
Eco Vehicles and the Circular Economy
Introduction
In this article, we will explore the significance and potential of eco vehicles and the circular economy in creating a sustainable ecosystem. We will provide a comprehensive overview, discussing its background, key concepts, discussion points, case studies, current trends, challenges, controversies, future outlook, and references.
Historical Background
The concept of eco vehicles emerged in response to environmental concerns associated with traditional transportation. Simultaneously, the circular economy gained traction as a solution to resource depletion and waste generation. These two concepts have intersected, giving rise to the notion of eco vehicles within the circular economy framework. Throughout history, various events and milestones have shaped the development of eco vehicles and the circular economy.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Eco vehicles refer to vehicles designed to minimize their environmental impact, often through alternative fuels or energy sources. The circular economy is an economic system aiming to eliminate waste and promote resource use through recycling, reuse, and regeneration. Within the context of sustainable ecosystems, we will introduce and explore key terms and concepts related to these principles.
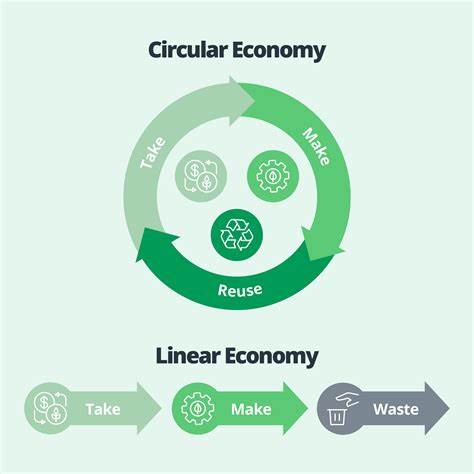
Main Discussion Points
Point: Environmental Benefits
Eco vehicles and the circular economy offer numerous environmental benefits. They significantly contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change. Through renewable energy sources and energy-efficient technologies, eco vehicles exemplify greener transportation. The circular economy promotes resource conservation through recycling and reuse, minimizing the extraction and depletion of natural resources. The integration of renewable energy sources in eco vehicles presents the potential for increased energy efficiency and reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
Point: Economic Advantages
The adoption of eco vehicles and the circular economy offers significant economic advantages. Resource efficiency and waste reduction lead to cost savings across industries as businesses optimize their processes and reduce production expenses. Furthermore, the transition to eco vehicles and the circular economy creates job opportunities and promotes economic growth, particularly in sectors related to renewable energy, recycling, and sustainable transportation. It also encourages the exploration of new business models and innovative technologies, fostering entrepreneurship and stimulating economic development.
Point: Social Implications
Eco vehicles and the circular economy have important social implications. By reducing pollution and improving air quality, eco vehicles contribute to improved public health, especially in densely populated areas. They can enhance communities’ quality of life by creating more livable and sustainable urban environments. However, it is crucial to address equity and inclusivity in this transition, ensuring that the benefits are accessible to all individuals and communities, regardless of socioeconomic status.
Case Studies or Examples
Real-world case studies and examples illustrate the successful implementation of eco vehicles and circular economy initiatives. These examples showcase projects from various regions or industries that have demonstrated positive outcomes. By highlighting these cases, we can learn valuable lessons and gain insights into practical approaches for adopting eco vehicles and the circular economy.

Current Trends or Developments
Staying up-to-date with the latest trends and developments in eco vehicles and the circular economy is essential. Ongoing research findings related to sustainable transportation and waste management inform advancements in these fields. Policy changes and industry developments play a significant role in shaping the future of eco vehicles and the circular economy. By understanding current trends, we can anticipate future implications and opportunities.
Challenges or Controversies
Despite the many advantages, there are challenges and controversies surrounding the widespread adoption of eco vehicles and the circular economy. Barriers, such as high upfront costs, limited infrastructure, and potential disruptions to existing industries, pose challenges to implementation. Differing viewpoints and controversies require careful consideration and dialogue. Exploring potential solutions and strategies that foster collaboration and address stakeholder concerns is important in overcoming these challenges.
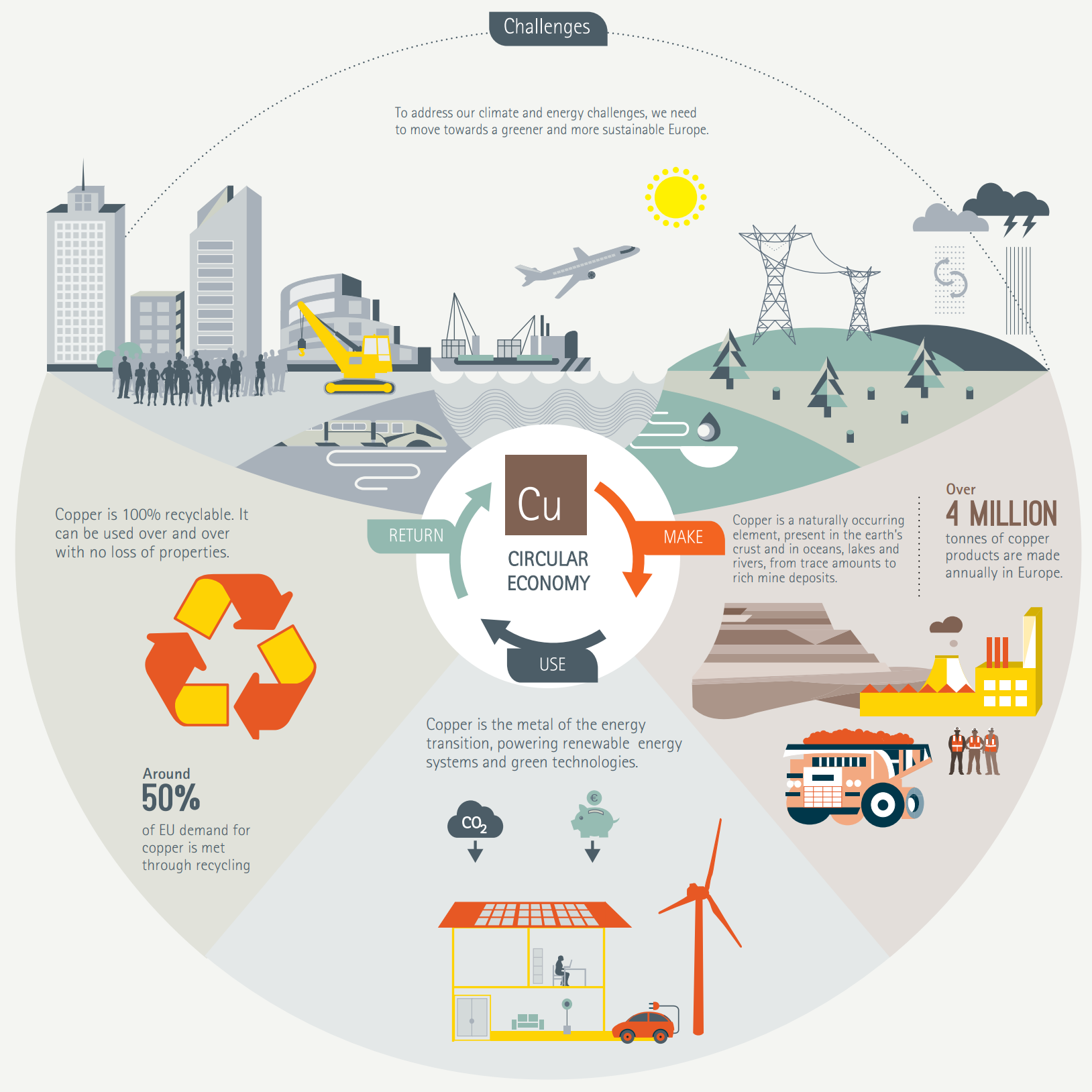
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the future of eco vehicles and the circular economy holds great promise. Advancements in technology and infrastructure will continue to drive innovation in sustainable transportation and resource management. The role of government, businesses, and individuals in shaping this future cannot be understated. By working together to implement supportive policies, foster innovation, and promote sustainable practices, we can create a more environmentally friendly and socially equitable future.
Conclusion
The integration of eco vehicles and the circular economy has the potential to create a sustainable ecosystem. By understanding their background, key concepts, discussion points, case studies, current trends, challenges, controversies, and future outlook, we can navigate the complexities of this important topic. Embracing the opportunities presented by eco vehicles and the circular economy will lead us towards a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future.




