
The Resourceful Potential of Biosolids: A Sustainable Solution for Wastewater Management
Introduction
Biosolids, derived from wastewater treatment processes, have emerged as a crucial resource with immense potential. This article delves into the importance of utilizing biosolids as a sustainable solution for wastewater management, emphasizing their relevance in terms of sustainability and environmental impact.
Historical Background
Wastewater disposal was initially seen as a problem, but with growing environmental concerns, biosolids were recognized as a valuable resource. This marked a turning point in wastewater management practices. Regulations and guidelines were introduced to ensure proper management of biosolids, promoting responsible usage.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Understanding the key concepts and definitions associated with biosolids is crucial. Biosolids are the residual materials generated from the wastewater treatment process. They are characterized by their nutrient-rich composition and potential for various applications. Resource recovery plays a vital role in biosolids utilization, as it involves harnessing their benefits in a sustainable manner.
Main Discussion Points
Point: Types of Biosolids and Their Applications
There are two main types of biosolids: Class A and Class B. Class A biosolids undergo extensive treatment processes, resulting in a product that meets strict quality standards. They can be safely used in various applications, such as agriculture and landscaping. On the other hand, Class B biosolids undergo a less intensive treatment process and have certain limitations on their uses, primarily due to potential health risks.
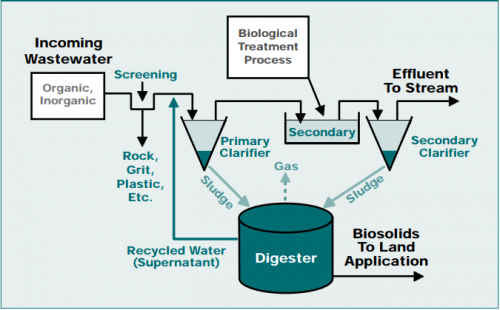
Point: Methods of Treating and Processing Biosolids for Safe Use
Two widely adopted methods for treating and processing biosolids are anaerobic digestion and composting. Anaerobic digestion involves the breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen, stabilizing biosolids and generating biogas for energy production. Composting utilizes natural biological processes to decompose biosolids, resulting in a nutrient-rich soil amendment.
Point: Benefits of Using Biosolids as a Resource
Utilizing biosolids as a resource offers numerous benefits. Firstly, they enrich the soil by providing essential nutrients, improving soil health, and promoting better crop yields. Additionally, biosolids can contribute to energy generation through anaerobic digestion, offering a renewable and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Finally, by using biosolids as a resource, the amount of waste requiring disposal in landfills is greatly reduced, minimizing the need for valuable landfill space.

Case Studies or Examples
City X serves as an excellent example of successful biosolids implementation. They have effectively utilized biosolids as a soil amendment, resulting in improved soil fertility and enhanced agricultural productivity. Furthermore, Company Y has pioneered the utilization of biosolids for energy generation, showcasing the immense potential for renewable energy production through anaerobic digestion.
Current Trends or Developments
Ongoing research focuses on evaluating the effectiveness and safety of biosolids application. Findings suggest that when managed properly, biosolids can be utilized without adverse effects on human health or the environment. Innovations in biosolids management technologies are continually being developed, allowing for more efficient and sustainable practices. Industries and municipalities are increasingly adopting biosolids utilization, recognizing the economic and environmental benefits it offers.
Challenges or Controversies
Despite the numerous benefits, biosolids face certain challenges and controversies. Public perception and opposition to biosolids use can hinder their widespread adoption. Addressing concerns about potential health and environmental risks is crucial in gaining public acceptance. Furthermore, ensuring compliance with regulations and managing potential risks associated with biosolids require careful attention.

Future Outlook
The future of biosolids utilization looks promising. There is growing recognition of their value across various sectors, including agriculture, energy, and construction. Integration of advanced technologies for sustainable biosolids management will further enhance their potential. Continued research and development will contribute to expanding their applications, making biosolids an integral part of sustainable wastewater management practices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, biosolids offer a resourceful solution for wastewater management. Their utilization addresses environmental concerns and provides economic and social benefits. It is crucial to recognize the significance of using biosolids as a resource from wastewater and to actively explore and adopt their utilization for a sustainable future.




