Introduction
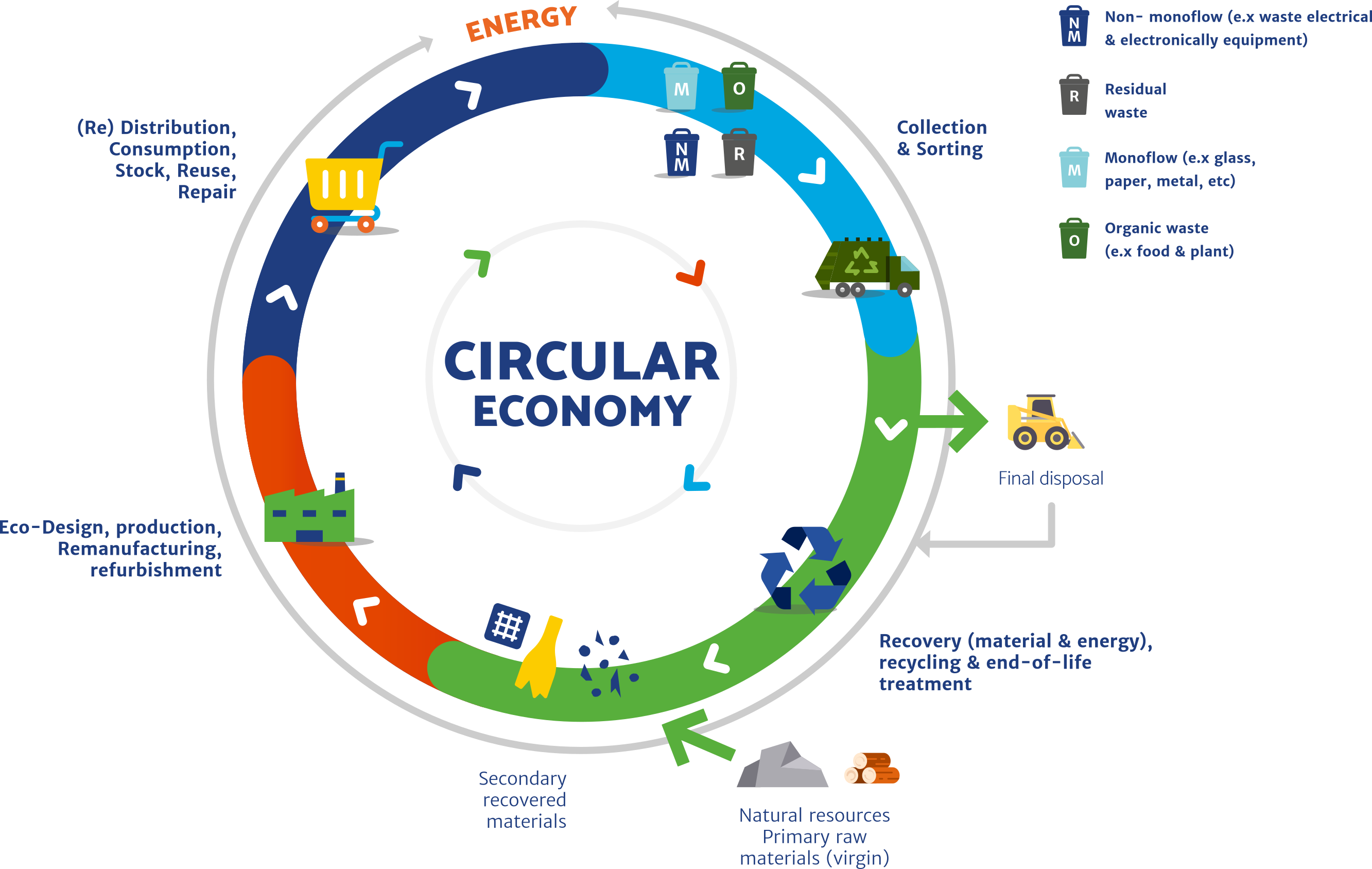
The concept of the circular economy has gained significant attention in recent years as a means to promote sustainability and reduce waste. In this article, we will explore the role of waste-to-energy (WtE) in circular economy initiatives and its importance in achieving a more sustainable future. By converting waste into valuable resources, WtE plays a crucial role in closing the loop and minimizing the negative impacts of waste disposal.
Historical Background
To understand the significance of waste-to-energy in the circular economy, it is important to examine the historical evolution of waste management practices. Traditionally, waste was disposed of in landfills or incinerated without much concern for resource recovery or environmental impact. However, with growing concerns about climate change and resource scarcity, the focus shifted towards circular economy thinking.
Key Concepts and Definitions
In this section, we will define the circular economy and its principles. The circular economy aims to keep resources in use for as long as possible, extracting the maximum value from them while minimizing waste and pollution. Waste-to-energy is a key component of the circular economy, encompassing various technologies such as incineration, anaerobic digestion, and gasification. These processes convert waste into energy, heat, or fuel, contributing to both waste management and energy generation.

Main Discussion Points
Benefits of WtE in Circular Economy Initiatives
Waste-to-energy brings numerous benefits to circular economy initiatives. Firstly, it effectively converts waste into valuable resources, reducing the need for raw materials. By harnessing the energy potential of waste, WtE helps mitigate the environmental impact of waste disposal. This includes the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and the prevention of land and water pollution. Additionally, WtE plays a crucial role in addressing waste management challenges and promoting resource efficiency.
Integration of WtE in Circular Economy Systems
The integration of waste-to-energy in circular economy systems is essential for achieving a sustainable future. WtE complements other circular economy initiatives such as waste prevention, recycling, and recovery. It helps close the loop by converting non-recyclable waste into energy, thereby reducing the reliance on fossil fuels. Integrating WtE into broader circular economy frameworks is vital to ensure a holistic approach to waste management and resource conservation.
Policy and Regulatory Considerations
The implementation of waste-to-energy technologies is influenced by policy and regulatory frameworks. The regulatory landscape for WtE varies across different regions and countries, with some providing supportive environments for its development, while others pose challenges. Government policies play a crucial role in promoting or hindering the growth of WtE projects. Challenges related to emissions control and public perception also need to be addressed through effective regulations and public engagement.

Case Studies or Examples
Real-world case studies provide valuable insights into the successful implementation of waste-to-energy projects. These case studies highlight the positive outcomes and lessons learned from various industries and regions. Municipal solid waste, agriculture, and industrial waste are just a few sectors where WtE has been successfully integrated, showcasing its potential in different contexts.
Current Trends or Developments
Continual innovation and advancements in waste-to-energy technologies are shaping the future of circular economy initiatives. Recent research findings have shed light on the efficiency and performance of WtE systems, further enhancing their viability. Emerging trends, such as the integration of WtE with renewable energy sources, offer promising possibilities for sustainable energy generation and waste management.
Challenges or Controversies
Despite its benefits, waste-to-energy faces several challenges and controversies. High costs associated with the construction and operation of WtE facilities often pose financial barriers. Public perception surrounding emissions control and environmental impact can also hinder the acceptance of WtE projects. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach, including technological advancements, policy interventions, and effective communication.

Future Outlook
Looking ahead, waste-to-energy is expected to play an increasingly prominent role in circular economy initiatives. With advancements in technology and practices, the potential for growth and scalability of WtE is significant. Continued research, collaboration, and investment in this field are crucial for unlocking the full potential of WtE and maximizing its contribution to a sustainable future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, waste-to-energy is a vital component of circular economy initiatives. By converting waste into valuable resources and addressing waste management challenges, WtE contributes to a more sustainable future. However, addressing challenges and controversies surrounding WtE is essential for its successful integration. Continued research, collaboration, and policy support will further strengthen the role of waste-to-energy in achieving circular economy goals.




