
The Ethical Dimensions of Genetic Modification in Vertical Farming
Introduction
Vertical farming and genetic modification are two rapidly growing fields with the potential to address global food security and sustainability challenges. This comprehensive article delves into the ethics of genetic modification in the context of vertical farming, exploring its benefits, concerns, regulatory framework, and future implications.
Historical Background
Vertical farming has its roots in the early 20th century, with experiments in multi-story greenhouse structures. Advancements in technology and agriculture practices led to the emergence of modern vertical farming systems. Simultaneously, genetic modification gained prominence in agriculture during the mid-20th century, driven by the need to enhance crop traits and increase yields.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Vertical farming involves cultivating crops in vertically stacked layers, often in controlled environments. Genetic modification refers to the deliberate alteration of an organism’s genetic material to introduce desired traits. The ethical considerations encompass potential risks, unintended consequences, and societal impacts.

Main Discussion Points
Point: Benefits and Advantages of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming offers numerous benefits, including increased crop yield, reduced water usage, and decreased reliance on pesticides. It has the potential to contribute to sustainable food production and address food security issues. Genetic modification enhances the efficiency and productivity of vertical farming by introducing traits like pest resistance and improved nutritional content.
Point: Ethical Concerns and Risks of Genetic Modification
The ethical concerns surrounding genetic modification include potential unintended consequences, loss of biodiversity, and impacts on natural ecosystems. Additionally, risks and uncertainties associated with genetically modified crops, such as allergenicity and gene flow, need careful evaluation. Patenting genetically modified crops raises ethical implications regarding corporate control over food production.
Point: Regulatory Framework and Public Perception
The regulatory framework for genetic modification varies across countries, with government agencies and international agreements ensuring safety and proper oversight. Public perception and attitudes towards genetic modification and vertical farming are diverse and shaped by transparency, public engagement, and informed consent processes.

Case Studies or Examples
Real-world examples of vertical farming projects utilizing genetic modification showcase the outcomes and impacts of these initiatives. These case studies shed light on the ethical considerations and controversies surrounding the integration of genetic modification into vertical farming systems.
Current Trends or Developments
Advancements in technology, new crop varieties, and innovative farming methods drive recent trends in vertical farming. Ongoing research in genetic modification reveals new breakthroughs with implications for vertical farming and its ethical dimensions.
Challenges or Controversies
The vertical farming industry and the genetic modification community face challenges and controversies, including debates regarding the ethics of genetic modification in the context of vertical farming. Conflicts arise between traditional farming practices, organic farming, and the adoption of genetically modified crops in vertical farming systems.
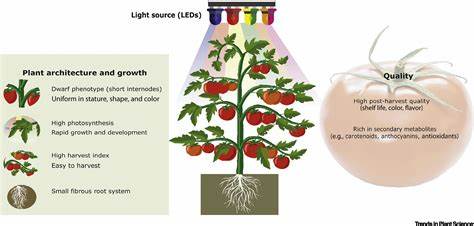
Future Outlook
Advancements in technology and genetic engineering techniques hold promise for shaping the future of vertical farming. However, the societal impacts and ethical dilemmas that may arise require careful consideration and ongoing dialogue.
Conclusion
The ethics of genetic modification in vertical farming are crucial in facing global food security and sustainability challenges. This in-depth article has explored the benefits, concerns, regulatory framework, and future implications of genetic modification in vertical farming. Emphasizing the need for further research, discussion, and dialogue, it highlights the importance of addressing the ethical dimensions of this critical topic.




