The Future of Landfills and Waste Disposal Sites
Introduction
The future of landfills and waste disposal sites is of growing importance in the realm of environmental sustainability and waste management. With the continuous increase in the global population, waste generation is also on the rise. This article aims to provide a concise overview of the topic and emphasize its significance in addressing the challenges associated with waste disposal.
Historical Background
Early waste disposal practices primarily involved simple methods such as open dumping and burning. However, as urbanization and industrialization progressed, more organized waste management strategies became necessary. The establishment of modern landfills, as we know them today, began to take shape during the mid-20th century. These sites were specifically designed to contain and isolate waste materials from their surrounding environment.
Key Concepts and Definitions
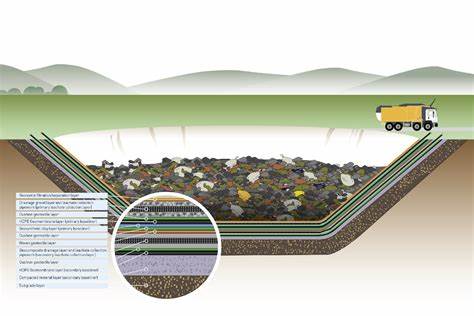
Landfills are engineered facilities that are exclusively designed for the disposal of solid waste. They are meticulously constructed and operated in order to minimize potential impacts on human health and the environment. Waste disposal sites, on the other hand, encompass a broader range of facilities, including landfills and incinerators. The most common type of landfill, known as sanitary landfills, are designed to isolate waste from the environment and prevent the release of harmful substances.

Main Discussion Points
Point: Modern landfill technologies and their impact on waste management
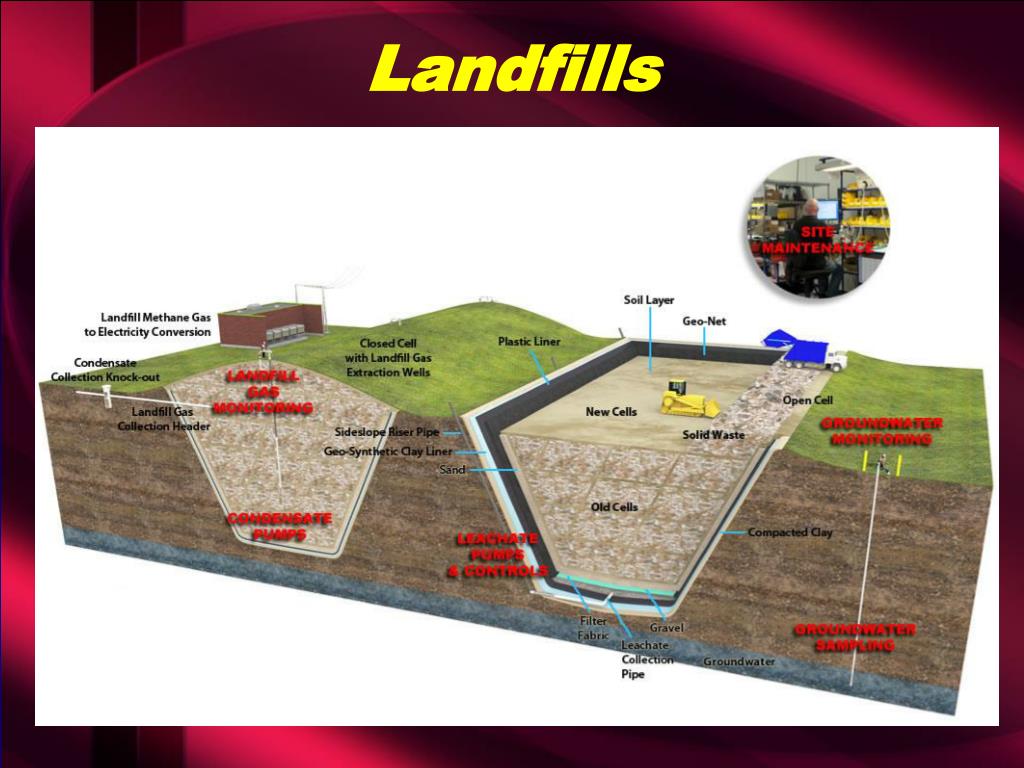
Modern landfill technologies have significantly improved waste management practices. For example, landfill gas management systems capture and utilize methane gas produced by decomposing waste. This not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also generates renewable energy. Additionally, leachate collection and treatment systems prevent groundwater contamination by capturing and treating the liquid that is generated within landfills. Enhanced landfill mining and resource recovery aim to extract valuable materials from old landfill sites, thereby reducing the need for raw material extraction.
Point: Alternative waste disposal methods and their potential
Alternative waste disposal methods offer promising solutions to the challenges of traditional landfilling. Waste-to-energy technologies, such as incineration and gasification, convert waste materials into usable heat or electricity. Recycling and reuse initiatives promote the diversion of waste from landfills by transforming materials into new products. Biological treatment options, such as composting and anaerobic digestion, break down organic waste in controlled environments, reducing methane emissions and producing valuable compost or biogas.
Point: The role of innovation and technology in shaping the future of landfills and waste disposal sites
Innovation and technology play a crucial role in shaping the future of waste management. Sensor technology enables real-time monitoring of landfill conditions, allowing for optimized waste placement and compaction. Robotics and automation are increasingly being utilized for waste sorting and management, enhancing efficiency and reducing the need for manual labor. Furthermore, artificial intelligence can be employed for waste management decision-making, optimizing waste collection routes and resource allocation.
Case Studies or Examples
Landfill gas recovery at Freshkills Park, NYC
Freshkills Park in New York City serves as an exemplary case of a landfill site being transformed into a sustainable public park. The landfill gas generated by decomposing waste is captured and used to generate renewable energy. This project showcases the potential for utilizing landfill resources and minimizing environmental impacts.
Sweden’s waste management system focused on recycling and energy recovery
Sweden has successfully implemented a waste management system that prioritizes recycling and energy recovery. Through a combination of legislation, public awareness campaigns, and infrastructure development, Sweden has reduced the amount of waste sent to landfills while maximizing resource recovery.
Current Trends or Developments
Advancements in landfill design and engineering to minimize environmental impacts
Ongoing advancements in landfill design and engineering focus on minimizing environmental impacts. These measures include liner systems to prevent leachate leakage, gas collection systems, and engineered caps to reduce odors and prevent the infiltration of rainwater.
Integration of renewable energy systems in waste management facilities
The integration of renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines, in waste management facilities is becoming increasingly common. These systems provide onsite renewable energy generation, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and further enhancing the sustainability of waste management practices.
Shift towards a circular economy and the concept of zero waste
There is a growing global shift towards a circular economy and the concept of zero waste. This approach aims to minimize waste generation through sustainable product design, extended producer responsibility, and increased recycling and reuse. It emphasizes the need to view waste as a valuable resource rather than a burden.
Challenges or Controversies
Public perception and acceptance of waste disposal sites
Public perception and acceptance of waste disposal sites can present significant challenges. Communities often resist the establishment of new landfills or waste management facilities due to concerns about noise, odor, and potential health risks. Effective communication and community engagement are crucial in addressing these concerns and gaining public support.
Potential health and environmental risks associated with landfills
Landfills have the potential to pose health and environmental risks if not properly managed. These risks include the release of harmful gases, contamination of groundwater, and the attraction of disease-carrying pests. Stringent regulations and proper monitoring and mitigation measures are necessary to minimize these risks.
Discrepancies in waste management practices and regulations across regions
Discrepancies in waste management practices and regulations across regions can hinder progress towards sustainable waste management. Standardized guidelines and international cooperation are essential in addressing these discrepancies and promoting best practices globally.
Future Outlook
Potential advancements in waste sorting and recycling technologies
The future holds potential advancements in waste sorting and recycling technologies. Innovations such as advanced sorting systems using artificial intelligence and robotics can improve recycling rates and the quality of recycled materials. This will further contribute to reducing the reliance on landfilling.
Transition towards decentralized waste management systems
There is a growing interest in transitioning towards decentralized waste management systems. These systems involve smaller-scale waste treatment facilities located closer to the source of waste generation. This decentralization can reduce transportation costs and environmental impacts associated with long-distance waste disposal.
Increased focus on waste reduction and prevention strategies
The future will see an increased focus on waste reduction and prevention strategies. This involves reevaluating consumption patterns, promoting sustainable product design, and implementing policies that incentivize waste reduction. By addressing waste generation at its source, the need for waste disposal sites can be minimized.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of landfills and waste disposal sites is closely tied to the broader goals of environmental sustainability and waste management. Through the implementation of modern landfill technologies, alternative waste disposal methods, and innovative solutions, it is possible to transform waste management practices and reduce environmental impacts. However, challenges related to public acceptance, health and environmental risks, and discrepancies in waste management practices must be addressed in order to achieve a sustainable future.
References
Smith, J. R. (2019). Sustainable solid waste management. John Wiley & Sons.
United Nations Environment Programme. (2020). Global waste management outlook 2. United Nations Publications.
United States Environmental Protection Agency. (2021). Landfills. Retrieved from https://www.epa.gov/landfills