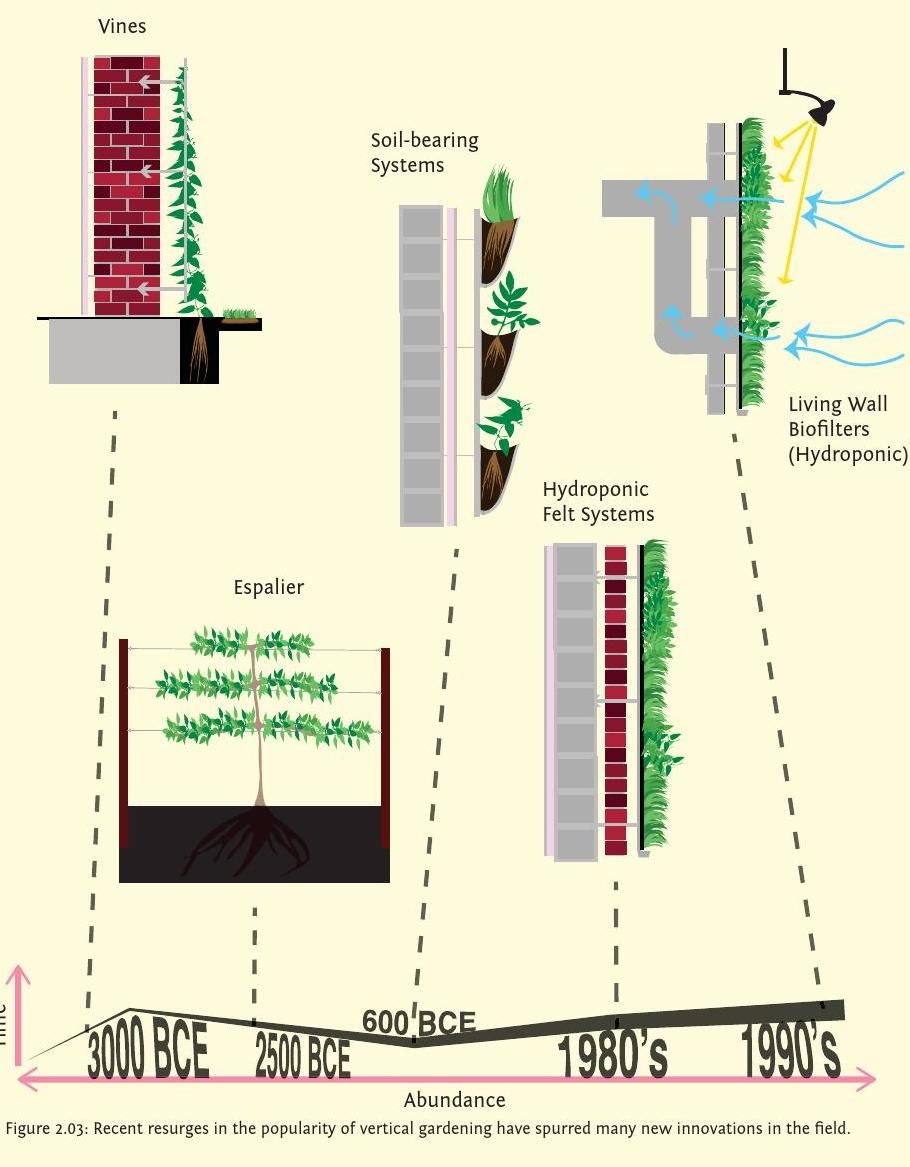
Case Studies or Examples
Successful vertical garden projects, such as the Bosco Verticale in Milan and the One Central Park in Sydney, serve as inspiring examples of the potential impact of vertical gardens. These projects have not only enhanced the visual appeal of the buildings but also improved air quality, reduced energy consumption, and provided habitat for local wildlife. However, challenges encountered during implementation highlight the need for careful planning and ongoing maintenance.
Current Trends or Developments
Vertical farming, the practice of growing crops in vertically stacked layers, is gaining traction as a solution to food production challenges in urban areas. Recent research and innovations have focused on optimizing vertical farming techniques to maximize yield and minimize resource usage. Additionally, sustainable architecture and urban planning are increasingly incorporating vertical gardens as a means to combat climate change and enhance the livability of cities.
Challenges or Controversies
Despite the numerous benefits, vertical garden technology still faces challenges and controversies. High installation and maintenance costs can limit widespread adoption, making it more accessible to affluent communities. Additionally, differing viewpoints exist regarding the environmental impact and effectiveness of vertical gardens, with some arguing that the resources required outweigh the benefits. Ongoing research and innovative solutions are crucial to overcoming these hurdles.

Future Outlook
The future of vertical garden technology holds significant promise. Advancements in technology and automation will further enhance the integration of vertical gardens into urban environments. Smart systems will optimize resource allocation, and advancements in materials and design will make vertical gardens more cost-effective and sustainable. By addressing urbanization and climate change, vertical gardens have the potential to shape the cities of tomorrow.
Conclusion
Vertical garden technology has come a long way, offering innovative solutions for urban environments. By enhancing sustainability, improving air quality, and providing aesthetic appeal, vertical gardens play a vital role in creating greener and more livable cities. Through further exploration and research, we can continue advancements in this field and make vertical gardens more accessible to communities worldwide.
References
Smith, J. (2019). Vertical Gardens: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Green Walls. New York: Skyhorse Publishing.
Wong, K. (2018). Vertical Gardens: Sustainable Living in the Urban Jungle. London: Thames & Hudson.
Velasco, A., & Galobart, X. (2020). Vertical Gardens: Landscape Design for the Urban Gardener. Barcelona: Monsa Publications.




