
The Growing Popularity and Importance of Vertical Gardens in Ecosystems
Introduction
Vertical gardens have witnessed a surge in popularity as an innovative approach to gardening and urban greening. These gardens, also known as green walls or living walls, are vertical structures that incorporate various plants and vegetation. This article explores the relevance and significance of vertical gardens in ecosystems, highlighting their role in biodiversity conservation, air quality improvement, and mitigating the urban heat island effect.
Historical Background
The concept of vertical gardens can be traced back to the legendary Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. However, it was not until the 20th century that the modern techniques and technologies for vertical gardens emerged. Significant milestones and developments have contributed to the increased use of vertical gardens in ecosystems.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Vertical gardens are intricate systems that involve various components, including support structures, irrigation systems, and plant selections. Understanding the concept of ecosystems is crucial in comprehending the relevance of vertical gardens. Ecosystems refer to the interconnected web of living organisms and their environment. Key terms such as biodiversity, ecological balance, and habitat restoration are vital in understanding the numerous benefits of vertical gardens in ecosystems.

Main Discussion Points
Point – The role of vertical gardens in biodiversity conservation
Vertical gardens provide vital habitats for a diverse range of plant and animal species. These gardens create opportunities for species to thrive in urban environments, offering shelter, food, and breeding grounds. By increasing plant diversity in urban areas, vertical gardens contribute to the preservation and conservation of biodiversity.
Point – The contribution of vertical gardens to air quality improvement
Vertical gardens act as natural air purifiers, absorbing harmful pollutants and releasing oxygen. Through the process of photosynthesis, plants in vertical gardens help reduce air pollution, enhancing overall air quality. Their ability to mitigate the negative impacts of pollution makes vertical gardens an essential tool in improving the health and well-being of urban dwellers.
Point – Vertical gardens as a solution for the urban heat island effect
Vertical gardens play a crucial role in mitigating the urban heat island effect, a phenomenon where cities experience significantly higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas. By cooling buildings and urban spaces through shading and evapotranspiration, vertical gardens help reduce energy consumption and create more comfortable living environments.
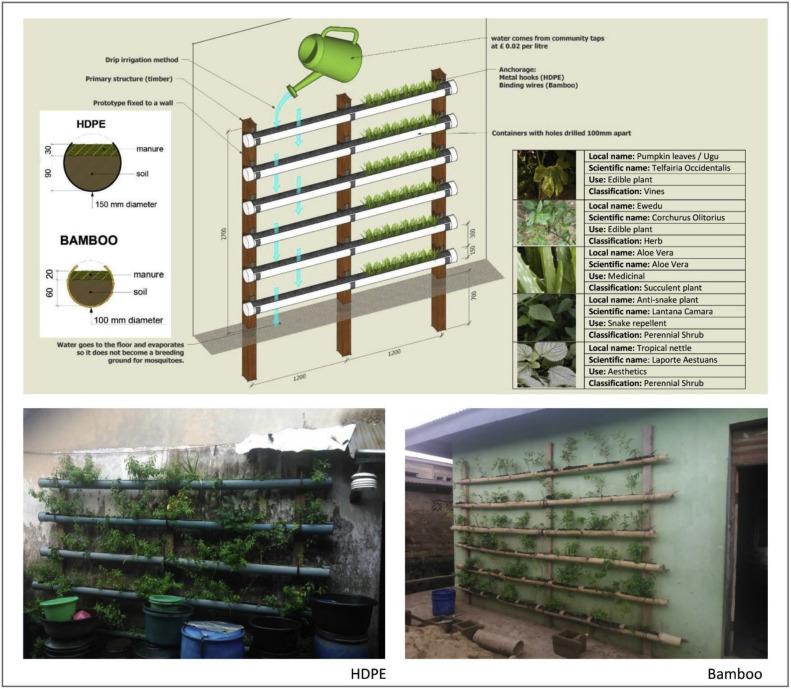
Case Studies or Examples
Successful vertical garden projects have been implemented in various ecosystems worldwide. Examples include the award-winning “Bosco Verticale” in Milan, Italy, and the “Gardens by the Bay” in Singapore. These case studies have demonstrated the ecological benefits of vertical gardens, such as improved air quality, increased biodiversity, and enhanced aesthetic appeal.
Current Trends or Developments
Recent research has highlighted the effectiveness of vertical gardens in ecosystem restoration. Innovative technologies and designs, such as modular systems and hydroponics, are being utilized in vertical garden installations, making them more accessible and efficient. The growing popularity of vertical gardens in urban planning and architecture reflects the increasing recognition of their multiple benefits.
Challenges or Controversies
Maintenance and sustainability are significant challenges associated with vertical gardens. Ensuring adequate irrigation, nutrient supply, and plant care can be demanding and require ongoing commitment. Additionally, differing viewpoints exist regarding the effectiveness of vertical gardens in conserving ecosystems, with some critics questioning their long-term ecological impact.

Future Outlook
The potential for the expansion and integration of vertical gardens in urban environments is promising. As cities strive to become more sustainable, vertical gardens offer a viable solution for greening vertical spaces. They can contribute to the creation of sustainable cities that prioritize ecosystem health, human well-being, and aesthetic appeal.
Conclusion
Vertical gardens have emerged as a valuable tool in enhancing ecosystems in urban areas. Their role in conserving biodiversity, improving air quality, and mitigating the urban heat island effect cannot be understated. Understanding the importance of vertical gardens in ecosystems is vital for creating sustainable and resilient cities that prioritize the well-being of both humans and the environment.
References
Blanc, P. (2008). The Vertical Garden: From Nature to the City. W. W. Norton & Company.
Bohn, K., et al. (2021). Vertical Greenery Systems and Urban Heat Islands: A Literature Review. Sustainability, 13(5), 2647.
Dunnett, N., & Kingsbury, N. (2018). Planting: A New Perspective. Timber Press.
Pyle, R. M. (1993). The Thunder Tree: Lessons from an Urban Wildland. Houghton Mifflin.
Wong, N. H., et al. (2018). A Review on Vertical Greenery Systems as a Passive Design Strategy for the Built Environment. Buildings, 8(1), 5.




