
Achieving Net-Zero Carbon Emissions in Smart Buildings: A Pathway to Sustainability
Introduction
As the world grapples with the urgent need to address climate change, achieving net-zero carbon emissions has emerged as a critical goal. Smart buildings, with their energy-efficient features and innovative technologies, play a pivotal role in this endeavor. This article explores the importance of achieving net-zero carbon emissions in smart buildings and their relevance to sustainability goals and environmental impact.
Historical Background
The evolution of smart buildings and their role in energy efficiency is crucial to understanding the current landscape. Past efforts and initiatives to reduce carbon emissions in buildings have paved the way for the development of advanced technologies and sustainable practices.
Key Concepts and Definitions
To comprehend the significance of net-zero carbon emissions in smart buildings, it is essential to delve into key concepts and definitions. This section provides a clear explanation of net-zero carbon emissions, as well as an overview of smart buildings and their features. Additionally, it outlines the roadmap to achieving net-zero carbon emissions, highlighting its various components.
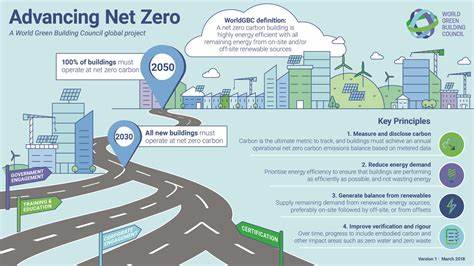
Main Discussion Points
Energy-efficient building design and construction
Energy-efficient building design and construction are fundamental to achieving net-zero carbon emissions. This section emphasizes the importance of sustainable building materials and practices, the integration of renewable energy sources, and the implementation of efficient HVAC systems and smart energy management.
Real-time monitoring and data analytics for energy optimization
Real-time monitoring and data analytics enable precise energy optimization in smart buildings. By utilizing sensors, IoT, and building automation systems, this section explores how data collection, analysis, and predictive modeling contribute to energy savings and the optimization of energy usage while ensuring occupant comfort.
Building retrofits and upgrades for energy efficiency
Building retrofits and upgrades offer significant potential for enhancing energy efficiency in existing structures. This section discusses the identification of areas for improvement through energy audits, the upgrading of insulation, windows, and lighting systems, and the retrofitting of existing buildings with smart technologies.
Case Studies or Examples
Examining real-life examples demonstrates the practical application and success of achieving net-zero carbon emissions in smart buildings. This section presents two case studies: a net-zero energy office building in Silicon Valley and the smart retrofit of a commercial building in New York City. It explores their designs, features, energy generation, consumption data, and the impact on carbon emissions.

Current Trends or Developments
Staying updated on current trends and developments is crucial for fostering progress in the field. This section explores the adoption of green building certifications and standards, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in smart buildings, and collaborative efforts and partnerships driving the advancement of net-zero goals.
Challenges or Controversies
While the benefits of achieving net-zero carbon emissions in smart buildings are evident, challenges and controversies persist. This section addresses the high upfront costs and return on investment considerations, data privacy and cybersecurity concerns, as well as resistance to change and lack of awareness among building owners.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the potential for scaling up net-zero carbon emissions in smart buildings is promising. This section discusses the role of government policies and regulations in driving adoption, the emergence of innovative technologies and solutions, and the overall trajectory towards a sustainable future.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the attainment of net-zero carbon emissions in smart buildings is integral to combating climate change and ensuring a sustainable future. This article emphasizes the significance of this achievement and summarizes the main points discussed throughout.
References
To further explore the topic, a comprehensive list of references is provided, including books, journals, research papers on sustainable building practices, websites of relevant organizations and industry associations, and reports and case studies from sustainability-focused initiatives.




