
Introduction
Biofuels have become essential in the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions, offering environmentally friendly and economically viable alternatives. This article delves into the realm of biofuels, providing a comprehensive exploration of their historical background, key concepts, and their role in achieving a sustainable future.
Historical Background
Biofuels have roots dating back to ancient civilizations, where biomass was utilized as a source of energy. However, the modern biofuel industry began to take shape in the 19th century with the invention of the internal combustion engine. Since then, significant milestones and developments have propelled biofuels into the limelight as a viable alternative to fossil fuels.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Biofuels encompass fuels derived from organic matter, including plants, crops, and waste materials. Their pivotal role in sustainable energy lies in their ability to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. It is important to distinguish between first-generation and second-generation biofuels. First-generation biofuels are typically derived from food crops like corn, sugarcane, or vegetable oils. In contrast, second-generation biofuels utilize non-food feedstocks, such as agricultural residues, energy crops, or algae. Additionally, the concept of carbon neutrality is vital in biofuel production, ensuring that the carbon emitted during the lifecycle of biofuels is balanced by the carbon absorbed during the growth of feedstocks.
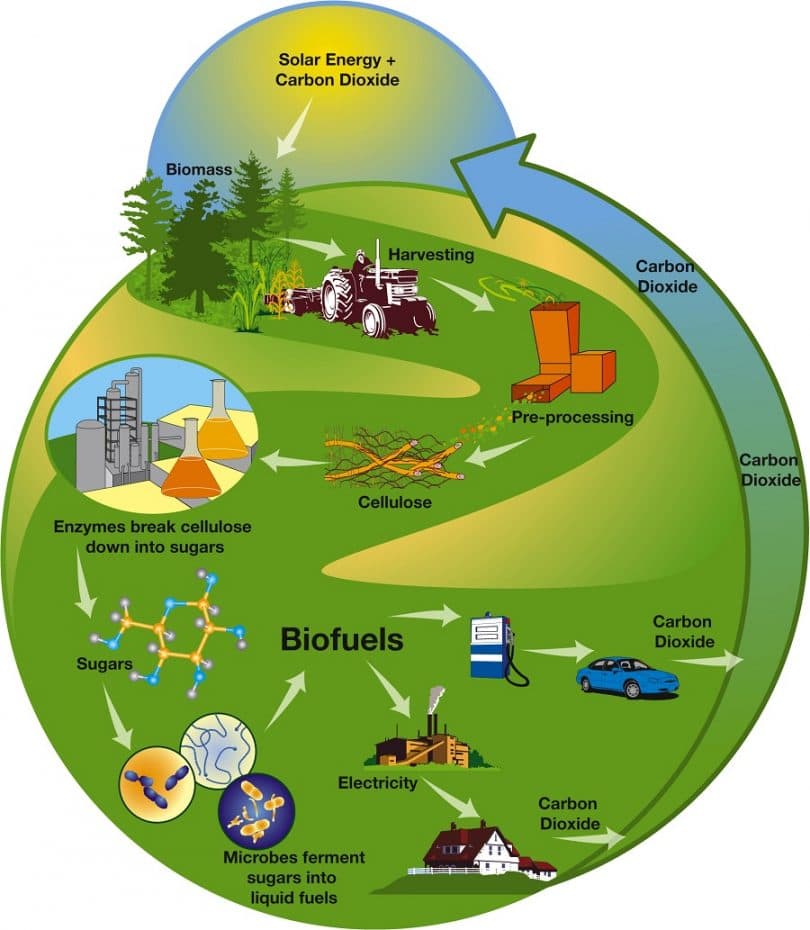
Main Discussion Points
Environmental Benefits of Biofuels
Biofuels offer significant environmental benefits by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By replacing fossil fuels, biofuels can help mitigate climate change and preserve natural resources and ecosystems.
Economic Implications of Biofuels
The biofuel industry has the potential to create employment opportunities, particularly in rural areas where agriculture is prominent. Moreover, reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels can enhance energy security and decrease vulnerability to fluctuating global oil prices. However, challenges such as initial investment costs and potential impacts on the existing energy sector need to be considered.
Energy Security and Independence
Biofuels play a crucial role in enhancing energy security by diversifying fuel sources. By utilizing locally available feedstocks, countries can reduce their dependence on foreign oil imports. Additionally, biofuels can help alleviate geopolitical tensions related to energy resources. However, concerns regarding the impact of biofuel production on food security must be addressed for a comprehensive approach to sustainable energy solutions.
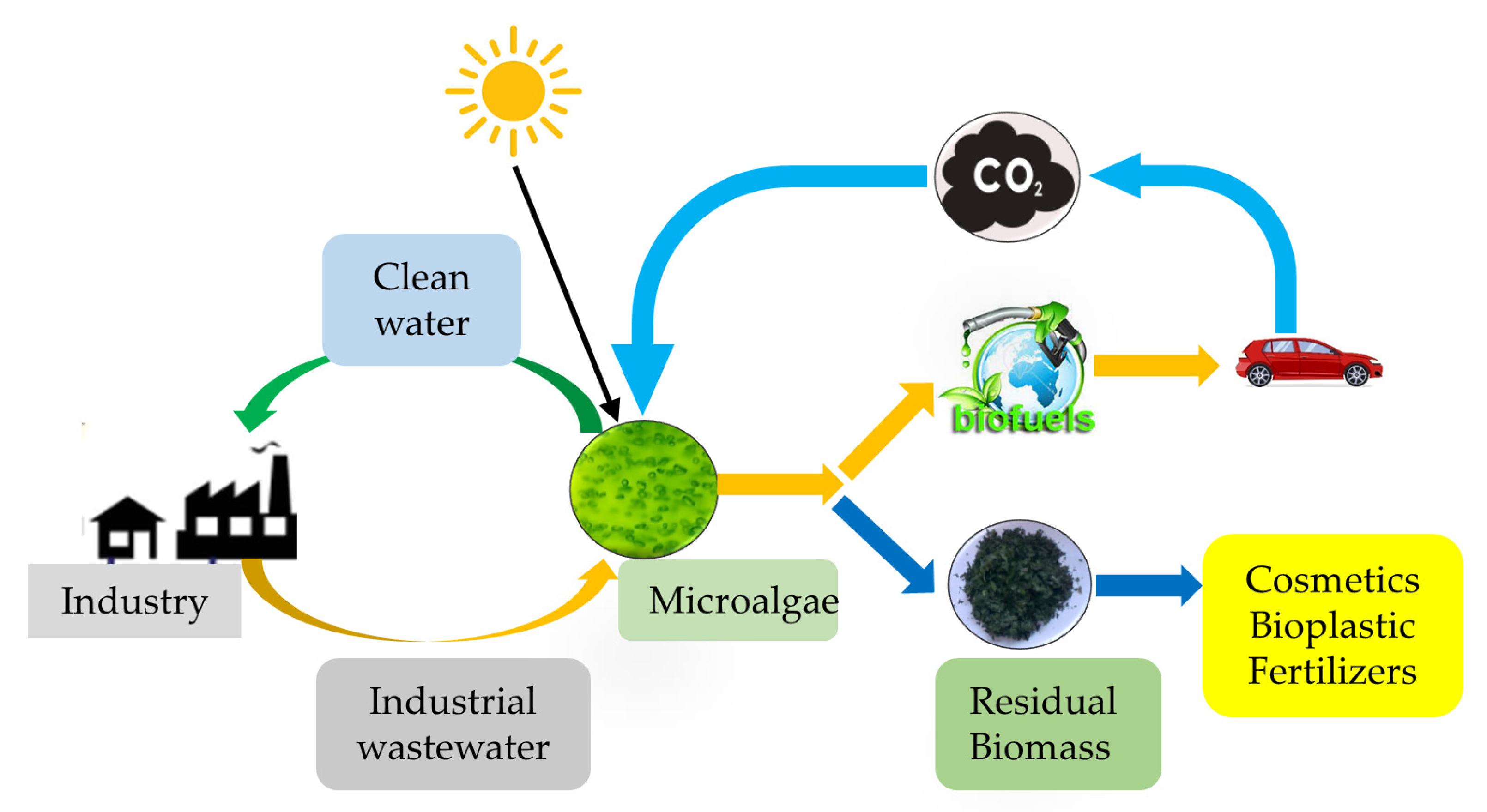
Case Studies or Examples
Successful biofuel initiatives from various regions provide compelling evidence of their benefits. For instance, Brazil has achieved significant progress in the production of ethanol from sugarcane, reducing dependence on imported gasoline and contributing to a more sustainable transportation sector. Similarly, the United States has seen success in producing biodiesel from soybeans, providing a renewable alternative to petroleum diesel.
Current Trends or Developments
Biofuel technology continues to advance, leading to more efficient and sustainable production methods. Recent breakthroughs include the use of genetically modified organisms to enhance the yield and quality of biofuel feedstocks. Additionally, researchers are exploring the potential of advanced biofuels, such as cellulosic ethanol, which can be produced from agricultural residues and dedicated energy crops.
Challenges or Controversies
The use of food crops for biofuel production has sparked controversy due to concerns over potential impacts on food prices and availability. Balancing biofuel production and food security remains a challenge. Furthermore, scalability and commercial viability of biofuel production methods pose significant hurdles that need to be addressed. Additionally, certain biofuel feedstocks, such as palm oil, raise environmental concerns due to deforestation and habitat destruction.
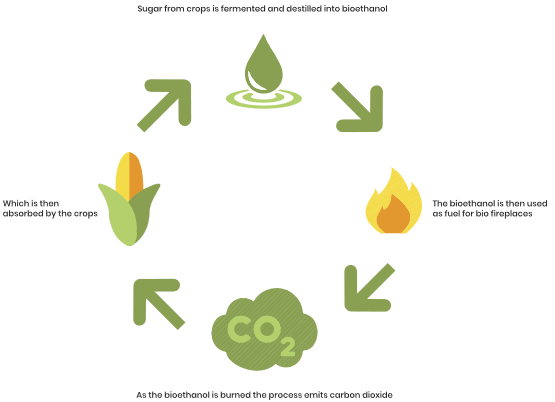
Future Outlook
Biofuels are poised to play a pivotal role in sustainable energy systems of the future. Advancements in technology and production methods will enhance their efficiency and reduce costs, making them a more viable and accessible option. However, anticipated challenges such as scaling up production and ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure need to be overcome to fully realize the potential of biofuels.
Conclusion
The adoption and promotion of biofuels are crucial in the journey towards a sustainable future. Their environmental benefits, economic implications, and potential for energy security make them essential components in the transition away from fossil fuels. By harnessing the power of biofuels, we can pave the way for a cleaner and more sustainable world.
References
Smith, R. D. (2019). Biofuels: Policies, Standards, and Technologies. Cambridge University Press.
Demirbas, A. (2020). Biofuels: Production, Applications, and Environmental Impact. CRC Press.
United Nations. (2021). Biofuels: A Regional Perspective. United Nations Publications.




