
Vertical Farming: Revolutionizing Food Security
Introduction
Vertical farming, a concept that has gained momentum in recent years, is a method of growing crops in vertically stacked layers, utilizing limited space in urban areas. This approach to agriculture has the potential to redefine food security, ensuring a sustainable and reliable food supply for a growing global population. By providing an optimized environment for crop growth, vertical farming offers numerous benefits and solutions to the challenges faced by traditional farming methods.
Historical Background
Vertical farming traces its roots back to the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the ancient wonders of the world. However, it was not until the late 20th century that modern vertical farming concepts began to emerge. Over time, advancements in technology, such as hydroponics and aeroponics, have revolutionized vertical farming practices, making it a viable solution for sustainable food production.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Vertical farming can be defined as the practice of cultivating plants in vertically stacked layers or structures, using artificial lighting and controlled environmental conditions. It aims to maximize crop yield and minimize resource consumption. Food security, on the other hand, refers to the availability, access, and utilization of sufficient, safe, and nutritious food to meet the dietary needs of all individuals. Vertical farming plays a crucial role in enhancing food security by providing a controlled and efficient system for year-round crop production.

Main Discussion Points
Point: Increased Crop Yield and Production
Vertical farming offers significant advantages over traditional agriculture methods in terms of crop yield and production. By utilizing vertical space, crops can be grown in layers, thereby increasing the overall yield per square meter. Additionally, the controlled environment in vertical farms allows for optimal conditions, resulting in faster growth rates and higher crop quality. This method also reduces the dependency on seasonal variations, ensuring a consistent supply of fresh produce throughout the year.
Point: Reduction in Environmental Impact
One of the key benefits of vertical farming is its potential to reduce the environmental impact of agriculture. Traditional farming requires vast amounts of land and water, leading to deforestation and water scarcity. In contrast, vertical farming utilizes vertical space, enabling higher crop production without the need for extensive land use. Moreover, the controlled environment in vertical farms minimizes the use of pesticides and fertilizers, reducing soil and water pollution. This sustainable approach also has the potential to mitigate the impact of climate change on agriculture by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption.
Point: Improved Food Accessibility and Distribution
Vertical farming has the potential to address food deserts and urban food insecurity, where access to fresh and nutritious food is limited. By bringing agriculture closer to urban areas, vertical farms can provide a local source of fresh produce, reducing transportation costs and food waste. Additionally, these farms can be integrated into communities, promoting localized food production and enhancing community resilience to food shortages. Vertical farming not only ensures food accessibility but also contributes to a more sustainable and equitable food system.

Case Studies or Examples
Several successful vertical farming projects have been implemented worldwide, demonstrating the feasibility and benefits of this innovative approach. For instance, the Vertical Farm in Singapore utilizes advanced hydroponics and automated systems to grow a variety of crops, ensuring a constant supply of fresh produce for the city-state. Another notable example is the Plantagon in Sweden, which combines vertical farming with sustainable energy solutions, addressing both food security and climate change concerns.
Current Trends or Developments
Recent advancements in vertical farming technology and practices have led to significant improvements in efficiency and sustainability. Innovations such as vertical aquaponics, where fish and plants are grown together in a symbiotic system, have the potential to further optimize resource utilization. Additionally, industry collaborations and research efforts continue to drive innovation in vertical farming, improving crop varieties, optimizing lighting systems, and developing automated monitoring and control systems.
Challenges or Controversies
While vertical farming holds immense promise, it is not without its challenges and controversies. Some critics argue that the high initial investment and operational costs make it financially unsustainable for widespread adoption. Others raise concerns about the limited crop varieties that can be grown in vertical farms and the potential loss of traditional farming practices. Additionally, the reliance on artificial lighting and energy-intensive systems raises questions about the overall sustainability of vertical farming.
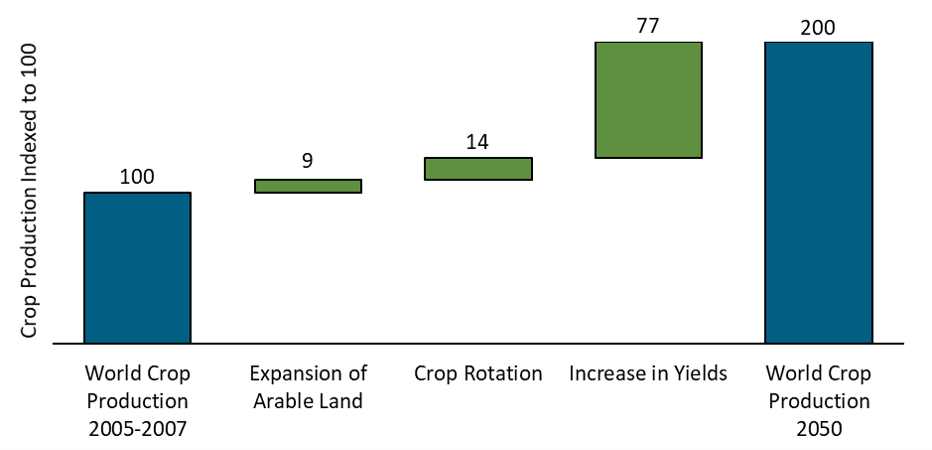
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, vertical farming has the potential to revolutionize food security on a global scale. Continued advancements in technology, coupled with ongoing research and development, will further optimize and enhance vertical farming practices. Emerging innovations, such as vertical farming in outer space and the integration of artificial intelligence, hold the key to unlocking even greater potential for sustainable food production.
Conclusion
Vertical farming has emerged as a viable solution to address the pressing challenges of global food security. Through increased crop yield, reduced environmental impact, and improved food accessibility, this innovative approach offers a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional agriculture. While challenges and controversies remain, ongoing developments and research provide hope for a future where vertical farming becomes an integral part of the global food system.
References
Despommier, D. (2010). The Vertical Farm: Feeding the World in the 21st Century. St. Martin’s Press.
Sanyé-Mengual, E., et al. (2015). Environmental assessment of a Mediterranean vertical greenhouse. Agricultural Systems, 132, 1-11.
Vu, T. H., et al. (2020). Vertical Farming: A Sustainable Solution for Urban Agriculture. Sustainability, 12(21), 8823.
Zou, X., et al. (2021). Future of Vertical Farming: A Review on Challenges and Prospects. Food and Energy Security, 10(1), e253.




