
Vertical Farming: Revolutionizing Sustainable Farm-to-Table Practices
Introduction
Vertical Farming is an innovative agricultural practice that has gained significant attention in recent years. It involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers, utilizing limited space and resources while maximizing yields. This article explores the concept of Vertical Farming and its relevance in promoting sustainable farm-to-table practices. It highlights the importance of Vertical Farming in addressing food security, urbanization, and environmental sustainability.
Historical Background
The origins of Vertical Farming can be traced back to the early 20th century when researchers and visionaries began exploring alternative methods of food production. However, it wasn’t until the 21st century that Vertical Farming gained traction as a viable solution to the challenges posed by traditional agriculture. The rising global population, limited arable land, and the need for more sustainable farming practices all played a role in the emergence of Vertical Farming.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Vertical Farming involves cultivating crops in vertically stacked layers, typically in urban environments. It utilizes advanced technologies such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and artificial lighting to create optimal growing conditions. Sustainable farm-to-table refers to a holistic approach that emphasizes local, organic, and environmentally friendly food production. It aims to reduce the carbon footprint associated with transportation and promote healthier and more sustainable food choices.

Main Discussion Points
Benefits of Vertical Farming
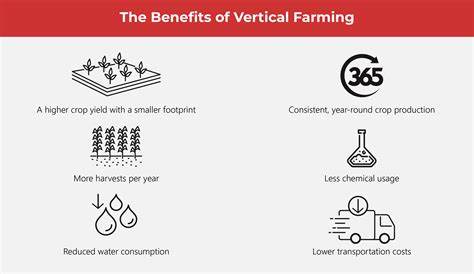
Vertical Farming offers numerous benefits that contribute to sustainable farm-to-table practices. Firstly, it allows for increased food production by utilizing vertical space, enabling farmers to grow more crops in a smaller area. Secondly, Vertical Farming reduces land and water usage as it requires less land and utilizes water more efficiently through recirculation systems. Additionally, vertical farms enable year-round cultivation, overcoming the limitations of traditional farming seasons. Lastly, Vertical Farming minimizes the use of pesticides, creating a healthier and more environmentally friendly approach to food production.
Technological Advancements in Vertical Farming
Technological advancements play a crucial role in facilitating Vertical Farming. Advanced lighting systems, such as LED lights, provide the necessary spectrum for optimal plant growth while minimizing energy consumption. Hydroponics, a soil-less cultivation method, allows for precise nutrient delivery to plants. Automation and AI integration enable efficient resource management, optimizing crop yields. Data analytics further enhance productivity by providing insights into crop health, resource allocation, and environmental conditions.
Integration of Vertical Farming into Sustainable Farm-to-Table Practices
Vertical Farming complements other sustainable practices, such as organic farming, permaculture, and agroforestry. By supplying local restaurants, farmers’ markets, and community-supported agriculture programs, vertical farms reduce the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation. This integration strengthens local food systems, promotes healthier eating habits, and supports local economies.
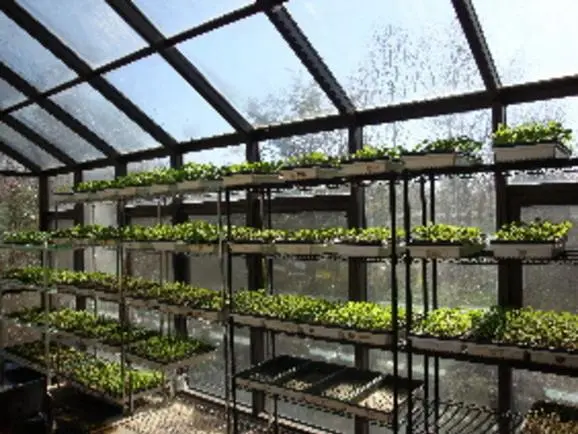

Case Studies or Examples
Several successful Vertical Farms have made a significant impact on local communities and food systems. AeroFarms, based in Newark, New Jersey, is one such example. It utilizes vertical hydroponics and LED lighting to grow leafy greens, herbs, and microgreens. AeroFarms’ vertical farm has reduced water usage by up to 95% and eliminated the need for pesticides. Another notable project is Gotham Greens, which operates rooftop greenhouses in several cities, supplying fresh produce to local markets and restaurants.
Current Trends or Developments
Vertical Farming technology continues to evolve, with new trends and developments emerging. Vertical hydroponics systems, which use stacked trays or columns, are gaining popularity due to their scalability and efficient use of space. Aeroponics, a system that delivers nutrients through misting, is also becoming more widespread. Additionally, the use of LED lights in Vertical Farming is increasing due to their energy efficiency and ability to provide specific light spectrums for different crops.
Challenges or Controversies
Vertical Farming faces certain challenges and controversies that need to be addressed. High upfront costs, including infrastructure and equipment, can be a barrier to entry for many farmers. Energy consumption is another concern, as indoor farming requires significant electricity for lighting, ventilation, and climate control. Additionally, limited crop diversity is a potential drawback of Vertical Farming, as some crops may not thrive in controlled environments.
Future Outlook
The future of Vertical Farming holds immense potential. As technology continues to advance and costs decrease, vertical farms have the potential to revolutionize food production. They could reshape urban landscapes, utilizing vacant buildings and rooftops to create sustainable farming hubs. Ongoing research and development will further enhance scalability, efficiency, and the global adoption of Vertical Farming.
Conclusion
Vertical Farming offers a sustainable solution to the challenges of traditional agriculture. By maximizing yields in limited space, reducing resource usage, and promoting local food production, it contributes to the evolution of sustainable farm-to-table practices. Vertical Farming has the potential to revolutionize food production, improve food security, and create a more sustainable future.
References
Despommier, D. (2010). The vertical farm: feeding the world in the 21st century. Picador.
Specht, K., Siebert, R., Hartmann, I., Freisinger, U. B., Sawicka, M., Werner, A., … & Thomaier, S. (2014). Urban agriculture of the future: an overview of sustainability aspects of food production in and on buildings. Agriculture and Human Values, 31(1), 33-51.
Mok, H. F., Williamson, V. G., Grove, J. R., & Burry, K. (2019). Multifunctional urban agriculture for sustainable land use planning in the United States. Sustainability, 11(5), 1446.




