Hybrid Cars: Exploring the Future of Automotive Technology
Introduction
Hybrid cars have gained popularity among environmentally conscious individuals who aim to reduce their carbon footprint without sacrificing performance. In this article, we will delve into the world of hybrid cars, exploring their historical background, key concepts, main discussion points, case studies, current trends, challenges, and future outlook. By the end of this comprehensive guide, readers will have a deep understanding of hybrid car technology and its potential to shape the future of the automotive industry.
Historical Background
Hybrid cars have a history dating back to the early 20th century, with notable advancements made by inventors such as Ferdinand Porsche and Thomas Edison. However, it was not until the late 1990s that hybrid cars gained mainstream attention, largely due to Toyota’s pioneering efforts with their iconic Prius model. Since then, hybrid car technology has continued to evolve, with major milestones including advancements in battery technology, increased efficiency, and the introduction of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs).
Key Concepts and Definitions
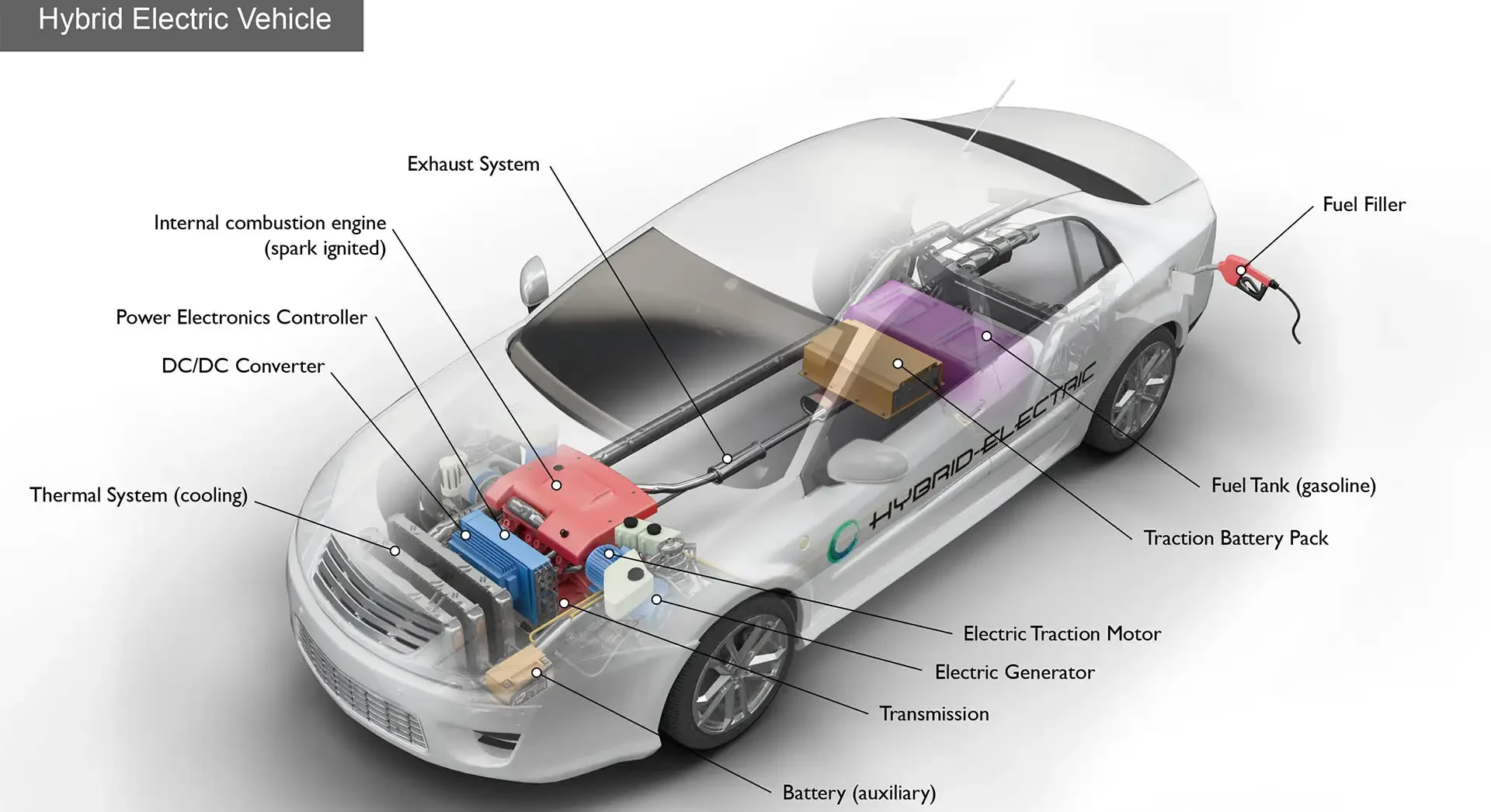
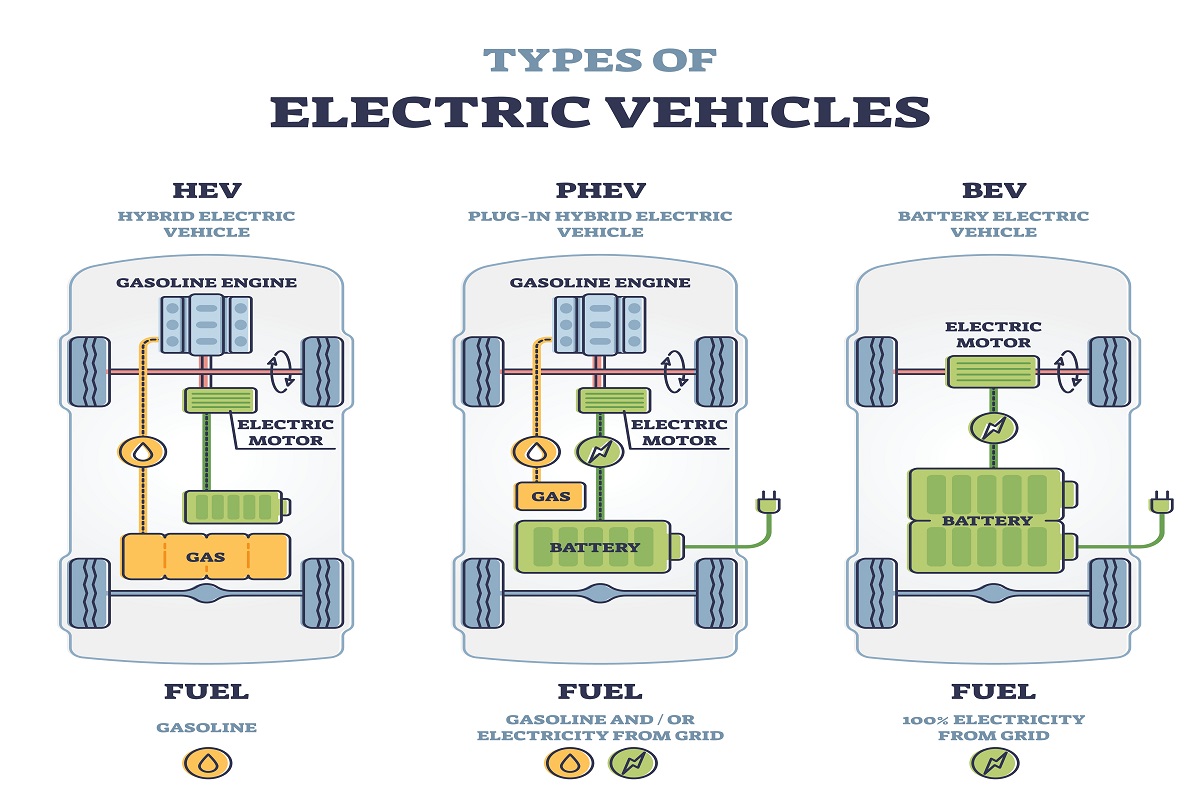
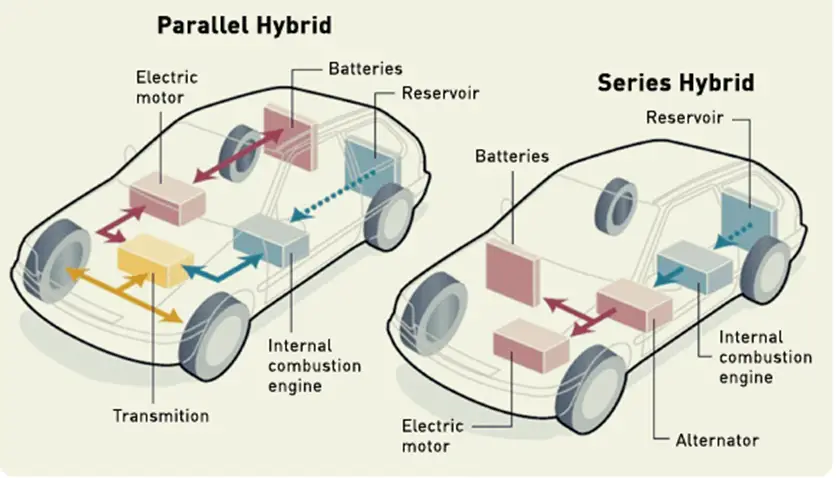
To fully grasp the intricacies of hybrid car technology, it is important to understand key concepts and definitions. A hybrid propulsion system combines an internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electric motor to power the vehicle. There are two main types of hybrid systems: series hybrid and parallel hybrid. In a series hybrid, the ICE acts as a generator, charging the batteries that power the electric motor. In a parallel hybrid, both the engine and electric motor work together to propel the vehicle. Additionally, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) allow for extended electric range by utilizing external charging stations.
Main Discussion Points
Different types of hybrid cars
Hybrid cars can be classified into three main types: series hybrid cars, parallel hybrid cars, and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). Series hybrid cars use the ICE solely to charge the batteries, which in turn power the electric motor. On the other hand, parallel hybrid cars combine the power of the engine and electric motor to drive the vehicle. PHEVs offer the flexibility of using both the engine and electric motor, with the added advantage of being able to charge the batteries externally.
Hybrid car technologies
Hybrid car technologies play a crucial role in improving efficiency and reducing emissions. Regenerative braking systems capture and convert kinetic energy into electrical energy during deceleration, which is then stored in the batteries for later use. Start-stop systems automatically shut off the engine when the vehicle is at a standstill, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Engine downsizing and turbocharging involve using smaller, more efficient engines with turbochargers to provide adequate power while maximizing fuel efficiency.
Emerging hybrid technologies
As hybrid car technology continues to evolve, new advancements are being made to further enhance efficiency and performance. Self-charging hybrid systems utilize regenerative braking and other methods to charge the batteries without the need for external charging. Fuel cell hybrid vehicles combine fuel cell technology with hybrid systems, using hydrogen gas to generate electricity and power the electric motor. While these technologies show promise, they also present certain limitations and challenges that need to be addressed.
Case Studies or Examples
To provide a practical understanding of hybrid car technology, let’s examine three notable examples: the Toyota Prius, Chevrolet Volt, and Tesla Model 3. The Toyota Prius is widely recognized as the pioneering hybrid car that introduced the concept of mass-market hybrid vehicles. The Chevrolet Volt is a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle that offers extended electric range and the convenience of an internal combustion engine. The Tesla Model 3 represents the electrification of hybrid technology, with its all-electric powertrain and cutting-edge features.
Current Trends or Developments
Hybrid cars have seen a significant increase in popularity and market share in recent years, driven by growing awareness of environmental issues and the desire for more sustainable transportation options. Advancements in battery technology have led to improved efficiency and longer electric ranges for hybrid vehicles. Additionally, government incentives and regulations promoting hybrid car adoption have further accelerated the growth of this segment.
Challenges or Controversies
While hybrid cars offer numerous benefits, there are also challenges and controversies associated with their adoption. The environmental impact of battery production and disposal raises concerns about the overall sustainability of hybrid vehicles. Cost considerations and the affordability of hybrid cars remain a barrier for many potential buyers. Moreover, range anxiety and the availability of charging infrastructure pose challenges for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs).
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the future of hybrid cars is promising. With the global shift towards cleaner transportation, fully electric vehicles are expected to become more prevalent. Additionally, the integration of autonomous driving technology in hybrid cars holds the potential to revolutionize the way we commute. Continued advancements in hybrid car technology and efficiency will further enhance their appeal and make them a viable option for a wider audience.
Conclusion
Hybrid cars represent an important step towards a more sustainable future for the automotive industry. Through our exploration of hybrid car technology, we have gained insights into its historical background, key concepts, main discussion points, case studies, current trends, challenges, and future outlook. As we continue to strive for greener and more efficient transportation solutions, it is crucial to explore and embrace different types of hybrid cars to pave the way towards a greener future.




