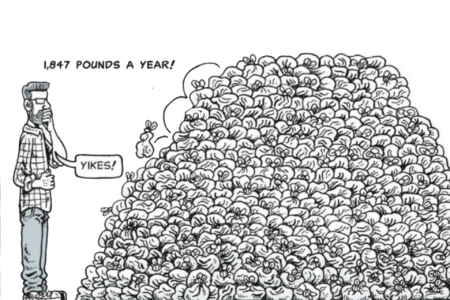
Introduction
The concept of the circular economy has gained significant attention in recent years as a solution to address global waste issues. In a world burdened by excessive consumption and waste generation, the circular economy offers a promising approach to sustainability, resource efficiency, and waste reduction. By eliminating the concept of waste and promoting the continuous use of resources, the circular economy presents a paradigm shift towards a more sustainable and regenerative economic model.
Historical Background
Origins and Evolution of the Circular Economy
The idea of the circular economy can be traced back to early civilizations that practiced resource reuse and recycling. However, it was not until the late 20th century that the concept gained prominence. In the 1970s, the concept of sustainable development emerged, emphasizing the need to balance economic growth with environmental protection. This laid the foundation for the circular economy to be recognized as a viable solution for global waste issues.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Defining the Building Blocks of the Circular Economy
In order to understand the circular economy, it is important to define key terms and concepts. The circular economy itself is an economic model that aims to eliminate waste and promote the continuous use of resources. It focuses on creating a closed-loop system where resources are kept in use for as long as possible, through strategies such as waste prevention, reuse, recycling, and resource recovery. This approach not only reduces the dependence on virgin resources but also minimizes environmental impacts and maximizes value.

Main Discussion Points
Principles, Benefits, and Policy Frameworks of the Circular Economy
One of the main discussion points surrounding the circular economy is its principles. These principles include waste prevention, reuse, recycling, and resource recovery. By adopting these strategies, the circular economy can contribute significantly to addressing global waste issues and achieving sustainable development goals. It can lead to reduced environmental impact, create new business opportunities, and promote economic growth.
Furthermore, the circular economy offers numerous benefits. It not only conserves resources but also reduces pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. By transitioning to circular economy practices, businesses can tap into new revenue streams and enhance their competitiveness in the market. Additionally, the circular economy can stimulate job creation and foster innovation.
To support the transition towards a circular economy, policy and regulatory frameworks play a crucial role. Governments and international organizations have a responsibility to promote and incentivize the adoption of circular economy practices. By implementing supportive policies, such as extended producer responsibility schemes and eco-design regulations, governments can create a conducive environment for circular economy initiatives to thrive.
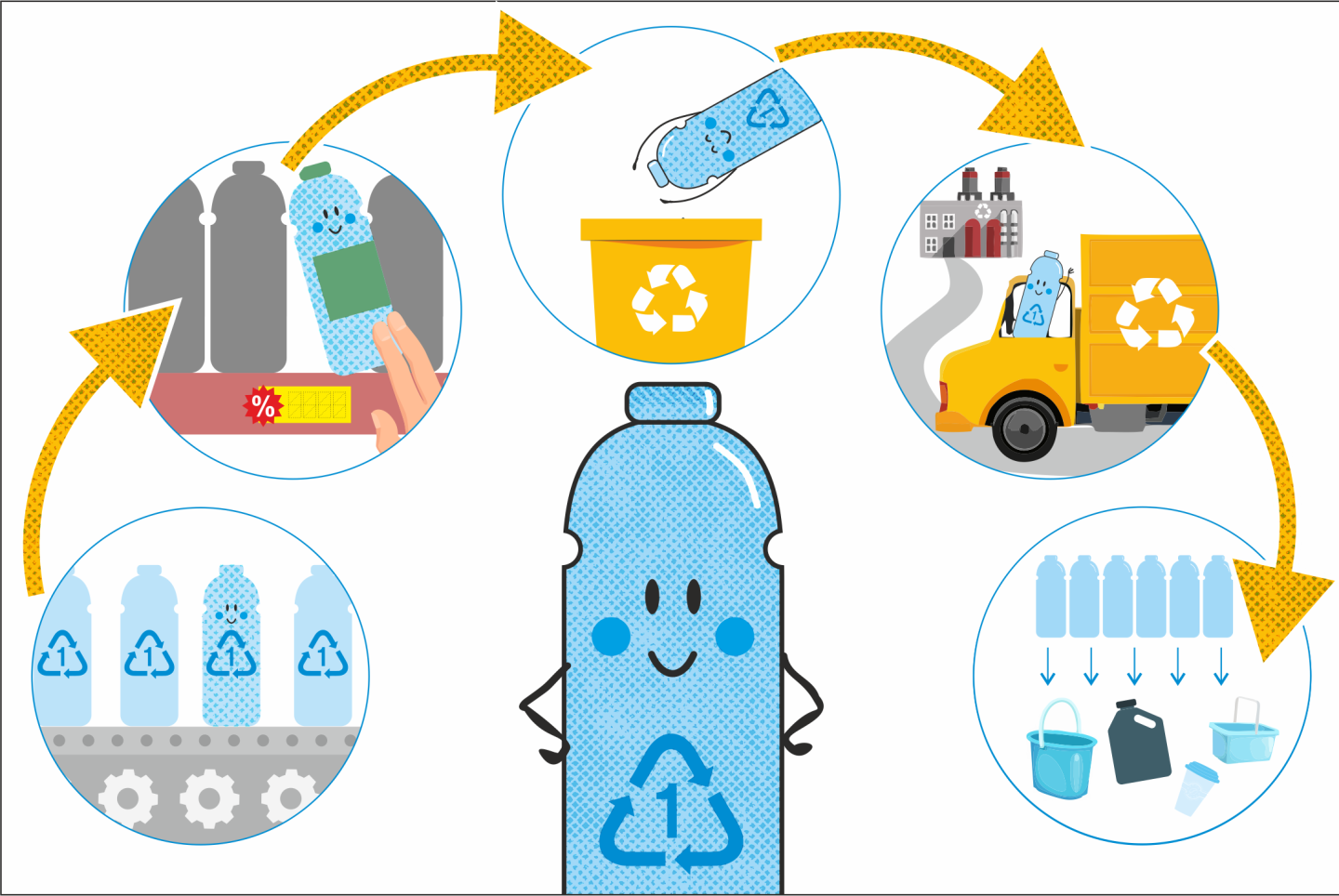
Case Studies or Examples
Real-world Success Stories of the Circular Economy
Real-world case studies and examples demonstrate the successful implementation of circular economy principles in addressing global waste issues. These case studies provide valuable insights into the strategies and outcomes of circular economy initiatives, showcasing key lessons and best practices. For instance, cities like Amsterdam and Copenhagen have implemented circular economy strategies, resulting in significant waste reduction and resource conservation. Companies like Patagonia and Interface have also adopted circular economy approaches in their business models, leading to improved environmental performance and enhanced customer loyalty.
Current Trends or Developments
Emerging Technologies and Innovations in the Circular Economy
The field of circular economy is constantly evolving, driven by recent trends, developments, and innovations. Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and 3D printing, are revolutionizing waste management and resource recovery processes. These technologies enable efficient tracking, sorting, and recycling of materials, contributing to the circular economy’s effectiveness.
Furthermore, new business models are emerging that support the circular economy. Collaborative consumption, product-as-a-service, and sharing economy models are gaining popularity, promoting resource sharing and reducing waste generation. These trends and developments are shaping the future of the circular economy and its application in global waste management.
Challenges or Controversies
Overcoming Barriers to Circular Economy Adoption
Despite its potential, the circular economy faces several challenges and controversies. Economic barriers, such as high initial costs and lack of financial incentives, can hinder the adoption of circular economy practices. Technological limitations, such as the lack of advanced recycling technologies for certain materials, also pose challenges. Additionally, resistance to change and the need for cultural shifts within businesses and societies can impede the transition towards a circular economy.
There are also debates surrounding the effectiveness and feasibility of the circular economy as a solution for global waste issues. Critics argue that the circular economy may not be applicable to all industries or regions and that it may not address the root causes of waste generation. However, proponents emphasize the need for systemic change and argue that the circular economy offers a comprehensive approach to sustainability and waste reduction.

Future Outlook
The Road Ahead for the Circular Economy
Looking towards the future, the circular economy holds great potential in addressing global waste issues. As the concept continues to evolve, advancements in technology, policy frameworks, and business models will shape its trajectory. Opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and investment in circular economy practices are likely to increase, driving further growth and adoption.
However, challenges and uncertainties remain. The circular economy must overcome economic, technological, and societal barriers to achieve widespread adoption. Continuous efforts in research, education, and awareness are crucial to foster a circular economy mindset and facilitate the necessary changes.
Conclusion
The Circular Economy: A Path to Sustainability
In conclusion, the circular economy presents a transformative approach to global waste issues. By embracing waste prevention, reuse, recycling, and resource recovery, the circular economy offers a sustainable and regenerative economic model. The adoption of circular economy principles and strategies is essential for promoting sustainability, resource efficiency, and waste reduction.
By highlighting successful case studies, discussing key concepts and benefits, and addressing challenges and controversies, this article has explored the significance of the circular economy. As the world grapples with mounting waste challenges, the circular economy offers a path towards a more sustainable future.
References:
- Smith, A. (2017). The circular economy: A powerful force for sustainable development. Journal of Cleaner Production, 143, 757-773.
- Ellen MacArthur Foundation. (2013). Towards the Circular Economy: Economic and Business Rationale for an Accelerated Transition.
- European Environment Agency. (2016). Circular Economy in Europe: Developing the Knowledge Base.
- Stahel, W. R. (2010). The performance economy: The circular way to sustainable growth. Palgrave Macmillan.