Introduction
The waste-to-energy sector has witnessed significant advancements in recent years in the field of biogas production. This article explores the various innovations in waste-to-energy technologies and their relevance in the context of environmental sustainability and renewable energy goals.
Historical Background
The evolution of waste management practices and the emergence of waste-to-energy concepts have paved the way for the development of biogas production and utilization. Early developments in this field laid the foundation for the milestones achieved in waste-to-energy innovations.
Key Concepts and Definitions
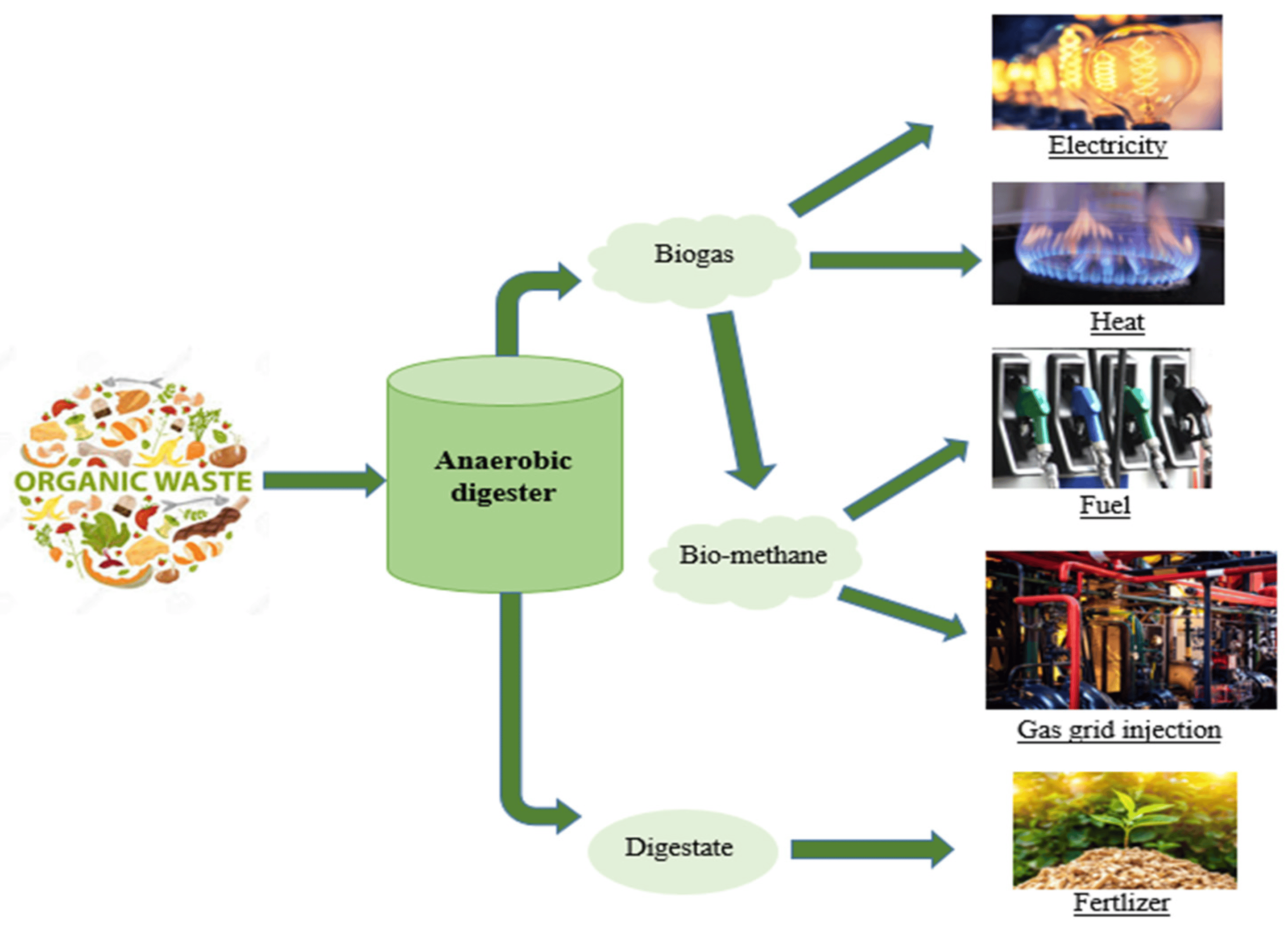
Waste-to-Energy involves the conversion of waste materials into usable forms of energy. Biogas, a key component in this process, is a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide derived from organic waste sources. Anaerobic digestion, a crucial process in biogas production, breaks down organic matter in the absence of oxygen. Combined Heat and Power (CHP) systems play a vital role in converting biogas into usable energy.
Main Discussion Points
Innovative Technologies in Biogas Production
Advancements in biogas production technologies have revolutionized the waste-to-energy sector. Advanced anaerobic digestion systems, such as high-solid anaerobic digestion and two-stage digestion processes, have significantly improved the efficiency of biogas production. Co-digestion of various waste streams has also proven to be an effective method in enhancing biogas yields.
Pre-treatment methods, including mechanical, thermal, and chemical processes, have been developed to optimize biogas production. These methods help in breaking down complex organic compounds and increasing the accessibility of organic matter to the anaerobic microbes.
Utilization and Conversion of Biogas
Biogas upgrading technologies play a crucial role in removing impurities from the biogas stream. Biogas purification is essential for the production of biomethane, a high-quality form of biogas suitable for injection into natural gas grids or as a vehicle fuel.
The applications of biogas and biomethane are diverse, ranging from electricity generation to heat production in industries and households. The potential for injecting biogas into natural gas grids provides an opportunity for renewable energy integration and decarbonization of the natural gas sector.
Integration of Waste-to-Energy Innovations
Waste-to-energy innovations, particularly in biogas production, can be integrated with other renewable energy sources to create a more sustainable energy mix. The coupling of biogas production with solar or wind energy can ensure a continuous and reliable supply of renewable electricity.
Integration with waste management systems is another crucial aspect. By utilizing organic waste streams, waste-to-energy technologies can divert significant amounts of waste from landfills, reducing environmental pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Moreover, waste-to-energy innovations align with the principles of the circular economy by promoting resource recovery and minimizing waste generation. The integration of biogas production with circular economy principles ensures a sustainable and closed-loop approach to waste management and energy production.

Case Studies or Examples
Successful implementation of waste-to-energy innovations in biogas production
Biogas production from agricultural waste
Industrial biogas plants
Current Trends or Developments
Recent advancements in biogas production technologies have focused on improving the efficiency and scalability of biogas plants. Research findings have shed light on optimizing biogas yields and quality through process optimization and microbial enhancements.
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in promoting waste-to-energy innovations. Many countries have implemented supportive policies to encourage the adoption of biogas production technologies, offering financial incentives and favorable regulatory frameworks.
Challenges or Controversies
While waste-to-energy innovations in biogas production offer numerous benefits, there are some challenges and controversies associated with this sector. Environmental concerns related to emissions from biogas production need to be addressed through advanced emission control technologies.
Land requirements and potential land-use conflicts pose challenges in scaling up waste-to-energy projects. Balancing the demand for land resources with the need for sustainable energy production requires careful planning and strategic decision-making.
Socio-economic considerations and public acceptance are also important factors. Engaging local communities and addressing any concerns or misconceptions regarding waste-to-energy technologies is crucial for their successful implementation.

Future Outlook
The potential for scaling up waste-to-energy innovations in biogas production is significant. As technologies continue to advance, biogas production can play a pivotal role in the transition to a low-carbon economy. The integration of biogas production with other renewable energy sources and waste management systems will further enhance its sustainability.
Emerging technologies and research directions, such as the use of microbial consortia and novel reactor designs, hold promise for improving biogas yields and quality. Continued research and development efforts, combined with supportive government policies, will contribute to the growth and widespread adoption of waste-to-energy innovations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, waste-to-energy innovations in biogas production offer a sustainable solution for renewable energy. The advancements in biogas production technologies, coupled with the integration of waste-to-energy concepts with other renewable energy sources, waste management systems, and circular economy principles, hold immense potential for creating a more sustainable and low-carbon future.




