
Financing and Investment in Vertical Farms: Unlocking the Potential of Sustainable Food Production
Introduction
Vertical farming is a revolutionary concept gaining popularity worldwide. This innovative approach to agriculture involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers, utilizing limited space and resources. As the demand for sustainable and locally sourced food increases, financing and investment in vertical farms play a crucial role in driving this industry forward. In this article, we will explore the historical background, key concepts, financing options, factors affecting investment, risk management strategies, case studies, current trends, challenges, future outlook, and the significance of financing and investment in vertical farms for sustainable food production.
Historical Background
Vertical farming has come a long way since its inception. The concept originated from the idea of growing plants indoors using artificial light sources. Over time, advancements in technology and agricultural techniques have allowed this concept to evolve into a viable solution for sustainable food production. The increasing concerns about climate change, limited arable land, and the need for resilient food systems have further spurred the development and adoption of vertical farming.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Vertical farming involves the cultivation of crops in vertically arranged layers, often within controlled environments. Different models of vertical farming include hydroponics, which uses nutrient-rich water solutions, aeroponics, which uses a mist to deliver nutrients, and aquaponics, which combines fish farming with plant cultivation.

Main Discussion Points
Financing Options for Vertical Farms
Traditional financing options for vertical farms include bank loans and grants. These options provide stability and funding for initial setup costs. However, alternative financing options such as crowdfunding and impact investing have gained traction. Crowdfunding allows individuals to contribute small amounts of money towards a project, while impact investing focuses on funding projects with social and environmental benefits.
Factors Affecting Investment in Vertical Farms
Several factors influence investment decisions in vertical farming. Market demand is a critical consideration, as vertical farms must meet the growing demand for locally sourced, pesticide-free, and fresh produce. Scalability and profitability are also crucial factors that potential investors assess. Additionally, sustainability is a key consideration, as investors seek to support environmentally conscious practices. Technology, automation, and operational efficiency play a pivotal role in attracting investment, as these factors contribute to higher yields and lower costs.
Risk Management in Vertical Farm Investments
Vertical farming investments come with inherent risks. These risks include market volatility, climate-related challenges, and operational risks. To mitigate these risks, diversification is essential. Investing in a variety of crops and vertical farm models helps spread the risk. Insurance is another risk management strategy, providing protection against unforeseen events such as crop failure or natural disasters. Feasibility studies and thorough due diligence are vital in making informed investment decisions, as they help assess the viability and potential returns of a vertical farming project.
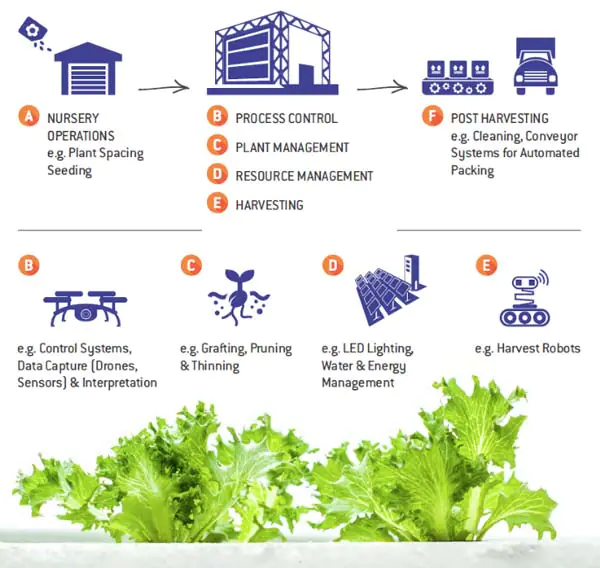
Case Studies or Examples
Real-world examples of successful financing and investment in vertical farms provide insights into the factors contributing to their success. These cases highlight the importance of strategic partnerships, innovative marketing approaches, and leveraging technology to optimize operations. Unique challenges, such as securing financing for large-scale vertical farms or navigating complex regulatory frameworks, are also explored.
Current Trends or Developments
The financing and investment landscape for vertical farms is constantly evolving. Technological advancements, such as improved LED lighting systems and automation, are driving efficiency and reducing costs. Regulatory changes, such as incentives and supportive policies, are further encouraging investment in the sector. Market demand for locally sourced and sustainable food continues to grow, presenting opportunities for investors to capitalize on this trend. Recent research findings and innovations, such as the integration of renewable energy sources and vertical farming, further contribute to the development of this industry.
Challenges or Controversies
Financing and investment in vertical farms face common challenges. Scalability and profitability remain topics of debate, as some argue that vertical farms may struggle to compete with traditional agricultural models. However, advancements in technology and operational practices are addressing these concerns. Potential solutions to overcome challenges include collaborative partnerships, knowledge sharing platforms, and continuous research and development.

Future Outlook
The future of financing and investment in vertical farms is promising. Advancements in technology will continue to optimize resource use, increase yields, and reduce costs. Market growth and consumer demand for sustainable food will create opportunities for profitable investments. Supportive policies and government initiatives can further accelerate the industry’s development. However, potential disruptions, such as the emergence of new agricultural technologies or changes in consumer preferences, should also be monitored closely.
Conclusion
Financing and investment play a vital role in unlocking the potential of vertical farms for sustainable food production. Through understanding the historical background, key concepts, financing options, factors affecting investment, risk management strategies, case studies, current trends, challenges, and the future outlook, stakeholders can make informed decisions to contribute to the growth and success of the vertical farming industry. Continued research and exploration of financing and investment in vertical farms are essential to address global challenges in food production and ensure a sustainable future.




