Introduction
Recycling plays a crucial role in resource conservation, ensuring the sustainable use of our planet’s limited resources. This article provides an in-depth exploration of recycling, highlighting its importance in current environmental discussions.
Historical Background
Recycling is not a modern concept; ancient civilizations practiced forms of recycling to reuse materials. As civilizations evolved, recycling practices also developed, particularly during the industrial era.
Key Concepts and Definitions
To fully understand recycling, it is important to define the concept and explore related ideas. Recycling is the process of converting waste into reusable materials, contributing to the circular economy. This section also delves into different types of recycling, such as paper, plastic, and metal recycling.

Main Discussion Points:
Environmental Benefits of Recycling
Recycling offers significant environmental benefits. Firstly, it reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills, alleviating the strain on these sites. Secondly, recycling conserves natural resources by reducing the need for raw material extraction. Lastly, it saves energy and reduces greenhouse gas emissions associated with manufacturing new products.
Economic Benefits of Recycling
Recycling is not only environmentally beneficial but also economically advantageous. It creates jobs in the recycling industry, providing employment opportunities. Additionally, businesses can achieve cost savings through material recovery, reducing the need for new purchases. Moreover, the circular economy presents various economic opportunities.
Social Benefits of Recycling
Recycling has wide-ranging social benefits. It fosters community engagement and raises awareness about environmental issues. Furthermore, recycling initiatives educate and empower individuals, promoting sustainable habits. Recycling also has the potential to address social inequalities through inclusive programs.
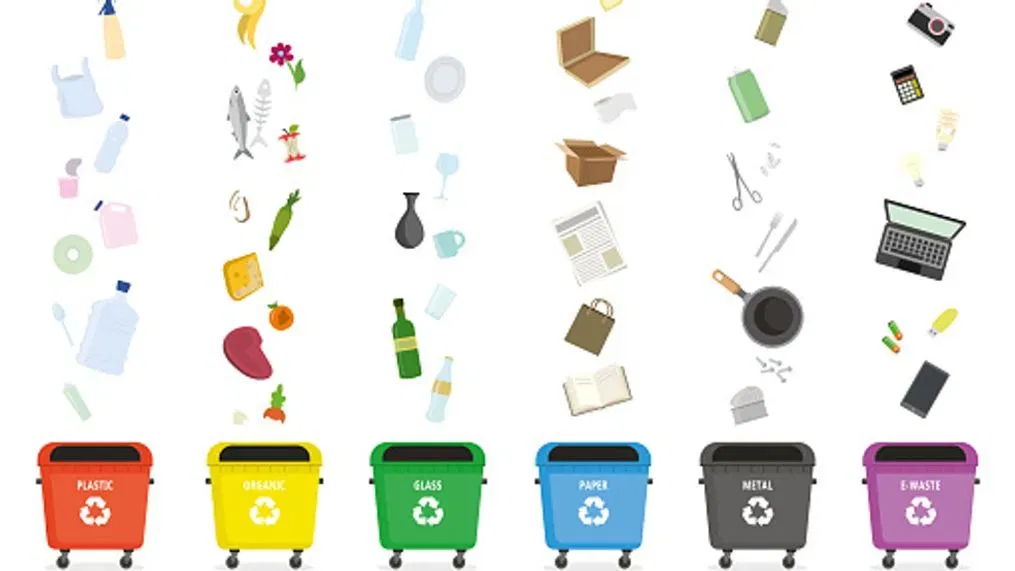

Case Studies or Examples
This section highlights successful recycling programs in cities or countries, showcasing their positive impact on resource conservation. Additionally, it explores innovative recycling projects and technologies, paving the way for more sustainable practices. Furthermore, it examines the impact of recycling on specific industries, such as the automotive and fashion sectors.
Current Trends or Developments
Advances in recycling technology, especially in plastic and electronic waste recycling, are transforming the industry. Moreover, global recycling rates are steadily increasing, indicating growing awareness and participation. The concept of extended producer responsibility is gaining prominence, emphasizing the role of manufacturers in the recycling process.
Challenges or Controversies
Recycling faces several challenges and controversies. Recycling contamination, caused by improper sorting or contamination of recyclables, hinders the efficiency of the recycling process. Limited infrastructure and resources pose obstacles in certain regions, hindering recycling efforts. Furthermore, debates exist regarding the effectiveness of recycling as a comprehensive waste management solution.

Future Outlook
Looking ahead, there is potential for increased recycling rates and improved recycling technologies. Integrating recycling into sustainable development goals will further promote resource conservation. Finally, policy and regulations play a vital role in driving recycling initiatives and ensuring a sustainable future.
Conclusion
Recycling is a pivotal component of resource conservation, offering environmental, economic, and social benefits. By summarizing the main points discussed, this section reinforces the significance of recycling in building a more sustainable society.