Circular Economy in the Automotive Industry: Closing the Sustainability Loop
Introduction
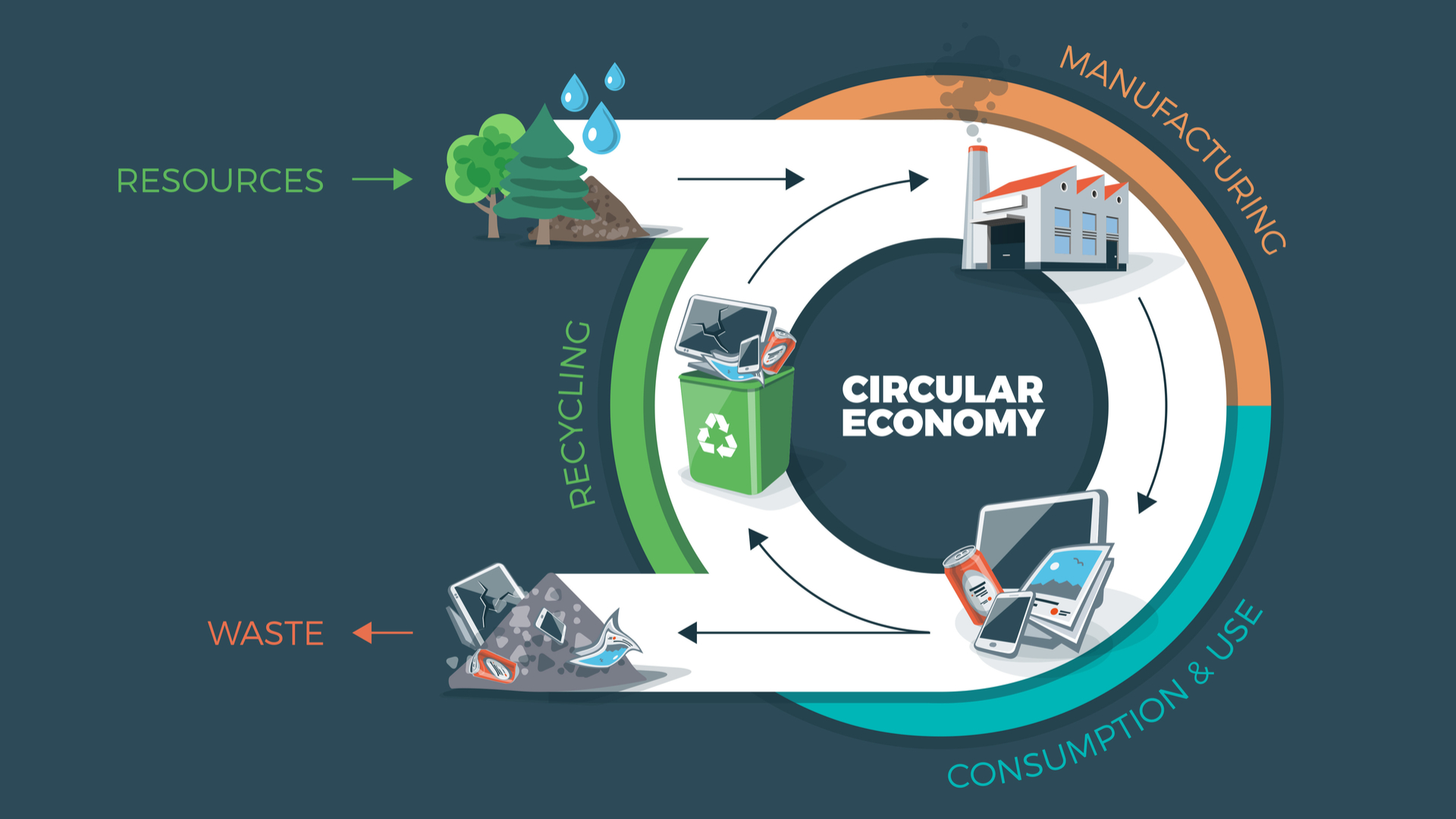
The circular economy in the automotive industry aims to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency throughout the entire lifecycle of vehicles. This system involves designing products with circularity in mind, implementing closed-loop recycling processes, promoting remanufacturing and refurbishment, and utilizing sharing and mobility services. Closing the sustainability loop in the automotive sector is crucial to reduce the environmental impact of the industry and ensure a more sustainable future.
Historical Background
The evolution of the automotive industry has had a significant impact on the environment. The production and use of vehicles contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, pollution, and resource depletion. Previous sustainability efforts in the automotive sector have focused on improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. However, there is a growing recognition of the need to adopt circular economy principles to address the broader environmental challenges associated with the industry.
Key Concepts and Definitions
The circular economy is a concept that emphasizes the importance of maintaining the value of products and materials for as long as possible. In the automotive industry, this concept involves designing products for durability, repairability, and recyclability, as well as promoting the reuse and remanufacturing of materials. The sustainability loop in the automotive industry refers to the application of circular economy principles to reduce waste, conserve resources, and promote a more sustainable and circular economy.

Main Discussion Points
Design for Circular Economy
Designing products with circularity in mind is essential for the automotive industry. By considering the entire lifecycle of a vehicle, automakers can incorporate design strategies that enable easy recycling or reuse. This includes using materials that are recyclable, reducing the number of different materials used, and designing components that can be easily disassembled. Examples of automakers implementing circular design principles include Ford’s use of recycled plastics in vehicle parts and Volvo’s commitment to using more sustainable materials.
Closed-loop Recycling
Closed-loop recycling is a process in which materials from end-of-life vehicles are recovered and reused in the manufacturing of new vehicles. This process helps reduce waste and conserves resources by keeping materials within the production cycle. Benefits of closed-loop recycling in the automotive industry include the reduction of environmental impact, cost savings, and the creation of a more sustainable supply chain. Successful closed-loop recycling initiatives in the automotive sector include BMW’s use of recycled aluminum in its i3 electric vehicles and Ford’s recycling program for vehicle batteries.
Remanufacturing and Refurbishment
Remanufacturing and refurbishment play a significant role in the circular economy of the automotive industry. These processes involve restoring used components to their original specifications and improving the condition and functionality of vehicles, respectively. By extending the lifespan of products, remanufacturing and refurbishment reduce waste and conserve resources. Automotive companies such as Caterpillar and Cummins have incorporated remanufacturing practices into their businesses, resulting in cost savings, reduced environmental impact, and increased customer satisfaction.
Sharing and Mobility Services
Sharing and mobility services, such as car-sharing and ride-sharing, contribute to the circular economy by optimizing the use of vehicles, reducing the need for private car ownership, and decreasing overall vehicle miles traveled. These services promote more efficient and sustainable transportation options, thereby reducing the environmental impact of the automotive industry. Successful examples of sharing and mobility services in the automotive sector include Zipcar and Uber.
Case Studies or Examples
Tesla’s approach to circular economy principles in design and manufacturing: Tesla has integrated circular economy principles into its design and manufacturing processes by using recyclable materials, implementing closed-loop recycling systems, and designing products for longevity and repairability.
Renault’s remanufacturing program for electric vehicle batteries: Renault has developed a remanufacturing program for electric vehicle batteries, which involves refurbishing and reusing batteries that are no longer suitable for electric vehicles. This initiative helps reduce waste and extends the lifespan of valuable battery components.
BMW’s car-sharing program and its impact on sustainability: BMW has launched a car-sharing program called ReachNow, which provides access to electric vehicles for short-term use. This program promotes sustainable mobility by reducing the number of privately owned vehicles and increasing the utilization of electric vehicles.
Current Trends or Developments
Advancements in recycling technologies for automotive materials are helping to improve the sustainability of the industry. Innovative processes, such as chemical recycling and pyrolysis, enable the recovery of valuable materials from complex automotive components. Additionally, the growing adoption of electric vehicles is driving the need for more sustainable practices in the automotive sector, such as efficient battery recycling and the use of renewable energy sources.
Challenges or Controversies
Automakers face obstacles in implementing circular economy principles, such as the high costs associated with redesigning products and processes. There are also controversies surrounding the environmental impact of electric vehicle battery disposal, as the recycling and disposal of these batteries require specialized infrastructure and technologies. Furthermore, differing viewpoints exist on the feasibility and effectiveness of circular practices in the automotive industry, with some stakeholders questioning their economic viability and scalability.
Future Outlook
The future of the circular economy in the automotive sector holds great potential. Advancements in technology and regulations are expected to promote circularity by incentivizing sustainable design, improving recycling infrastructure, and encouraging the adoption of sharing and mobility services. Circular practices will have a significant impact on sustainability and resource conservation, helping the automotive industry transition towards a more sustainable and circular future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the circular economy is crucial for the automotive industry to close the sustainability loop and reduce its environmental impact. Designing products with circularity in mind, implementing closed-loop recycling processes, promoting remanufacturing and refurbishment, and utilizing sharing and mobility services are key strategies to achieve a more sustainable automotive sector. The adoption of circular practices will contribute to resource conservation, waste reduction, and a more sustainable future for the industry.




