Introduction
The topic of comparing environmental impact to fossil fuels is of utmost importance in today’s world. As the effects of climate change become more apparent, it is crucial to understand how different energy sources contribute to environmental degradation. This article aims to delve into the various aspects of environmental impact assessment in relation to fossil fuels, highlighting its relevance and importance in shaping a sustainable future. Furthermore, it will shed light on who may be impacted by these findings, including policymakers, industries, and individuals alike.
Historical Background
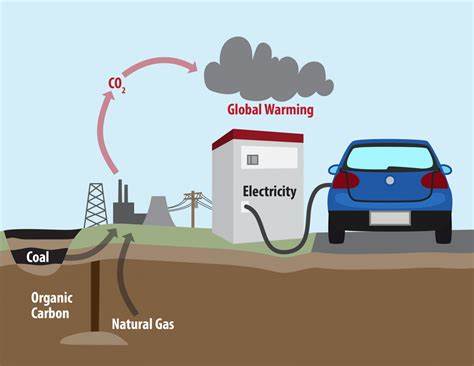
Fossil fuel usage has a long-standing history, dating back to the Industrial Revolution. Since then, the impact of burning fossil fuels on the environment has become increasingly evident. The combustion of coal, oil, and natural gas releases significant amounts of greenhouse gases, which contribute to global warming and climate change. Over the years, milestones such as the discovery of the ozone hole and the signing of international agreements like the Kyoto Protocol have brought environmental impact assessment to the forefront of discussions surrounding fossil fuels.
Key Concepts and Definitions
In order to understand and compare the environmental impact of fossil fuels, it is necessary to define key terms and concepts. Environmental impact assessment involves evaluating the effects of human activities on the environment. Methodologies and criteria used for such assessments vary, but generally include analyzing greenhouse gas emissions, air and water pollution, land degradation, habitat loss, water consumption, and contamination. Fossil fuels can exhibit different types of environmental impacts, depending on their composition and extraction methods.
Main Discussion Points
Analyzing greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels
Fossil fuels are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, mainly carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. The burning of coal, oil, and natural gas releases these gases into the atmosphere, trapping heat and leading to global warming. Comparing the environmental impact of different fossil fuels reveals variations in their greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, coal emits more carbon dioxide per unit of energy produced compared to natural gas.

Evaluating air and water pollution from fossil fuel extraction and combustion
Fossil fuel extraction and combustion processes release pollutants into the air and water. These pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, contribute to air pollution and can have detrimental effects on human health and the environment. Different extraction methods, such as fracking and mountaintop removal, also exhibit varying levels of environmental impact. It is crucial to assess and compare these impacts to make informed decisions about energy sources.
Assessing land degradation and habitat loss due to fossil fuel activities
Fossil fuel activities can lead to land degradation and the loss of natural habitats. The extraction of fossil fuels often requires clearing large areas of land, disrupting ecosystems and displacing wildlife. This encroachment can result in the loss of biodiversity and the destruction of delicate ecosystems. Comparisons between different fossil fuel activities can provide insights into which methods have a lower impact on land and habitat preservation.
Examining the water consumption and contamination associated with fossil fuel operations
Fossil fuel extraction and processing require significant amounts of water, often leading to water scarcity in areas with high energy production. Moreover, accidents such as spills and leaks can contaminate water sources, posing risks to both human and environmental health. Understanding the water requirements, usage, and potential for contamination from different fossil fuel operations is crucial for sustainable water management.
Case Studies or Examples
Real-world examples and case studies are powerful tools for demonstrating the environmental impact of fossil fuels. These studies provide tangible evidence of the consequences associated with fossil fuel usage. They may include analyses of specific regions affected by air pollution, water contamination, or habitat destruction. The findings and implications of these studies serve as a foundation for further research and action.
Current Trends or Developments
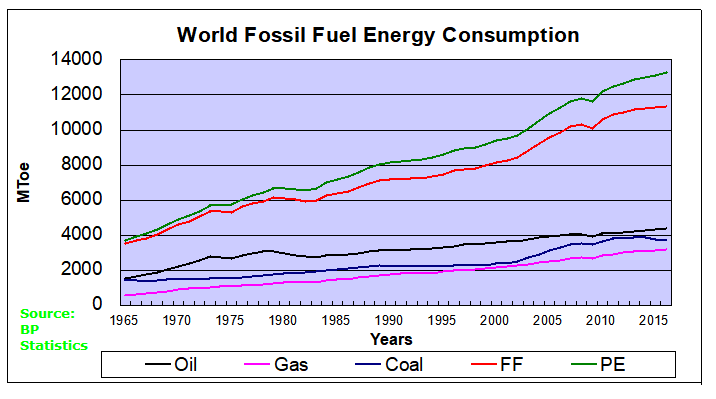
Environmental impact assessment of fossil fuels is a dynamic field with ongoing trends and developments. Recent advancements include the integration of new technologies and innovations aimed at reducing the environmental impact of fossil fuels. For example, the development of carbon capture and storage technologies is gaining momentum as a means to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, recent research findings continuously contribute to our understanding of the environmental implications of fossil fuels.
Challenges or Controversies
Comparing environmental impacts across different energy sources presents several challenges. Evaluating impacts can be complex due to the wide range of methodologies, criteria, and variables involved. Additionally, controversies may arise regarding the significance of environmental impact assessment itself. Differing viewpoints and vested interests can influence the perception of the environmental consequences of fossil fuels.

Future Outlook
Looking ahead, comparing environmental impact to fossil fuels will continue to shape energy policies and advancements. The transition to renewable energy sources and the adoption of sustainable practices are crucial for mitigating the environmental impact. Policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting cleaner extraction methods, and conserving natural habitats will play a vital role in shaping a sustainable future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, comparing environmental impact to fossil fuels is essential for understanding the consequences associated with different energy sources. By analyzing greenhouse gas emissions, air and water pollution, land degradation, and water consumption, we can make informed decisions about energy production and consumption. The significance of this assessment lies in shaping a sustainable future that prioritizes environmental preservation.




