
The Future of Farming: Exploring the Potential of Vertical Farms
Introduction
Vertical Farms have emerged as a promising solution for sustainable urban planning. With the increasing need for food security, environmental sustainability, and urban development, Vertical Farms offer a unique approach to growing food in urban areas. This article will explore the concept of Vertical Farms and their relevance in sustainable urban planning.
Historical Background
The concept of Vertical Farms has a rich history, with pioneering projects and notable milestones. Over the years, the evolution of sustainable urban planning has been closely linked to the emergence of Vertical Farms. These innovative farming systems have revolutionized the way we think about food production in urban areas.
Key Concepts and Definitions
To understand Vertical Farms, it is important to define and explain their design, structure, and operation. These farms utilize vertical space to grow crops, often utilizing techniques such as hydroponics or aeroponics. Additionally, key terms and concepts related to sustainable urban planning, including urban agriculture, food deserts, and green infrastructure, play a crucial role in the understanding of Vertical Farms.
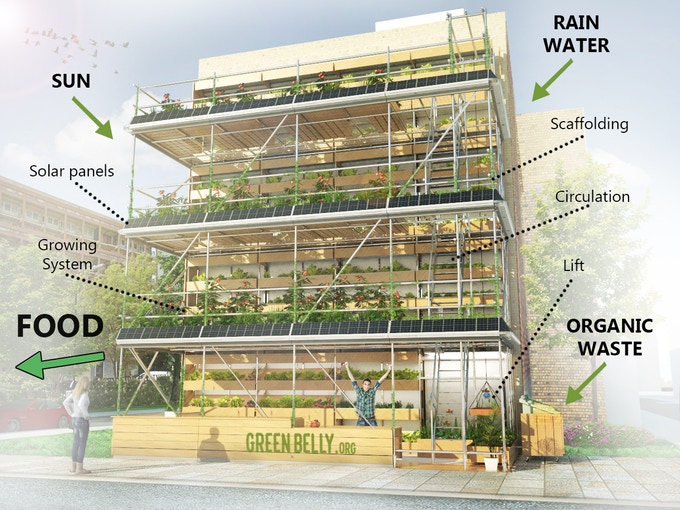
Main Discussion Points
Environmental Benefits of Vertical Farms
Vertical Farms have the potential to significantly reduce the ecological footprint of food production. By growing crops in controlled environments, Vertical Farms can conserve resources, reduce pollution, and mitigate climate change. The use of advanced technologies ensures optimal use of water and energy, making Vertical Farms an environmentally-friendly solution.
Social and Economic Impacts of Vertical Farms
Vertical Farms offer a promising solution for addressing food insecurity and improving access to fresh produce in urban areas. These farms can be established in food deserts, providing communities with nutritious and locally grown food. Additionally, Vertical Farms create economic opportunities and job creation, contributing to the socio-economic development of urban areas.
Integration of Vertical Farms in Urban Planning
Vertical Farms can be seamlessly integrated into urban planning strategies. By incorporating these farms into mixed-use developments and public spaces, cities can create sustainable and self-sufficient communities. Vertical Farms not only provide a source of fresh food but also serve as educational and recreational spaces for residents.

Case Studies or Examples
Real-world examples of successful Vertical Farms highlight their impact on urban planning. These case studies demonstrate the scalability and replicability of Vertical Farms in different urban contexts. From vertical gardens on skyscrapers to multi-story indoor farms, these projects showcase the potential of Vertical Farms as a viable solution for sustainable urban development.
Current Trends or Developments
Vertical Farm technology is constantly evolving, with new trends and advancements. Hydroponics, aeroponics, and vertical stacking systems are some of the recent developments in Vertical Farming. These technologies ensure efficient use of resources and maximize crop yields. Moreover, there is a growing interest and investment in Vertical Farms from governments, private sectors, and community organizations, further driving the development of this innovative farming solution.
Challenges or Controversies
While Vertical Farms offer numerous benefits, they also face challenges and controversies. High initial costs and energy consumption are some of the potential challenges associated with Vertical Farms. Critics also raise concerns about the impact of Vertical Farms on traditional agriculture and land use. Addressing these challenges and controversies is crucial for the successful integration of Vertical Farms in sustainable urban planning.

Future Outlook
Looking ahead, Vertical Farms have a promising future in sustainable urban planning. Advancements in technology and policy can accelerate the adoption of Vertical Farms, leading to transformative change in urban agriculture. The potential for Vertical Farms to revolutionize food production and create sustainable urban environments is immense.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Vertical Farms have emerged as a catalyst for sustainable urban planning. Their potential to address food security, environmental sustainability, and urban development is significant. By integrating Vertical Farms into urban planning strategies, cities can create self-sufficient and resilient communities. The future of farming lies in Vertical Farms, and their transformative potential cannot be overlooked.
References
For further reading and research on Vertical Farms and sustainable urban planning, the following sources are recommended:
Despommier, D. (2010). The Vertical Farm: Feeding the World in the 21st Century.
Specht, K., et al. (2014). Urban Agriculture of the Future: An Overview of Sustainability Aspects of Food Production in and on Buildings.
Sanyé-Mengual, E., et al. (2015). Rooftop Vertical Farming as a Potential Strategy to Increase Urban Food Security.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. (2017). Urban Agriculture for Sustainable Cities – Using Wasted Space to Feed Cities.




